Professional Documents
Culture Documents
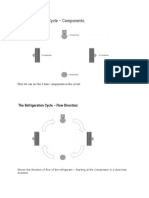
Figure 1: The Flows of How Air Condition Works
Uploaded by
womanequinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Figure 1: The Flows of How Air Condition Works
Uploaded by
womanequinCopyright:
Available Formats
DATA
Air conditioning unit uses chemicals that convert from gas to liquid and back again quickly. These
chemicals transfer the heat from the air inside your property to the outside air.
The AC unit has three key parts. These are the compressor, the condenser, and the evaporator.
Your unit’s compressor and condenser are typically located in the outside part of the air conditioning
system. Inside the house is where you will find the evaporator.
The cooling fluid reaches the compressor as a low-pressure gas. The compressor squeezes this
gas/fluid, and the molecules in the liquid are packed closer together. The closer the compressor forces
these molecules together, the higher the temperature and energy rise.
Based on the data there are three different that can be analyze between cooling and heating
mode which are the air flow, the temperature at the component in the system and the condition of
reversing valve. The cooling is typically achieved through a refrigeration cycle, but sometimes evaporation
or free cooling is used. For the cooling mode, the cold air into capillary tube to the compressor and change
the cold air into hot air. The hot, compressed refrigerant vapor is now at a temperature and pressure at
which it can be condensed and is routed through a condenser. Then, hot air flow through valve and back
to capillary tube and change it back into cold air.
Figure 1: The flows of how air condition works.
You might also like
- Functioning of ChillersDocument22 pagesFunctioning of ChillersAnonymous b9fcR5No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document59 pagesChapter 5Nur Ain ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- Split Air Conditioner Learning SimulationDocument19 pagesSplit Air Conditioner Learning SimulationkablasNo ratings yet
- Performance and Efficiency Test of A Refrigeration PlantDocument17 pagesPerformance and Efficiency Test of A Refrigeration Plantjun75% (4)
- HVAC SystemDocument66 pagesHVAC Systemmrccahmed100% (1)
- Working Principle of An Air Conditioner: 31/10/2021 Arch. Services IiiDocument5 pagesWorking Principle of An Air Conditioner: 31/10/2021 Arch. Services IiiSNEHA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Ac Compressor OperationDocument3 pagesAc Compressor OperationshalabyahmedNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- Performance and Efficiency Test of A Refrigeration PlantDocument17 pagesPerformance and Efficiency Test of A Refrigeration PlantAllen Espeleta0% (1)
- Split Type of Air ConditionerDocument8 pagesSplit Type of Air ConditionersadNo ratings yet
- Mapua Institute of Technolog1Document15 pagesMapua Institute of Technolog1Ian KasaiNo ratings yet
- 1,2 - Unit 1Document137 pages1,2 - Unit 1Saran T SNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Report.Document15 pagesAir Conditioning Report.Ethan XavierNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump AssignmentDocument10 pagesHeat Pump AssignmentOmer NadeemNo ratings yet
- Performance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration PlantDocument26 pagesPerformance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration PlantGigi Sales100% (2)
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Document33 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Christina OhNo ratings yet
- Mechanical-Compression Refrigeration SystemsDocument4 pagesMechanical-Compression Refrigeration Systemsaruna MoonNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Basic Refrigerationsystem and ComponentsDocument25 pagesGroup 2 Basic Refrigerationsystem and ComponentsVipin VetriNo ratings yet
- Basics of Air Conditioning PDFDocument3 pagesBasics of Air Conditioning PDFMarcelo RibeiroNo ratings yet
- OJT Outputs: Raphael Justine D. Hismana Bsme 5Document27 pagesOJT Outputs: Raphael Justine D. Hismana Bsme 5Khaster NavarraNo ratings yet
- Part 3 Phase Change of The Refrigerant in The CycleDocument7 pagesPart 3 Phase Change of The Refrigerant in The CycleKenneth JameroNo ratings yet
