Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NAME OF DRUGS: Erythropoietin Therapeutic Class: Pharmacological Class: DOSAGE: 10,000 Units Route:Sq Frequency
Uploaded by
Jhoanna Bautista0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views9 pagesLanoxin
Original Title
Drug Study
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLanoxin
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views9 pagesNAME OF DRUGS: Erythropoietin Therapeutic Class: Pharmacological Class: DOSAGE: 10,000 Units Route:Sq Frequency
Uploaded by
Jhoanna BautistaLanoxin
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
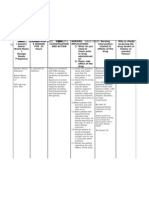
NAME OF DRUGS: Erythropoietin THERAPEUTIC CLASS: anti anemic PHARMACOLOGICAL CLASS: glycoprotein
DOSAGE: 10,000 units ROUTE:SQ FREQUENCY:
ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION SIDE EFFECTS NURSING PATIENT RATIONALE
MANAGEMENT TEACHINGS
Erythropoietin or - Treatment of anemia due Contraindicated in patients CNS: headache, seizures, paresthesia, • For HIV-infected - Explain
exogenous epoetin to Chronic Kidney with uncontrolled fatigue, asthenia, dizziness. patients treated with importance of
alfa binds to the Disease (CKD) in patients hypertension and CV: hypertension, edema. zidovudine, regularly
erythropoietin on dialysis and not on hypersensitivity to mammal GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. measure hematocrit monitoring blood
receptor (EPO-R) dialysis. cell-derived products or Metabolic: hyperuricemia, once weekly until pressure because
and activates - treatment of anemia due albumin (human). hyperphosphatemia, hyperkalemia. stabilized and then of potential drug
intracellular signal to zidovudine in patients Musculoskeletal: arthralgia. periodically. effects.
transduction with HIV-infection. Respiratory: cough, shortness of • Most patients - Advise patient to
pathways [3]. The - treatment of anemia due breath. eventually require adhere to dietary
affinity (Kd) of to the effects of Skin: rash, urticaria. supplemental iron restrictions during
EPO for its concomitant Other: increased clotting of therapy. Before and therapy. Make
receptor on human myelosuppressive arteriovenous grafts, pyrexia, during therapy, sure he
cells is ∼100 to chemotherapy, and upon injection site reactions. monitor patient’s understands that
200 pM [4]. Upon initiation, there is a iron stores, drug won’t
binding to EPO-R minimum of two including serum influence disease
on the surface of additional months of ferritin and process.
erythroid planned chemotherapy. transferrin
progenitor cells, a - reduction of allogeneic saturation.
conformational RBC transfusions in • If a patient fails to
change is induced patients undergoing respond to epoetin
which brings EPO- elective, noncardiac, alfa therapy,
R-associated Janus nonvascular surgery. consider the
family tyrosine following possible
protein kinase 2 causes: vitamin
(JAK2) molecules deficiency, iron
into close deficiency,
proximity. JAK2 underlying
molecules are infection, occult
subsequently blood loss,
activated via underlying
phosphorylation, hematologic
then phosphorylate disease, hemolysis,
tyrosine residues in aluminum
the cytoplasmic intoxication, osteitis
domain of the fibrosa cystica, or
EPO-R that serve increased dosage of
as docking sites for zidovudine.
Src homology 2- • Routine
domain-containing monitoring of CBC
intracellular with differential
signaling and platelet counts
proteins [3]. The is recommended.
signalling proteins • Measure
include STAT5 that hematocrit twice
once weekly until it has
phosphorylated by stabilized and
JAK2, dissociates during adjustment
from the EPO-R, to a maintenance
dimerizes, and dosage in patients
translocates to the with chronic renal
nucleus where they failure. An interval
serve as of 2 to 6 weeks may
transcription elapse before a
factors to activate dosage change is
target genes reflected in the
involved in cell hematocrit level.
