Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ochempal: Aldol Condensation
Uploaded by
sachin jakharOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ochempal: Aldol Condensation
Uploaded by
sachin jakharCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Get neighbourhood answers
Ask neighbours questions. Share local expertise.
play.google.com
2 Thousands of free eBooks.
Read in 6 languages Get the Free Kindle app play.google.com
OChemPal
Aldol Condensation
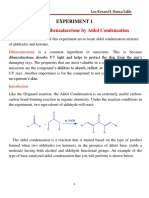
Enolizable aldehydes and enolizable ketones, in the presence of an acid or base catalyst in aqueous
medium at high temperature, undergo a reaction, giving an α, β-unsaturated aldehyde or an α, β-un-
saturated ketone, respectively, as the product. This reaction is known as aldol condensation. The
base-catalyzed aldol condensation, in which the catalyst is usually the hydroxide ion, is more
common.
eg:
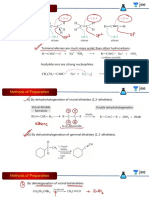
Mechanism:
Step 1: The hydroxide ion deprotanates the aldehyde reversibly.
Step 2: Enolate ion 1 adds to the unreacted aldehyde.
Step 3: Alkoxide ion 2 is protonated by water.
Step 4: Aldol 3 is an enolizable aldehyde. A small amount of it is converted to the corresponding eno-
late ion (4) by the hydroxide ion.
Step 5: Enolate ion 4 loses a hydroxide ion.
Step 1 through 3 are an aldol reaction, steps 4 and 5 a 1,2-elimination via E1cB mechanism. Thus, al-
dol condensation is aldol reaction followed by 1,2-elimination.
OCHEMPAL IS NOW IN THE FORM OF A BOOK
Title: The Elements of Organic Chemistry; Subtitle: A Compendium of Terminology, Definitions, and
Concepts for the Beginner.
Available at Amazon or the publisher’s website: http://linusbooks.com/?wpsc-product=the-elements-
of-organic-chemistry
The book contains everything on OChemPal except some recent additions, a few biochemical terms,
and the Mastery Check feature. So, if you prefer reading a book to reading a screen, the book is for
you.
You might also like
- 3.3 Reactions and Synthesis of Alkenes PPT 1Document16 pages3.3 Reactions and Synthesis of Alkenes PPT 1Vergil HashimotoNo ratings yet
- Aldol Condensation 1Document8 pagesAldol Condensation 1Bilal100% (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Oxidation of Cyclohexanol To CyclohexanoneDocument5 pagesOxidation of Cyclohexanol To CyclohexanoneChandrani Chakraborti100% (2)
- Aldol Notes PDFDocument8 pagesAldol Notes PDFAna100% (1)
- Experiment 123456 1 PDFDocument18 pagesExperiment 123456 1 PDFHardi Ahmed100% (1)
- Chapter 12 Mechanism of Reaction: Aldol CondensationDocument17 pagesChapter 12 Mechanism of Reaction: Aldol CondensationTiya KapoorNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Reactions PDFDocument39 pagesCarbonyl Reactions PDFAtikah RoselyNo ratings yet
- Aldol CondensationDocument4 pagesAldol CondensationSreeja SatheeshNo ratings yet
- Aldol Condensation Chem 12Document21 pagesAldol Condensation Chem 12Let's Start GamingNo ratings yet
- Lab 6-283gDocument11 pagesLab 6-283gAnonymous 4KuItFhNo ratings yet
- Aldol CondesationDocument13 pagesAldol CondesationRonny AlexNo ratings yet
- Reaksi Kondensasi Karbonil - OKDocument23 pagesReaksi Kondensasi Karbonil - OKMOCHILNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of AlcoholDocument4 pagesPhysical Properties of AlcoholrhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document52 pagesChapter 4Daniel McDermottNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Aliphatic HydrocarbonsDocument16 pagesModule 7 Aliphatic HydrocarbonsDana MikaelaNo ratings yet
- Name Reactions 2Document45 pagesName Reactions 2saheedvkNo ratings yet
- (Lecture 3) Carbonyls and AminesDocument34 pages(Lecture 3) Carbonyls and AminesKasraSrNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesDocument58 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesNur Aliyah Abdul RazakNo ratings yet
- Test For Aldehyde/Ketone: Course No. Chem 222/ 122 Course Name: Organic Chemistry SessionalDocument31 pagesTest For Aldehyde/Ketone: Course No. Chem 222/ 122 Course Name: Organic Chemistry SessionalHasan RabyNo ratings yet
- Elimination of Alcohols To Alkenes With POCl3 - Master Organic ChemistryDocument17 pagesElimination of Alcohols To Alkenes With POCl3 - Master Organic ChemistryBiswa Bhusan NayakNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project: Aldol Condensation o IntroductionDocument10 pagesChemistry Project: Aldol Condensation o IntroductionVidur GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mapua Institute of Technology: School of Chemical Engineering and ChemistryDocument12 pagesMapua Institute of Technology: School of Chemical Engineering and ChemistryVon Joby RomeroNo ratings yet
