Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03 Continuous Intravenous Sedation PDF
03 Continuous Intravenous Sedation PDF
Uploaded by
donut258Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
03 Continuous Intravenous Sedation PDF
03 Continuous Intravenous Sedation PDF
Uploaded by
donut258Copyright:
Available Formats
Program Anestesiologi & Cawangan Kualiti Penjagaan Kesihatan, BPP, KKM
ICU Management protocol No. 3
CONTINUOUS INTRAVENOUS SEDATION
Sedative medications are widely used in the intensive care unit. Titrating the
dose of the medication based on a sedation scale will help prevent oversedation,
treat undersedation as well as restlessness and agitation.
Nurses and doctors are encouraged to change the sedative infusion rate based on
this protocol.
1. Patients are to be assessed for sedation and agitation based on the revised
Riker Sedation and Agitation scale every 4 hours. The worst score within the
last 4 hours is to be recorded.
2. Titrate the sedative infusion rate with the aim of keeping the sedation score
between -1 to +1
3. Exceptions to keeping the sedation score between -1 and +1:
a. head injured on cerebral protection: sedation score -3
b. severe sepsis on high inotropic support: sedation score of at least -1
c. ARDS on high ventilatory support: sedation score of at least -2
d. tetanus: sedation score of at least -2
4. The standard sedative infusion to be used in patients admitted to ICU is
midazolam and morphine. 30mg midazolam and 30mg morphine is diluted
in up to 30mls normal saline. The infusion may be started between 2 – 3mls
per hour
5. Fentanyl may be used instead of midazolam and morphine in the following
conditions:
a. renal failure
b. hepatic failure
6. 200mcg Fentanyl is diluted in up to 20mls normal saline. The infusion rate
is between 2 - 5mls per hour (20 -50mcg/hour)
7. Postoperative cases that are for overnight ventilation may be put on
a. morphine + propofol
b. dexmedetomidine (only for 24 hours)
8. Consider daily interruption of continuous sedative infusion at a fixed time
every morning.
NAICU/ ICU Management protocol/ Continuous Intravenous Sedation/ August 2006 1
Program Anestesiologi & Cawangan Kualiti Penjagaan Kesihatan, BPP, KKM
9. If sedation score is +2, exclude other causes of agitation such as pain, hypoxia
etc. Calm patient down by communicating with him. Increase the sedative
infusion rate. There may be a need to add further sedation
For example: Tab. Lorazepam 1-2 mg ON / bd
Tab. Alprazolam 0.5mg bd / tds
10. If sedation score +3, exclude other causes of agitation. Bolus
midazolam/morphine and increase infusion rate except in non ventilated
patients. IV haloperidol will probably be indicated:
Age < 60 years: 5 -10mg PRN / 4 -6hourly
Age > 60 years: 2.5 -5 mg PRN / 6 hourly
11. If sedation score: -2, half the intravenous sedative infusion. Decrease the
sedative infusion every 4 hours until a score of -1 is achieved
12. If sedation score: -3, off sedative infusion. Assess 4 hours later. Restart at
half the infusion rate once a score of -1 has been reached.
13. Patients that are paralysed need not be scored and should be denoted with
a capital “P”
References:
1. Clinical practice guidelines on the sustained use of sedatives and analgesics in
the critically ill. Judith Jacobi et al: Crit Care Med 2002; Vol 30
NAICU/ ICU Management protocol/ Continuous Intravenous Sedation/ August 2006 2
Program Anestesiologi & Cawangan Kualiti Penjagaan Kesihatan, BPP, KKM
Revised Riker Sedation Agitation Scale
Score Description Definition
+3 Agitated and restless When awaken or otherwise, pulling at ETT,
trying to remove catheters or requires
physical restraints
+2 Awake but mildly agitated Anxious but mildly agitated. Attempts to sit
up but calms down with verbal instructions
+1 Awake and calm Awake, calm and easily follows commands
0 Aroused by voice and Awakens easily to verbal stimuli. Remains
remains calm awake, calm and easily follows command
-1 Aroused by movement Awakens to loud verbal stimuli or gentle
shaking. Has eye contact for at least 10
seconds but drifts off to sleep
OR
Awakens to loud verbal stimuli or gentle
shaking and follows simple commands
-2 Aroused by painful stimuli Localising or flexion to pain. Does not
communicate or follow commands
-3 Unarousable Extension, minimal or no response to painful
stimuli
Assessment:
1. Observe patient: is the patient awake and calm? If yes, score +1
Does the patient have behavior consistent with restless or agitation? If yes, score +2
or +3 based on the criteria above
2. If the patient is not awake, call the patient’s name out or lightly tap on the
shoulder. If awakens and remains awake, score is 0 but if drifts off to sleep
after eye contact, score is -1
3. If does not respond to voice or gentle tapping, physically stimulate the patient.
Observe response and score using the criteria above.
NAICU/ ICU Management protocol/ Continuous Intravenous Sedation/ August 2006 3
Program Anestesiologi & Cawangan Kualiti Penjagaan Kesihatan, BPP, KKM
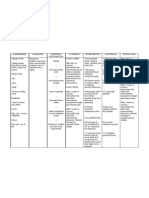
Algorithm for titration of continuous intravenous sedation using the
Revised Riker Sedation Agitation Scale
Patient admitted to ICU
Sedation needed?