division or
differentiation,
including the
apoptosis inhibitor
Bcl-x [3]. The
inhibition of
apoptosis by the
EPO-activated
JAK2/STAT5/Bcl-
x pathway is
critical in erythroid
differentiation. Via
JAK2-mediated
tyrosine
phosphorylation,
erythropoietin and
epoetin alfa also
activates other
intracellular
proteins involved
in erythroid cell
proliferation and
survival, such as
Shc ,
phosphatidylinosito
l 3-kinase (PI3K),
and phospholipase
C-γ1
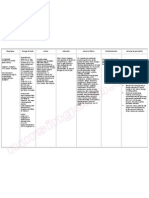
NAME OF DRUGS: Coralan THERAPEUTIC CLASS: PHARMACOLOGICAL CLASS:
DOSAGE:5mg ROUTE: oral FREQUENCY:
ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION SIDE EFFECTS NURSING PATIENT RATIONALE
MANAGEMENT TEACHINGS
Ivabradine is a pure Ivabradine is indicated by the FDA Luminous phenomena in the visual
heart rate-lowering to reduce the risk of hospitalization field (phosphenes), blurred vision,
agent, acting by for worsening heart failure in adult bradycardia, other cardiac
selective and patients with stable, symptomatic arrhythmias, syncope, hypotension,
specific inhibition chronic heart failure with left asthenia, fatigue, headache, dizziness,
of the cardiac ventricular ejection fraction ≤35%, nausea, constipation, diarrhoea,
pacemaker. If who are in sinus rhythm with dyspnoea, muscle cramps, skin
Current that resting heart rate ≥70 beats per reactions, angioedema,
controls the minute and either are on maximally hyperuricaemia, eosinophilia,
spontaneous tolerated doses of beta-blockers or elevated blood-creatinine
diastolic have a contraindication to beta- concentrations.
depolarization in blocker use. Recently the FDA has
the sinus node and added a new indication for
regulates heart rate. treatment of stable symptomatic
The cardiac effects heart failure as a result of dilated
are specific to the cardiomyopathy for pediatric
sinus node with no patients 6 months of age or more
effect on intra-
atrial,
atrioventricular or
intra ventricular
conduction times,
nor on myocardial
contractility or
ventricular
repolarisation.
NAME OF DRUGS: Movelax THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Laxative PHARMACOLOGICAL CLASS: Disaccharide
DOSAGE 30 cc ROUTE: FREQUENCY:
ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION SIDE EFFECTS NURSING PATIENT RATIONALE
MANAGEMENT TEACHINGS
The drug passes -Treatment of chronic and Galactosaemia, GI GI:flatulence, borborygmi, -After giving drug -Instructed
unchanged into habitual constipation. obstruction, digestive belching, abdominal through nasogastric patient to
the colon where perforation or risk of cramps,pain,and distention tube, flush tube notify health
bacteria break it -Prevention and treatment of digestive perforation. (initial dose);diarrhea with water to clear care provider if
down to organic it and ensure
portal systemic Patient on low galactose (excessive dose); she has
acids that passage of drug to
encephalopathy(PSE) diet. nausea, vomiting, colon diarrhea.
increase the stomach.
osmotic pressure including the stages of accumulation of hydrogen -Dilute drug with - Advised
in the colon and hepatic pre-coma and coma. gas; hypernatremia" water or fruit juice patient to take
slightly acidify to minimize its drug with juice
the clonic -For patients with sweet taste. - Don’t
contents, hemorrhoids, after colon/ -For oral administer drug
resulting in an anal surgery or other administration, with other
increase in stool conditions where a soft stool reconstitute powder laxatives
softening, is beneficial by dissolving 10- to because resulting
laxative action. 20-g packet in 120 loose stools may
This also results ml of water. falsely indicate
in migration of - For adequate dosage
blood ammonia administration by of lactulose.
into the colon retention enema,
contents with patient should
subsequent retain drug for 30
trapping and to 60 minutes. If
expulsion of retained less than
feces. 30 minutes, repeat
dose immediately.
Begin oral therapy
before
discontinuing
retention enemas.
• Monitor serum
potassium,
chloride, and
carbon dioxide
levels in long-term
treatment.