- Aldol Reaction - Addition - Condensation - Mechanism - AdichemistryDocument7 pagesAldol Reaction - Addition - Condensation - Mechanism - AdichemistryBiswa Bhusan NayakNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties: Terminal Alkynes Are Much More Acidic Than Other HydrocarbonsDocument17 pagesPhysical Properties: Terminal Alkynes Are Much More Acidic Than Other HydrocarbonsVidhan PatniNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Aldehyde KetonesDocument20 pagesReactions of Aldehyde Ketonesinushanth inuNo ratings yet
- Org 2Document30 pagesOrg 2rearachel25No ratings yet
- Synthesis of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionDocument43 pagesSynthesis of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionttinbddinNo ratings yet
- Lectures Named ReactionsDocument26 pagesLectures Named ReactionsEshaNo ratings yet
- ALKENESSDocument16 pagesALKENESSFrancine MaramagNo ratings yet
- Organic AssignmentDocument9 pagesOrganic AssignmentSaud AlamNo ratings yet
- Name Reactions 1Document81 pagesName Reactions 1Anjish PatelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 WordsDocument5 pagesLecture 6 WordsDonald LetsoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes: © 2006 Thomson Higher EducationDocument70 pagesChapter 7 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes: © 2006 Thomson Higher EducationmacybnzNo ratings yet
- Week 12 Alkohol Dan PhenolDocument62 pagesWeek 12 Alkohol Dan PhenolAgitha FarihaNo ratings yet
- Chap 7Document35 pagesChap 7أسامة المنتصرNo ratings yet
- Enols and EnolatesDocument36 pagesEnols and EnolatesManuel Curitol PiutrinNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds and Redox Reactions: Lectures Written by Melanie Harvey & Krista Thomas, Johnson County CCDocument33 pagesCarbonyl Compounds and Redox Reactions: Lectures Written by Melanie Harvey & Krista Thomas, Johnson County CCStephany Mae ChiNo ratings yet
- Carberylic Acid.Document22 pagesCarberylic Acid.afrNo ratings yet
- Ethers and Epoxides: Ethers Nomenclature of EthersDocument10 pagesEthers and Epoxides: Ethers Nomenclature of EtherssarahNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones by Group 6 - 20230920 - 072912 - 0000Document18 pagesAldehydes and Ketones by Group 6 - 20230920 - 072912 - 0000ۦۦ CristineNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Reactions of AlkynesDocument54 pagesWeek 6 Reactions of AlkynesKate Arianne CabreraNo ratings yet
- CHEM 4113 Organic Chemistry Ii Lecture Notes: Eq - 5 Eq - 7Document9 pagesCHEM 4113 Organic Chemistry Ii Lecture Notes: Eq - 5 Eq - 7Kuandi TanNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Applications of Aldol CondensationDocument17 pagesPharmaceutical Applications of Aldol CondensationIshan PatelNo ratings yet
- CHEM35.1 E5 Aldol Condensation: Synthesis of DibenzalacetoneDocument3 pagesCHEM35.1 E5 Aldol Condensation: Synthesis of DibenzalacetoneGlenn Vincent Tumimbang50% (2)
- Aldehydes & Ketones: Sorsogon State CollegeDocument12 pagesAldehydes & Ketones: Sorsogon State CollegeElizabeth BáthoryNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Converted 1Document13 pagesUNIT IV ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Converted 1Kausik SenNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: Teacher OrientationDocument9 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: Teacher OrientationAnand RawatNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CondensatsDocument8 pagesCarbonyl CondensatssachinkurhekarNo ratings yet
- Kondensasi Karbonil FarDocument71 pagesKondensasi Karbonil Faragus raharjaNo ratings yet
- ReactionDocument54 pagesReactionAhmed ImranNo ratings yet
- Chem 332 Exam 1 ReviewDocument6 pagesChem 332 Exam 1 ReviewhddriNo ratings yet
- Alkene 2Document16 pagesAlkene 2Nadzirah YusopNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Topic: Organic ChemistryDocument23 pagesAn Overview of The Topic: Organic ChemistryEniolaNo ratings yet
- SKO3013 Aldehyde Ketone-Student NoteDocument51 pagesSKO3013 Aldehyde Ketone-Student NoteMike EzioNo ratings yet
- Reactions at the Compounds: α-Carbon of CarbonylDocument46 pagesReactions at the Compounds: α-Carbon of CarbonylDaniel McDermottNo ratings yet
- Intermediates Generated From OlefinsDocument25 pagesIntermediates Generated From OlefinsshubhamNo ratings yet
- The Hydrogenation of AlkenesDocument8 pagesThe Hydrogenation of AlkenesMuhamad Nazrul BoyoteenNo ratings yet
- Methods for Oxidation of Organic Compounds V1: Alcohols, Alcohol Derivatives, Alky Halides, Nitroalkanes, Alkyl Azides, Carbonyl Compounds Hydroxyarenes and AminoarenesFrom EverandMethods for Oxidation of Organic Compounds V1: Alcohols, Alcohol Derivatives, Alky Halides, Nitroalkanes, Alkyl Azides, Carbonyl Compounds Hydroxyarenes and AminoarenesNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesFrom EverandTransition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesNo ratings yet