Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CTM Tutorial 3
Uploaded by
crsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CTM Tutorial 3
Uploaded by
crsCopyright:
Available Formats
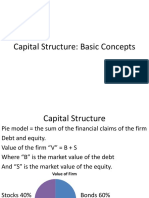
1. The following is the balance sheet of RC Resources Bhd as at Sept 30, 2014.
Balance sheet RM
Ordinary Shares of 25 cents each 250,000
Reserves 350,000
7% preference shares of $1 each 250,000
15% Unsecured loan stock 150,000
Total 1,000,000
The ordinary shares are currently quoted at RM1.25 each, the loan stock is trading at
RM 85 per RM 100 nominal and the preference shares at RM 0.65 each.
Calculate the gearing ratio for RC Resources using:
Gearing Ratio = Preference share + Loan / Equity
(a) Book Value
Book Value = (250,000 + 150,000) / 250,000 + 350,000
= 0.667 @ 66.7%
(b) Market Value
Outstanding Share = Price X Shares Outstanding = $0.25 X ($250,000 / $0.25 share)
=$ 1,250,000
Preference Share = Price X Shares Outstanding = $0.65 X ($250,000 / $1 share)
=$ 162,000
Loan Stock = Price X Unit Loan Stock issues = $85 X ( $150,000/$100) =$ 127,500
Total Firm Value = $ 1,540,000
Gearing ratio = (Preference share + Loan) / equity = (162,500 + 127,500) / 1,250,000
=0.232 @ 23.2%
2. The profit and loss account of Robbie Corp for the year ending June 30, 2014 shows the
following figures:
Income Statement RM
Operating Profit 100,000
Interest Payable 40,000
Profit before Tax 60,000
Corporation Tax 18,000
Profit after tax 42,000
Calculate the interest coverage for Robbie Corp on its borrowings
Interest Coverage = EBIT / Interest payable
= 100,000 / 40,000
=2.5 Times
Therefore Robbie Corporation would have 2.5 times earning ability to pay off the
interest payable.
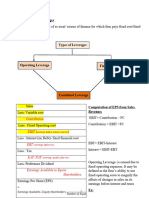
3. Calculate the operating leverage and financial leverage for year 1 and year 2 based on
the following figures:
Profit/Loss Year 1 (RM) Year 2 (RM) %
Sales 1,000,000 1,100,000 10
Variable Cost (400,000) (440,000)
Fixed Cost (200,000) (200,000)
Operating Profit 40000 460,000 15
(EBIT)
Interest Payment (50,000) (50,000)
Profit before Tax 350,000 410,000 17.1
What does the result of Operating and financial leverage implies based on your answer
above?
Operating leverage can also be measured in terms of change in operating income for a
given change in sales (revenue). Operating leverage is a financial efficiency ratio used to
measure what percentage of total costs are made up of fixed costs to generate profits.
Operating Leverage = Contribution / EBIT = (Selling Price -Variable Cost) / EBIT
Year 1 = (1,000,000 – 400,000) / 400,000
= 1.5 Times
Year 2 = (1,100,000 – 440,000) / 460,000
Financial Leverage = EBIT/PBT = 400,000/ 350,000 =1.14 times year 1
= 1.12 times year 2
Therefore year 1 was still found high financial leverage compare to year 2.
Financial leverage is the degree to which a company uses fixed-income securities such
as debt and preferred equity. The more debt financing company uses, the higher its
financial leverage. A high degree of financial leverage means high interest payments,
which negatively affect the company’s bottom-liner
4. Assume RM 1.00 shares quoted at RM 2.50, dividend just paid of 20 cents. Calculate the
cost of equity.
Dividend Growth Model = (D1/ P0)+g
= 0.20/ 2.50
= 0.08 @ 8%
P0=D1/K-G
Price= 2.50
Dividend paid =D0 = 0.20
Growth rate = Nil
5. Assume cost of equity is 8% or 0.08 cents the dividend just paid of 20 cents. Calculate
the market value per share.
P0 =D1/K-G
Price= 0.2/0.08
= 2.50
Dividend paid =D0 = 0.20
Growth rate = Nil
6. Assume RM1.00 shares quoted at RM 2.50 cum dividend of 20 cents, calculate the cost
of equity.
Dividend Growth Model = (D1/ P0)+g
= 0.20/ 2.50- 0.20
= 0.0869 @ 8.69%
P0=D1/K-G
Price= 2.50
Dividend paid =D0 = 0.20 cum dividend ( newly paid dividend)
Growth rate = Nil
7. Assume the current market price of a share is RM 2.50. A dividend of 20 cents has just
been paid i.e. ex-d. Assuming the expected annual growth rate for the dividend is 5% to
infinity i.e. perpetuity, calculate the cost of equity.