NAME OF DRUGS: Metoclopramide THERAPEUTIC CLASS: PHARMACOLOGICAL CLASS:
DOSAGE: 1 amp ROUTE: FREQUENCY:
ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION SIDE EFFECTS NURSING PATIENT RATIONALE
MANAGEMENT TEACHINGS
Dopamine Gastrointestinal motility, nausea, GI: hemorrhage, Restlessness, drowsiness, -give 30 mins before -Instructed
antagonist that acts vomiting of central and epileptics, fatigue, insomnia, headache, meals and at bed patient to avoid
by increasing peripheral origin associated hypersensitivity, dizziness, nausea time driving and other
receptor with surgery lactation, pts. With -assess mental hazardous
activities for
sensitivity and breast cancer. status during
atleast 2 hours.
response of upper treatment
-Instructed
GIT tissues to patient to avoid
acetylcholine. other CNS
depressant that
enhance
NAME OF DRUGS: Lanoxin THERAPEUTIC CLASS: antiarythmic PHARMACOLOGICAL CLASS: Cardiac Glycoside
DOSAGE: 0.25mg ROUTE: IV FREQUENCY:
ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION SIDE EFFECTS NURSING PATIENT RATIONALE
MANAGEMENT TEACHINGS
Digoxin increases the Mild-to-moderate heart failure Contraindicated in patients CNS: fatigue, generalized muscle • Inform patient
strength and vigor of (with a diuretic and an ACE hypersensitive to drug and in weakness, agitation, and responsible
heart contraction and inhibitor when possible). Increase those with digitalis-induced hallucinations, headache, malaise, family member
is useful in the myocardial contractility in toxicity, ventricular dizziness, vertigo, stupor, about drug action,
treatment of heart pediatrics with heart failure. fibrillation, or ventricular drug regimen,
paresthesia.
failure. It inhibits the Control of ventricular response tachycardia unless caused by ways to take pulse,
activity of an enzyme rate in chronic atrial fibrillation. heart failure. CV: arrhythmias (most reportable signs,
that controls Use very cautiously in commonly, conduction and follow-up
movement of elderly patients and in disturbances with or without AV plans. Patient must
calcium, sodium and patients with acute MI, block, PVCs, and supraventricular understand
potassium into heart incomplete AV block, sinus arrhythmias) that may lead to importance of
muscles. Calcium bradycardia, PVCs, chronic increased severity of heart follow-up
controls the force of constrictive pericarditis, failure and hypotension. laboratory tests
contraction hypertrophic EENT: yellow-green halos and have access to
,inhibiting ATPase cardiomyopathy, renal around visual images, blurred outpatient
increases calcium in insufficiency, severe laboratory
vision, light flashes, photophobia,
heart muscle and pulmonary disease, facilities.
therefore increases hypothyroidism, and in diplopia. • Instruct patient
the force of heart. patients with hypokalemia or GI: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, not to take an
hypomagnesemia. diarrhea, abdominal pain. extra dose of
digoxin if dose is
missed.
• Tell patient to
report severe
nausea, vomiting,
or diarrhea
because these
conditions may
make patient more
susceptible to
toxicity.
• Advise patient to
use the same brand
consistently.
• Tell patient to
call before using
OTC or herbal
preparations,
especially those
high in sodium.
