Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ace 1
Uploaded by
Dilshan WickramanayakaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ace 1
Uploaded by
Dilshan WickramanayakaCopyright:
Available Formats
We report that the inhibition of the angiotensin converting enzyme is an effective short-term treatment
of low-renin hypertension in acute glomerulonephritis (AGN). We treated 9 patients who had AGN with
moderate to severe hypertension and suppressed plasma renin activity with 25-50 mg of captopril per
os every 6-8 hours. Control of blood pressure was achieved in 1-2 hours and maintained thereafter.
Captopril therapy was associated with an increase in plasma renin activity, a decrease in plasma
aldosterone and an increase in the urinary excretion of prostaglandin E2 and kallikrein, independent of
changes in urine output. Creatinine clearance increased 39.6 +/- SE 15.2% with captopril and decreased
in the postcaptopril period, suggesting that captopril exerted a reversible effect on glomerular filtration
rate, possibly modifying intrarenal vasoconstriction. Our study shows that rapid control of hypertension
in AGN may be obtained with oral inhibition of the angiotension converting enzyme. Stimulation of PGE2
and kinins, as well as angiotensin II blockade appear to contribute to the hypotensive effect of the drug;
by inference, the suppressed activity of vasodilator systems seems to play a significant role in the
hypertension of AGN.
In summary, the combination of an ACE inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blocker with a calcium channel
blocker (long-acting dihydropyridine or non-dihydropyridine) and a diuretic may be effective to attain
the target BP and to reduce the amount of urinary protein excretion in patients with chronic GN.
Guidelines for the management of hypertension in CKD are that for diabetic and non diabetic
proteinuric patients with CKD, anti-hypertensive therapy should include ACEI or ARB. For patients with
non diabetic nonproteinuric CKD, anti-hypertensive therapy should include either ACEI, ARB, diuretic, b-
blocker, or longacting CCB61,62. These drugs should be used with caution, with strict monitoring of the
renal function and plausibly temporarily withdrawn during situations of low renal flow (e.g. major
surgeries, hypovolemic situations).
Recommendation: Nifedipine should be used in controlling hypertension in acute post streptococcal
glomerulonephritis.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- KSM Membership Application FormDocument2 pagesKSM Membership Application FormDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- KSM Membership Application FormDocument2 pagesKSM Membership Application FormDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Blank CV Template Microsoft WordDocument2 pagesBlank CV Template Microsoft WordDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument1 pageEnglishDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
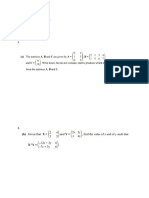
- Matrices: Question Paper Paper 1Document10 pagesMatrices: Question Paper Paper 1Dilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Matrics Paper - Allocated Marks - 1Document1 pageMatrics Paper - Allocated Marks - 1Dilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Matrics Question Paper - 3Document6 pagesMatrics Question Paper - 3Dilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Matrics Question Paper - 3 Time Allowed: 30 MinutesDocument6 pagesMatrics Question Paper - 3 Time Allowed: 30 MinutesDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Matrices: Question Paper Paper 2Document10 pagesMatrices: Question Paper Paper 2Dilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- MS Cambridge O Admath-P1 MatricesDocument9 pagesMS Cambridge O Admath-P1 MatricesDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Sample Size For A Case-Control StudyDocument14 pagesCalculating Sample Size For A Case-Control StudyFakher KhaliliNo ratings yet
- VISA - Form ThailandDocument2 pagesVISA - Form ThailandPamuditha DehigaspitiyaNo ratings yet
- Forrester Et Al-2017-Tropical Medicine & International HealthDocument10 pagesForrester Et Al-2017-Tropical Medicine & International HealthDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- VISA FormDocument20 pagesVISA FormDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Matrices J 2011 - 2014Document6 pagesMatrices J 2011 - 2014Dilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme - 1Document4 pagesMark Scheme - 1Dilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Master of Science in Occupational Health and SafteyDocument3 pagesMaster of Science in Occupational Health and SafteyDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Digestion QuestionsDocument1 pageDigestion QuestionsTassie777No ratings yet
- Module Titles List 2018 - FinalDocument6 pagesModule Titles List 2018 - FinalDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- The Kandy Society of Medicine: Tel: 081-2201702 Fax: 081-2233336 Email: WebsiteDocument1 pageThe Kandy Society of Medicine: Tel: 081-2201702 Fax: 081-2233336 Email: WebsiteDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- 4PH0 2P Que 20160125 PDFDocument20 pages4PH0 2P Que 20160125 PDFdadajee420No ratings yet
- Cells Tissues QuestionsDocument1 pageCells Tissues QuestionsJosephine Charles HoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Study GuideDocument5 pagesFinal Exam Study GuideDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- PrintDocument24 pagesPrintDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Clinical CaseDocument10 pagesClinical CaseDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Salm I PDFDocument24 pagesSalm I PDFDilshan Wickramanayaka100% (1)
- Lecture 2 MSC Epid 280017aDocument77 pagesLecture 2 MSC Epid 280017aDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Eras in EpidemiologyDocument12 pagesEras in EpidemiologyDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Errors in EpidemiologyDocument13 pagesErrors in EpidemiologyDilshan Wickramanayaka0% (1)