Dividend Growth Model = (D1/ P0)+g
= (0.21/ 2.50) +0.05
= 0.134 @ 13.4%
P0=D1/K-G
Price= 2.50
Dividend paid =D0 = 0.20
D1 = D0 (1+G) = 0.2 (1+0.05) = 0.21
Growth rate = 0.05
8. Assume the current market price of a share is RM 2.00. A dividend of 20 cents per share
has just been paid. Assuming that the dividend is expected to decline by 2% per annum
in perpetuity. Calculate the cost of equity
Dividend Growth Model = (D1/ P0)+g
= (0.196/ 2.00) - 0.02
= 0.078 @ 7.8%
P0=D1/K-G
Price= 2.00
Dividend paid =D0 = 0.20
D1 = D0 (1+G) = 0.2 (1-0.02) = 0.196
Growth rate = -0.02
9. Using CAPM model, calculate the cost of equity assuming an equity beta of 1.4, an
expected market return of 16% and a risk free rate of 10%
Cost of equity = Ke
1. CAPM model
CAPM = rfr + beta(Rm-rfr)
= 0.1+1.4(0.16-0.1)
= 18.4%
Beta (Rm-rfr)= risk premium
(Rm-rfr) = market risk premium
You might also like
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Some Exercises On Capital Structure and Dividend PolicyDocument3 pagesSome Exercises On Capital Structure and Dividend PolicyAdi AliNo ratings yet
- Bmmf5103 861024465000 Managerial Finance - RedoDocument14 pagesBmmf5103 861024465000 Managerial Finance - Redomicu_san100% (1)
- Accounting and Financial ManagementDocument7 pagesAccounting and Financial ManagementMelokuhle MhlongoNo ratings yet
- 2 - Topic 2 Capital StructureDocument22 pages2 - Topic 2 Capital StructureCOCONUTNo ratings yet
- Quiz 6 NotesDocument14 pagesQuiz 6 NotesEmily SNo ratings yet
- Leverage: Dr. Sonia Baghla Assistant Professor Baba Farid College BathindaDocument37 pagesLeverage: Dr. Sonia Baghla Assistant Professor Baba Farid College Bathindadr. soniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 LectureDocument6 pagesChapter 5 LectureSaadNo ratings yet
- RADHA Financial ASSIGNMENTDocument4 pagesRADHA Financial ASSIGNMENTradha sharmaNo ratings yet
- Capital StructureDocument21 pagesCapital StructureRameen Jawad MalikNo ratings yet
- LeveragesDocument12 pagesLeveragesjoshipragati123No ratings yet
- Sem 2 Question Bank (Moderated) - Financial ManagementDocument63 pagesSem 2 Question Bank (Moderated) - Financial ManagementSandeep SahadeokarNo ratings yet
- Leverages: Raksha Khetan-23 Saumitra Kumar-26 Saqib Azam Qadri-42Document21 pagesLeverages: Raksha Khetan-23 Saumitra Kumar-26 Saqib Azam Qadri-42sampdalvi07No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Chapter 3: Financial Forecasting and PlanningDocument35 pagesChapter 3 - Chapter 3: Financial Forecasting and PlanningAhmad Ridhuwan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Finance For Managers-Module 4B-LeveragesDocument27 pagesFinance For Managers-Module 4B-LeveragesChayaGandhiNo ratings yet
- Leverage Unit-4 Part - IIDocument34 pagesLeverage Unit-4 Part - IIAstha ParmanandkaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Dividend - DividendPolicy - FM - Mahesh MeenaDocument9 pages6 - Dividend - DividendPolicy - FM - Mahesh MeenaIshvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Fitriyanto - Financial Management Asignment - CH 14 15Document6 pagesFitriyanto - Financial Management Asignment - CH 14 15iyanNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTING & FIN LST 113547Document12 pagesACCOUNTING & FIN LST 113547Joshua RisinamhodziNo ratings yet
- ACF 103 - Fundamentals of Finance Tutorial 10 - SolutionsDocument9 pagesACF 103 - Fundamentals of Finance Tutorial 10 - SolutionsThảo Trần Thị ThuNo ratings yet
- ACF 103 - Fundamentals of Finance Tutorial 10 - SolutionsDocument9 pagesACF 103 - Fundamentals of Finance Tutorial 10 - SolutionsRiri FahraniNo ratings yet
- Optimal Financing MixDocument4 pagesOptimal Financing MixSana SarfarazNo ratings yet
- LeveragesDocument51 pagesLeveragesmaitrisharma131295100% (1)