- Performance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration Sysytem: (Mel Lab 3 Report)Document14 pagesPerformance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration Sysytem: (Mel Lab 3 Report)Yhan SombilonNo ratings yet
- Portable Air ConditonerDocument4 pagesPortable Air ConditonerAmit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- UCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)Document11 pagesUCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)shehan harshithaNo ratings yet
- Principle of VRFDocument5 pagesPrinciple of VRFghazanfarhayat456No ratings yet
- Part 3 Phase Change of The Refrigerant in The CycleDocument7 pagesPart 3 Phase Change of The Refrigerant in The CycleKenneth JameroNo ratings yet
- Heat Ventilating and Air Conditioning (Hvac)Document3 pagesHeat Ventilating and Air Conditioning (Hvac)Den Mas DeepNo ratings yet
- The Language of HVACDocument4 pagesThe Language of HVACkash30No ratings yet
- The Working Processing of An AirDocument1 pageThe Working Processing of An Airanhtuan_bkNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument4 pagesAbstractafiqzalhasmiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Heat PumpsDocument13 pagesThermodynamics: Heat PumpsRoanne Maye Oligario ArqueroNo ratings yet
- How It WorksDocument6 pagesHow It WorksFaizal IsmailNo ratings yet
- HVAC Unit 1&2Document22 pagesHVAC Unit 1&2LOYOLA RS 200No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning Systemabenezer1425No ratings yet
- M&E Assignment 3Document12 pagesM&E Assignment 3han0701No ratings yet
- What Makes A Good Refrigerant?: GeneralDocument1 pageWhat Makes A Good Refrigerant?: GeneralkprasannanNo ratings yet
- An Air Conditioner Has 5 Main Parts:: 1. RefrigerantDocument11 pagesAn Air Conditioner Has 5 Main Parts:: 1. RefrigerantRitu SinghNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsAhmad MujahidNo ratings yet
- Building Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1Document32 pagesBuilding Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1TaanayaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument7 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningManjunatha EikilaNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CycleDocument3 pagesRefrigeration CycleJaime Alava MontalvoNo ratings yet
- R&AC Lab ManualDocument29 pagesR&AC Lab ManualPARAMESHNo ratings yet
- Heat Energy Hvac Vapor-Compression RefrigerationDocument2 pagesHeat Energy Hvac Vapor-Compression RefrigerationanandanNo ratings yet
- (@) Air Conditioning Using Exhaust Gas of AutomobilesDocument28 pages(@) Air Conditioning Using Exhaust Gas of AutomobilesJithin JoseNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning ........ 1Document12 pagesAir Conditioning ........ 1Candra riyan AndonoNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CycleDocument5 pagesRefrigeration CycleMa Zaira ObilloNo ratings yet
- LiteratureDocument4 pagesLiteratureHarvey MartinezNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Theory PDFDocument13 pagesAir Conditioning Theory PDFJan AmoresNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanism and PrincipleDocument2 pagesBasic Mechanism and PrinciplesahilkaushikNo ratings yet
- Refregeration UnitDocument24 pagesRefregeration UnitEZWANNo ratings yet
- Basic On CycleDocument12 pagesBasic On CycleSantosh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument11 pagesAir ConditioningBrilliantJohnMalandacRubiaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.2: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExperiment No.2: Objectiveمیاں اسامہ صفدرNo ratings yet
- Bu ResearchDocument10 pagesBu ResearchToteng TanglaoNo ratings yet
- How Do Chillers Work by Nathan SchumacherDocument5 pagesHow Do Chillers Work by Nathan SchumacherNathan SchumacherNo ratings yet
- Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning by Krishnanand MDocument15 pagesHeating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning by Krishnanand MMystic Prince XNo ratings yet
- Main and Auxiliary Parts of ACDocument9 pagesMain and Auxiliary Parts of ACRicaMyrivilleArellagaNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Condenser For A Room Air Conditioning System (Rep1.)Document40 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Condenser For A Room Air Conditioning System (Rep1.)Satish Alan100% (1)
- Draft Basic AirconDocument37 pagesDraft Basic AirconcspolaNo ratings yet