You might also like
- Brand Name Generic Name Indication and Contraindication Nursing Consideration Action of The Drug Dose and Administration Side EffectsDocument2 pagesBrand Name Generic Name Indication and Contraindication Nursing Consideration Action of The Drug Dose and Administration Side EffectsCarla Dana GozumNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyGeraldine Gallaron - CasipongNo ratings yet
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Arixtra Drug StudyDocument2 pagesArixtra Drug StudyEdelweiss Marie Cayetano100% (1)
- Drug Study ClonidineDocument2 pagesDrug Study ClonidineCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studywarlocke100% (2)
- Drug Study AtorvastatinDocument1 pageDrug Study AtorvastatinEzron Kendrick DuranNo ratings yet
- EsmololDocument2 pagesEsmololtherock316_995149No ratings yet
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyCrystal Queen MarquezNo ratings yet
- MIDAZOLAM DRUG STUDYDocument5 pagesMIDAZOLAM DRUG STUDYShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NewDocument4 pagesDrug Study NewJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniNo ratings yet
- WVSU College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument2 pagesWVSU College of Nursing Drug StudyTrina Joy Domantay100% (1)
- Fondaparinux and Clopidogrel Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesFondaparinux and Clopidogrel Nursing ConsiderationsShayneAngelMarieMatubangNo ratings yet
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Lowering Cholesterol with EzetimibeDocument2 pagesLowering Cholesterol with EzetimibeFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- Enoxaparin (Lovenox)Document1 pageEnoxaparin (Lovenox)ENo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone Drug StudyRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Clonidine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageClonidine HydrochlorideLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyYanna N. Cuaki100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJan Lianne BernalesNo ratings yet
- Name of Drugs Kaligen 8Document2 pagesName of Drugs Kaligen 8mellany100% (1)
- Drug Study NorepinephrineDocument2 pagesDrug Study NorepinephrinePearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 pagesDrug Study GuideAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Buminate (Albumin)Document2 pagesBuminate (Albumin)lpetallo100% (2)
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium BicarbonateDocument5 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium BicarbonatehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B ComplexDocument2 pagesVitamin B ComplexCar_Mi_3606No ratings yet
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Heparin InjectionDocument2 pagesHeparin InjectiongagandipkSNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY SpironolactoneDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY SpironolactoneJerremy LuqueNo ratings yet
- Ethosuximide - (Zarontin)Document2 pagesEthosuximide - (Zarontin)Roshleen Ann De Pedro0% (1)
- Pantoprazole DrugDocument1 pagePantoprazole Drugman12No ratings yet
- Clonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyDocument3 pagesClonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageDrug Study Calcium GluconateLarah Mae AndogNo ratings yet
- Trandate (Labetalol)Document3 pagesTrandate (Labetalol)ENo ratings yet
- Filgrastim Boosts Neutrophil Recovery After ChemotherapyDocument3 pagesFilgrastim Boosts Neutrophil Recovery After ChemotherapyKyla Barrera TabungarNo ratings yet
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDan Dan Soi T50% (2)
- MethylprednisoloneDocument4 pagesMethylprednisoloneapi-3797941100% (2)
- Drug Study CISPLATINDocument1 pageDrug Study CISPLATINIrish Jane Gallo100% (1)
- DexmedetomidineDocument2 pagesDexmedetomidineapt48 ukwmsNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis FelodipineDocument2 pagesDrug Analysis FelodipineNika LoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Amoxicillin Mechanism and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Amoxicillin Mechanism and Nursing ResponsibilitiesKrzia TehNo ratings yet
- Warfarin Dosing and Monitoring GuidelinesDocument4 pagesWarfarin Dosing and Monitoring GuidelinesbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloe100% (1)
- Ondansetron Antiemetic Blocks Serotonin 5-HT3 ReceptorsDocument2 pagesOndansetron Antiemetic Blocks Serotonin 5-HT3 ReceptorshauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- BuscopanDocument2 pagesBuscopancen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- West Visayas Nursing Drug StudyDocument1 pageWest Visayas Nursing Drug StudyKhryss Paula BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDenise Louise Po100% (4)
- 1 DrugsDocument2 pages1 DrugsPatricia Lucero100% (2)
- Drug Study LosartanDocument2 pagesDrug Study LosartanIris BalinoNo ratings yet
- Anti-Anemia and Hematopoietic Growth FactorsDocument8 pagesAnti-Anemia and Hematopoietic Growth FactorsIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Hipereusinofil PMCDocument23 pagesHipereusinofil PMCaperireNo ratings yet
- Epoetin Alfa Drug StudyDocument1 pageEpoetin Alfa Drug StudyAnni Barba100% (1)
- Proteins: Prepared By: Dayle Daniel G. Sorveto, RMT, MSMTDocument64 pagesProteins: Prepared By: Dayle Daniel G. Sorveto, RMT, MSMTDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- DRUGS DURING PREGNANCY (Feso4, Folic Acid)Document2 pagesDRUGS DURING PREGNANCY (Feso4, Folic Acid)Angelyn Bucaso50% (2)
- Anemia in SNDocument8 pagesAnemia in SNNurulSyaidahNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Hydroxide: Acid-Base Balance Overview of Acids and Bases DescriptionDocument15 pagesHydrogen Hydroxide: Acid-Base Balance Overview of Acids and Bases DescriptionElisha WorworNo ratings yet
- ACOG All About Exercise During PregnancyDocument4 pagesACOG All About Exercise During PregnancyriasahNo ratings yet
- Medical Coding Training - CPC (PDFDrive)Document214 pagesMedical Coding Training - CPC (PDFDrive)Esther Rani100% (6)
- Keratosis Types and TreatmentsDocument30 pagesKeratosis Types and TreatmentsLydia WangNo ratings yet
- English For Nursing Topic 13 Reinforcing A Dietary ProgramDocument7 pagesEnglish For Nursing Topic 13 Reinforcing A Dietary ProgramAyu AndiniiNo ratings yet
- Em Form NktiDocument7 pagesEm Form NktiJerico Wendell Gee RubioNo ratings yet
- Crush Injuries and RhabdomyolysisDocument15 pagesCrush Injuries and RhabdomyolysisUday SankarNo ratings yet
- English Model Paper 6 emDocument5 pagesEnglish Model Paper 6 emReddy GmdNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hypertension - The Mosaic Theory and Beyond - JURNALDocument17 pagesPathophysiology of Hypertension - The Mosaic Theory and Beyond - JURNALidham shadiqNo ratings yet
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso)Document15 pagesTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso)Dhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument40 pagesChronic Renal FailureSarumathy PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Outcomes of Implementing A National Shypilis Follow-Up SystemDocument12 pagesChallenges and Outcomes of Implementing A National Shypilis Follow-Up SystemnskhldNo ratings yet
- Carilion Clinic 2018 Fact SheetDocument2 pagesCarilion Clinic 2018 Fact Sheetphv209No ratings yet
- Reliability of Neonatal Screening ResultsDocument55 pagesReliability of Neonatal Screening ResultsJose PérezNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Blueprints NotesDocument96 pagesPediatric Blueprints NotesPisiform90100% (2)
- Respiratory Cytology I PDFDocument13 pagesRespiratory Cytology I PDFafdsdgsd100% (1)
- Nuclear Cardiology Study Guide: Andrzej Moniuszko B. Adrian KesalaDocument293 pagesNuclear Cardiology Study Guide: Andrzej Moniuszko B. Adrian KesalaAnuNo ratings yet
- 37221-Texto Del Artículo-110845-1-10-20231129Document20 pages37221-Texto Del Artículo-110845-1-10-20231129Hector OrgenaneroNo ratings yet
- Drug Dose Determination Using Pharmacokinetic PrinciplesDocument36 pagesDrug Dose Determination Using Pharmacokinetic PrinciplesSreya Sanil100% (1)
- Hair Care BSC N First YearDocument4 pagesHair Care BSC N First YearNeelofur Ibran AliNo ratings yet
- New PMDC Neb Format 2011Document28 pagesNew PMDC Neb Format 2011AliHazratNo ratings yet
- The Case of The Tired GrandmaDocument8 pagesThe Case of The Tired Grandmaapi-322303922No ratings yet
- FILARIASIS PPT FINALDocument39 pagesFILARIASIS PPT FINALBinita Shakya100% (1)
- Dr. Ralph Moss Interview: Medical Writer, Author, and FilmmakerDocument27 pagesDr. Ralph Moss Interview: Medical Writer, Author, and FilmmakerRosa AlvarezNo ratings yet
- The Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument40 pagesThe Upper Respiratory Tract Infectionssalma100% (1)
- Name: NIM: Class:: Medical InstrumentsDocument9 pagesName: NIM: Class:: Medical InstrumentsNessyaa SyahnaNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument83 pagesClassificationDisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Focal Atrial Tachycardia I: Clinical Features, DiagnosisDocument10 pagesFocal Atrial Tachycardia I: Clinical Features, Diagnosisapi-26166949No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 ElectrolytesDocument115 pagesChapter 13 Electrolytessisay SolomonNo ratings yet
- Controles BioradDocument2 pagesControles BioradDeqsa Corporativo0% (1)