- ACF 103 Tutorial 10 SolnsDocument9 pagesACF 103 Tutorial 10 SolnsTroisNo ratings yet
- LeverageDocument7 pagesLeverageKomal ThakurNo ratings yet
- Capital Structure: Rakesh ArrawatiaDocument38 pagesCapital Structure: Rakesh ArrawatiashravaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 44Document14 pagesAssignment 44Khadar MaxamedNo ratings yet
- Dividend Policy Question and AnswerDocument7 pagesDividend Policy Question and AnswerBella CynthiaNo ratings yet
- 2015 - Valuation of SharesDocument31 pages2015 - Valuation of SharesGhanshyam KhandayathNo ratings yet
- Homework Set IvDocument3 pagesHomework Set IvSteven HouNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Statement of Profit or Loss and Other Comprehensive IncomeDocument40 pagesConsolidated Statement of Profit or Loss and Other Comprehensive IncomeSing YeeNo ratings yet
- Share & Business Valuation Case Study Question and SolutionDocument6 pagesShare & Business Valuation Case Study Question and SolutionSarannyaRajendraNo ratings yet
- Investment/ Financing Decisions: S.ClementDocument33 pagesInvestment/ Financing Decisions: S.Clementjohnkm28No ratings yet
- MGT201 Subj SHortnotesDocument15 pagesMGT201 Subj SHortnotesmaryamNo ratings yet
- PERMALINO - Learning Activity 19. Working Capital ManagementDocument3 pagesPERMALINO - Learning Activity 19. Working Capital ManagementAra Joyce PermalinoNo ratings yet
- AC6101 Lecture 3 - Capital Structure (M&M) - Xid-2956908 - 1Document28 pagesAC6101 Lecture 3 - Capital Structure (M&M) - Xid-2956908 - 1Kelsey GaoNo ratings yet
- Residual Income Valuation - UrpDocument18 pagesResidual Income Valuation - Urparmando.chappell1005100% (1)
- Performance MGMT Discussion QuestionsDocument7 pagesPerformance MGMT Discussion QuestionsSritel Boutique HotelNo ratings yet
- FM Assignment 7 - Group 4Document7 pagesFM Assignment 7 - Group 4Puspita RamadhaniaNo ratings yet
- Olinde Electronics IncDocument3 pagesOlinde Electronics IncRo Papa0% (1)
- Everage: Sales (S) 90,000 90,000 3000 Units at Rs. 30/-Per Unit 15 Per Unit 45,000 45,000Document20 pagesEverage: Sales (S) 90,000 90,000 3000 Units at Rs. 30/-Per Unit 15 Per Unit 45,000 45,000anon_67206536260% (5)
- Leverages ProblemsDocument4 pagesLeverages Problemsk,hbibk,n0% (1)
- Leverage: Prepared By:-Priyanka GohilDocument23 pagesLeverage: Prepared By:-Priyanka GohilSunil PillaiNo ratings yet
- LEVERAGE - Hons.Document7 pagesLEVERAGE - Hons.BISHAL ROYNo ratings yet
- Look Before You Leverage SymondsDocument7 pagesLook Before You Leverage SymondsRaffin AdarshNo ratings yet
- Ch.6 Point of IndifferenceDocument15 pagesCh.6 Point of IndifferenceMark KaiserNo ratings yet
- FIN 213 Review Questions: Question OneDocument16 pagesFIN 213 Review Questions: Question OneJustus MusilaNo ratings yet
- FM AssignmentDocument7 pagesFM Assignmentkartika tamara maharaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document5 pagesChapter 10Usman KhalidNo ratings yet
- FINAN204-21A - Tutorial 7 Week 10Document6 pagesFINAN204-21A - Tutorial 7 Week 10Danae YangNo ratings yet
- Finman Q2Document14 pagesFinman Q2Rhn SbdNo ratings yet
- Maf 620 Dutch LadyDocument9 pagesMaf 620 Dutch LadyNur IfaNo ratings yet
- Ratio of Price To Book 2.22Document14 pagesRatio of Price To Book 2.22Lê Hữu LựcNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Case 24Document11 pagesSummary of The Case 24farisa.oeNo ratings yet
- Problem BankDocument10 pagesProblem BankSimona NistorNo ratings yet
- Exam #1 ReviewDocument5 pagesExam #1 ReviewThùy DươngNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems Cost of CapitalDocument16 pagesSolved Problems Cost of CapitalPrramakrishnanRamaKrishnan0% (1)
- 8-Security-Valuation 2Document29 pages8-Security-Valuation 2saadullah98.sk.skNo ratings yet