Yes
Start continuous IV sedation (CIVS)
Do Revised Riker Score every 4 Exceptions to keeping the score - 1
hours with the aim of keeping the to + 1: head injury, ARDS, severe
score between -1 to +1 sepsis and tetanus
Adequate
Oversedated sedation Undersedated
Sedation score - 2: Sedation score +2 (exclude reversible
Half the sedative infusion causes of agitation: pain, hypoxia etc):
Continue at Calm patient down, increase CIVS +
same Lorazepam or alprazolam
infusion rate
Sedation score - 3: Sedation score +3 (exclude reversible
Off sedative infusion. causes of agitation):
Restart at half the rate when Bolus sedative infusion + haloperidol
score is -1
Sedative infusion to be Alprazolam: 0.5mg bd/tds IV Haloperidol:
started: midazolam + <60yrs: 5 -10mg PRN/
morphine at 2 -3 mls/hr. Lorazepam: 1-2mg ON/bd 4 – 6 hourly
Titrate based on the Riker >60yrs: 2.5 -5 mg PRN
score 4 -6 hourly
Note: Consider daily interruption of CIVS at a fixed time every
morning. Exceptions to this would be head injured on cerebral
protection, acute myocardial infarct
NAICU/ ICU Management protocol/ Continuous Intravenous Sedation/ August 2006 4
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Day Spa Business PlanDocument33 pagesDay Spa Business PlanPreeti Dhaka33% (3)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Pulsar ProjectDocument61 pagesThe Pulsar ProjectRadu Marinescu100% (4)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- A Modern History of Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing PDFDocument7 pagesA Modern History of Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing PDFdedisukasusuNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Social Work Case Management DocumentationDocument10 pagesGuidelines For Social Work Case Management DocumentationBetty Weese Holdread100% (2)
- Preparation of Plans and Design of Sanitary Landfill (Including Signatures of Professional Engineers)Document1 pagePreparation of Plans and Design of Sanitary Landfill (Including Signatures of Professional Engineers)Temoteo L Pupa IIINo ratings yet
- Report in Anger ManagementDocument22 pagesReport in Anger ManagementHarold TaylorNo ratings yet
- Life Coaching Certifications: DisclaimerDocument2 pagesLife Coaching Certifications: DisclaimerEugenia PregoNo ratings yet
- Uaspl InfoDocument2 pagesUaspl InfoDilipraja KolliNo ratings yet
- The Impacts of Autism On The FamilyDocument4 pagesThe Impacts of Autism On The FamilyRuth Arcibal RomeroNo ratings yet
- C40 The Gonadal Hormones & Inhibitors: Anita Q. Sangalang, MD, Mhped, Fpogs Faculty of Pharmacy University of Santo TomasDocument7 pagesC40 The Gonadal Hormones & Inhibitors: Anita Q. Sangalang, MD, Mhped, Fpogs Faculty of Pharmacy University of Santo TomasHydieNo ratings yet
- PEP20 02 01 004 - Final - 508Document346 pagesPEP20 02 01 004 - Final - 508Amel EzNo ratings yet
- Aesthetic Management of Immediate Anterior Tooth Replacement With Ovate Pontic: A Case Report PDFDocument5 pagesAesthetic Management of Immediate Anterior Tooth Replacement With Ovate Pontic: A Case Report PDFAnita PrastiwiNo ratings yet
- Neo Vascular Glaucoma (NVG) PPT GAURAVDocument73 pagesNeo Vascular Glaucoma (NVG) PPT GAURAVGaurav shuklaNo ratings yet
- Perineal CareDocument5 pagesPerineal CareTomi AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Spa Beautiful BrochureDocument16 pagesSpa Beautiful BrochureDavid RalphNo ratings yet
- Palliative CareDocument6 pagesPalliative CareVILLEJO JHOVIALENNo ratings yet
- CataractsDocument17 pagesCataractsdubutwice29No ratings yet
- Wellness Tourism: An Initiative For Comprising Wellness Tourism Vacations Within The Corporate Wellness StrategyDocument16 pagesWellness Tourism: An Initiative For Comprising Wellness Tourism Vacations Within The Corporate Wellness StrategyYuni DwitriNo ratings yet
- A Life Less Anxious - Freedom From Panic AttacksDocument112 pagesA Life Less Anxious - Freedom From Panic AttacksAlex Burduja100% (1)
- Diverticular Disease and Intestinal ObstructionDocument31 pagesDiverticular Disease and Intestinal ObstructionPauLa Cheneree Peña ÜNo ratings yet
- Granny's List July 2011Document543 pagesGranny's List July 2011renaxgade81No ratings yet
- FentanylDocument3 pagesFentanylDavid Villanueva67% (3)
- Upper Back ExercisesDocument2 pagesUpper Back ExercisesMarco NgNo ratings yet
- Medical Emergencies PosterDocument1 pageMedical Emergencies Posterlaur_rbNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Resuscitation PDFDocument1 pageNeonatal Resuscitation PDFOdessa EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Monthly Census of Chemotherapy Administration-Surgery-1Document13 pagesMonthly Census of Chemotherapy Administration-Surgery-1myvi317No ratings yet
- Imbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging.Document1 pageImbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging.Senyorita KHayeNo ratings yet
- Department of Labor: cm-915Document2 pagesDepartment of Labor: cm-915USA_DepartmentOfLaborNo ratings yet
- Philippine Laws Governing Health CareDocument5 pagesPhilippine Laws Governing Health Carebanyenye25100% (3)
- Pharmacoeconomics: Basic Concepts and Terminology: T. Walley & A. HaycoxDocument6 pagesPharmacoeconomics: Basic Concepts and Terminology: T. Walley & A. HaycoxIndra PratamaNo ratings yet