0% found this document useful (0 votes)
230 views2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Cardiac Patients
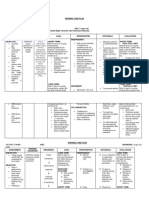
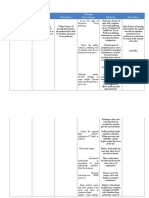
The nursing care plan assessed a client with decreased cardiac output related to an altered heart rate and rhythm due to a myocardial infarction. The short-term goal was for the client to demonstrate hemodynamic stability with a 20-30% increase in blood pressure and cardiac output within 30 minutes. The long-term goal was for a 31-80% increase in hemodynamic stability by the end of 8 hours. Nursing interventions included monitoring vital signs, administering medications, and assessing symptoms. The plan was partially met after 8 hours, with slight disturbance in cardiac monitoring but improved pressure and output.
Uploaded by
James Czar FontanillaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
230 views2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Cardiac Patients
The nursing care plan assessed a client with decreased cardiac output related to an altered heart rate and rhythm due to a myocardial infarction. The short-term goal was for the client to demonstrate hemodynamic stability with a 20-30% increase in blood pressure and cardiac output within 30 minutes. The long-term goal was for a 31-80% increase in hemodynamic stability by the end of 8 hours. Nursing interventions included monitoring vital signs, administering medications, and assessing symptoms. The plan was partially met after 8 hours, with slight disturbance in cardiac monitoring but improved pressure and output.
Uploaded by
James Czar FontanillaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd