Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abstract of E-Cash Payment System
Uploaded by
saloni kumariOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract of E-Cash Payment System
Uploaded by
saloni kumariCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract of E-Cash Payment System
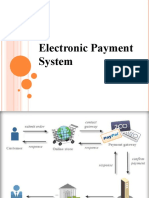
Electronic payment systems come in many forms including digital checks, debit
cards, credit cards, and stored value cards. The usual security features for such
systems are privacy (protection from eavesdropping), authenticity (provides user
identification and message integrity), and no repudiation (prevention of later
denying having performed a transaction).
The type of electronic payment system focused on in this paper is electronic cash.
As the name implies, electronic cash is an attempt to construct an electronic
payment system modelled after our paper cash system. Paper cash has such
features as being: portable (easily carried), recognizable (as legal tender) hence
readily acceptable, transferable (without involvement of the financial network),
untraceable (no record of where money is spent), anonymous (no record of who
spent the money) and has the ability to make "change." The designers of
electronic cash focused on preserving the features of untraceability and
anonymity. Thus, electronic cash is defined to be an electronic payment system
that provides, in addition to the above security features, the properties of user
anonymity and payment untraceability.
Electronic Payment
The term electronic commerce refers to any financial transaction involving the
electronic transmission of information. The packets of information being
transmitted are commonly called electronic tokens . One should not confuse the
token, which is a sequence of bits, with the physical media used to store and
transmit the information.
We will refer to the storage medium as a card since it commonly takes the form
of a wallet-sized card made of plastic or cardboard. (Two obvious examples are
credit cards and ATM cards.) However, the "card" could also be, e.g., a computer
memory.
A particular kind of electronic commerce is that of electronic payment . An
electronic payment protocol is a series of transactions, at the end of which a
payment has been made, using a token issued by a third party. The most common
example is that of credit cards when an electronic approval process is used. Note
that our definition implies that neither payer nor payee issues the token.
You might also like
- Beyond Cash - The Evolution of Digital Payment Systems and the Future of Money: Alex on Finance, #3From EverandBeyond Cash - The Evolution of Digital Payment Systems and the Future of Money: Alex on Finance, #3No ratings yet
- Hacking Point of Sale: Payment Application Secrets, Threats, and SolutionsFrom EverandHacking Point of Sale: Payment Application Secrets, Threats, and SolutionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electronic Cash: Energy Efficient SystemsDocument12 pagesElectronic Cash: Energy Efficient SystemsAkshay GattawarNo ratings yet
- E Cash Payment System PaperDocument37 pagesE Cash Payment System Paperakash0% (1)
- E Cash: Token Forgery Is Not The Same Thing As Signature ForgeryDocument8 pagesE Cash: Token Forgery Is Not The Same Thing As Signature ForgeryYv Pradeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Report On: "Safety of e Cash Payment"Document19 pagesA Seminar Report On: "Safety of e Cash Payment"Abhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- EcashDocument33 pagesEcashapi-3746880No ratings yet
- E CashDocument33 pagesE CashVijay Krishna BoppanaNo ratings yet
- E-Cash Report CSE SeminarDocument35 pagesE-Cash Report CSE Seminarz1230% (1)
- E Cash Payment SystemDocument29 pagesE Cash Payment Systemhareesh64kumar100% (2)
- Jaya Gowri RtoDocument3 pagesJaya Gowri RtosivapathasekaranNo ratings yet
- The Cryptography of Anonymous Electronic CashDocument62 pagesThe Cryptography of Anonymous Electronic Cashscott timmsNo ratings yet
- Types of Electronic Payment SystemsDocument20 pagesTypes of Electronic Payment SystemsRushyanth VattikondaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Payment SystemDocument23 pagesElectronic Payment SystemSongs Punjabi ShareNo ratings yet
- EFT Guide to Electronic Fund TransfersDocument23 pagesEFT Guide to Electronic Fund TransfersMahesh NannepaguNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce and Its Application: Unit-IVDocument37 pagesE-Commerce and Its Application: Unit-IVVasa VijayNo ratings yet
- Electronic Payments SystemDocument13 pagesElectronic Payments Systemmehak nangiaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Payment System Implementation through CryptographyDocument8 pagesElectronic Payment System Implementation through CryptographySK Sayeed SidNo ratings yet
- Electronic Payment System An Implementation Through CryptographyDocument8 pagesElectronic Payment System An Implementation Through CryptographyYamla SrinuNo ratings yet
- Digital Cash and the Future of MoneyDocument13 pagesDigital Cash and the Future of MoneyNithin AntonyNo ratings yet
- ECOMMERCE Unit 3Document195 pagesECOMMERCE Unit 3Urooj Alam FarooquiNo ratings yet
- E Commerce PresentationDocument30 pagesE Commerce PresentationRajiv Ranjan100% (1)
- E-CASH': A Seminar ReportDocument15 pagesE-CASH': A Seminar ReportPushkar WaneNo ratings yet
- Electronic Payments. Finaldocx 2Document31 pagesElectronic Payments. Finaldocx 2Quame Enam KunuNo ratings yet
- Electronic Payment SystemDocument20 pagesElectronic Payment SystemTsz Yeung YipNo ratings yet
- Digital CashDocument3 pagesDigital CashAtharvaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument12 pagesReportSanchay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Payment Systems ReviewDocument16 pagesElectronic Payment Systems ReviewMahimalluru Charan KumarNo ratings yet
- E-Business Application: Benefits of E-Cash, E-Cheque and Smart CardsDocument21 pagesE-Business Application: Benefits of E-Cash, E-Cheque and Smart CardsYashi BokreNo ratings yet
- Digital Currencies ExplainedDocument5 pagesDigital Currencies ExplainedAnkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Ecash: What Is E-Cash?Document6 pagesEcash: What Is E-Cash?Aarchi MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- General Structure of Digital Cash TransactionsDocument9 pagesGeneral Structure of Digital Cash Transactionsbaranidharan .kNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 - Electronic Payment SystemDocument67 pagesUnit - 2 - Electronic Payment Systemvisdag100% (2)
- Electronic Payment SystemDocument23 pagesElectronic Payment System741Mohd Saif AnsariNo ratings yet
- E-Payment Systems ExplainedDocument10 pagesE-Payment Systems ExplainedAakash RegmiNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument6 pagesDefinitionSaifur Rahman SteveNo ratings yet
- Electronic Payment System Digital Cash, Plastic Card, PSO and PSP Sept 2023Document16 pagesElectronic Payment System Digital Cash, Plastic Card, PSO and PSP Sept 2023Meraj TalukderNo ratings yet
- Explain Business Models, Their Types and Examples of EachDocument8 pagesExplain Business Models, Their Types and Examples of EachShriya JainNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document13 pagesUnit 4Vinayak SanbhadtiNo ratings yet
- Review of Literature:: Definition of Electronic Payment SystemsDocument3 pagesReview of Literature:: Definition of Electronic Payment SystemsAvula Shravan YadavNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 E-COMM NotesDocument13 pagesUNIT 3 E-COMM NotesVikash kumarNo ratings yet
- E Payment SystemsDocument17 pagesE Payment SystemsdeekshaNo ratings yet
- IEEE FormateDocument12 pagesIEEE FormateLekha WararkarNo ratings yet
- Money Pad The Future WalletDocument18 pagesMoney Pad The Future Walletrakeshraushan1411100% (2)
- Everything You Need to Know About Electronic Payment SystemsDocument76 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Electronic Payment Systemsaxn8inNo ratings yet
- Payment SystemDocument11 pagesPayment SystemTrifan_DumitruNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Online Payment SystemDocument5 pagesLiterature Review of Online Payment Systemrobin75% (4)
- Money PadDocument14 pagesMoney PadAfreen ShaikNo ratings yet
- E Commerce NotesDocument3 pagesE Commerce NotesBlack CloverNo ratings yet
- Eb Unit - 3Document40 pagesEb Unit - 3Chandhini RNo ratings yet
- ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS GUIDEDocument47 pagesELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEMS GUIDEMilan Jain100% (1)
- Electronic Payment Systems Security and Protocols ExplainedDocument36 pagesElectronic Payment Systems Security and Protocols ExplainedPaksmilerNo ratings yet
- Money Pad The Future WalletDocument17 pagesMoney Pad The Future WalletUsha Madanala0% (1)
- Meaning and Definition of Plastic MoneyDocument21 pagesMeaning and Definition of Plastic Moneykhushboolangalia100% (2)
- Electronic Payment System: Presented By: Richa Somvanshi (85) Sachin Goel (68) Sahar AiromDocument43 pagesElectronic Payment System: Presented By: Richa Somvanshi (85) Sachin Goel (68) Sahar AiromSiti Zalikha Md JamilNo ratings yet
- Electronic Payment SystemDocument46 pagesElectronic Payment SystemNakul Chawda100% (2)
- Money PadDocument14 pagesMoney PadRavi SawantNo ratings yet
- E Commerce AssignDocument4 pagesE Commerce AssignMargo ShaezNo ratings yet
- Electronic Cheque and Electronic CashDocument9 pagesElectronic Cheque and Electronic CashArya More100% (1)
- Abstract of Cloud ComputingDocument2 pagesAbstract of Cloud Computingsaloni kumariNo ratings yet
- ChaptersDocument1 pageChapterssaloni kumariNo ratings yet
- ChaptersDocument31 pagesChapterssaloni kumariNo ratings yet
- ChaptersDocument31 pagesChapterssaloni kumariNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesBenefits of Cloud Computingsaloni kumariNo ratings yet