- Section A: Gross ProfitDocument8 pagesSection A: Gross ProfitkangNo ratings yet
- MPA 10703 Financial Management Cost of CapitalDocument40 pagesMPA 10703 Financial Management Cost of CapitalMaryam BielaNo ratings yet
- CTM Tutorial 5Document2 pagesCTM Tutorial 5crsNo ratings yet
- CTM Tutorial 2Document4 pagesCTM Tutorial 2crsNo ratings yet
- Palamon Capital Partners Darden PDFDocument20 pagesPalamon Capital Partners Darden PDFcrsNo ratings yet
- Case 51 Palamon Capital Partners Team System SPADocument10 pagesCase 51 Palamon Capital Partners Team System SPAcrs50% (2)
- CVP Considerations in Choosing A Cost StructureDocument3 pagesCVP Considerations in Choosing A Cost StructureJonna LynneNo ratings yet
- Prithvi Sehgal: Improvement of Vehicle Turn-Around TimeDocument1 pagePrithvi Sehgal: Improvement of Vehicle Turn-Around TimeprithvisehgalNo ratings yet
- MF DoneDocument10 pagesMF DoneVIREN GOHILNo ratings yet
- Airasia Quarter ReportDocument34 pagesAirasia Quarter ReportChee Meng TeowNo ratings yet
- FB - JPM Research Report - Oct 2012Document17 pagesFB - JPM Research Report - Oct 2012ishfaque10No ratings yet
- Budget Terminology PDFDocument4 pagesBudget Terminology PDFronNo ratings yet
- Actis VcircleDocument2 pagesActis VcircleAanubhav KackerNo ratings yet
- Florist Shop Business PlanDocument37 pagesFlorist Shop Business Planloowtkinuy50% (2)
- Dynamics AX - Financial Series ModuleDocument3 pagesDynamics AX - Financial Series ModuleBA Training SchoolNo ratings yet
- Oyu Tolgoi Appoints General Manager For Underground DevelopmentDocument5 pagesOyu Tolgoi Appoints General Manager For Underground Developmentbeku_ggs_bekuNo ratings yet
- Business Combination 1Document31 pagesBusiness Combination 1Leo DanuartaNo ratings yet
- Form Lab 25 Goal StrategyDocument6 pagesForm Lab 25 Goal StrategyGenti MadhiNo ratings yet
- Real Estate: (Industry Guide) By:-Aamir SaleemDocument18 pagesReal Estate: (Industry Guide) By:-Aamir SaleemAamir SaleemNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Company Law TribunalDocument15 pagesAnalysis of Company Law TribunalAyush RaoNo ratings yet
- 1830 AH RulesDocument16 pages1830 AH RulestobymaoNo ratings yet
- Seigniorage in The United States: How Much Does US Government Make From Money ProductionDocument12 pagesSeigniorage in The United States: How Much Does US Government Make From Money ProductionCervino InstituteNo ratings yet
- Intro Erp Using Gbi Case Study Fi A4 en v2 20Document22 pagesIntro Erp Using Gbi Case Study Fi A4 en v2 20Diane PascualNo ratings yet
- Superdry Annual Report 2017Document156 pagesSuperdry Annual Report 2017GabrellaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance and The Role of Institutional InvestorsDocument47 pagesCorporate Governance and The Role of Institutional InvestorsSaritaMeenaNo ratings yet
- Verso ReleaseDocument2 pagesVerso ReleaseNEWS CENTER MaineNo ratings yet
- BusinessDocument18 pagesBusinessNLainie OmarNo ratings yet
- Investment Screener Results 9Document1 pageInvestment Screener Results 9Adeniyi AleseNo ratings yet
- FM ProblemsDocument2 pagesFM ProblemsAjeet YadavNo ratings yet
- Feasibilty StudyDocument39 pagesFeasibilty StudyRusty Sabado PizarroNo ratings yet
- 1425 BdoDocument20 pages1425 Bdodaniel.radz9010No ratings yet
- Old Theories of Imperialism PDFDocument11 pagesOld Theories of Imperialism PDFserbannerNo ratings yet
- Ae 19Document18 pagesAe 19mary rose silaganNo ratings yet
- The University of AlbertaDocument27 pagesThe University of Albertadilipkhatri019255No ratings yet
- BBPW3103 Financial Management I - Smay19 (RS & MREP)Document397 pagesBBPW3103 Financial Management I - Smay19 (RS & MREP)donmakemesad100% (1)
- New Technological Innovations in The Banking SectorDocument5 pagesNew Technological Innovations in The Banking SectorlapogkNo ratings yet