Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Species Epidemiology Mechanism of Action Clinical Signs
Uploaded by
mariaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Species Epidemiology Mechanism of Action Clinical Signs
Uploaded by
mariaCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardiovascular Toxicity
PLANT SPECIES EPIDEMIOLOGY MECHANISM OF ACTION CLINICAL SIGNS
Oleander- Nerium oleander We recognize two syndromes. Bufadienolides and Cardenolides GIT- Bloat and diarrhea
CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES
Tulp- Moraea spp Acute:- caused by all these plants Inhibits Na/K-ATPase enzyme. Cardiovascular-
Slangkop- Drimia sanguinea chronic paralytic syndrome: Interferes with tachyarrhythmias
Plakkie- Cotyledon orbiculate “Krimpsiekte” caused by certain transmembrane potential of cells and Neuromuscular- tremors and
Kripsiektebossie members of the Crassulaceae. consequently there are conduction posterior paresis
disturbances eg Respiratory- Dyspnoea
arrhythmias.
Hyperkalaemia
Gifblaar- Dichapetalum cymosum Sudden mortality of ruminants, especially Monofluoroacetate Animal drops dead after drinking
GIFBLAAR
cattle, which usually occurs in late winter/early
TOXICITY
Stops TCA cycle, catastrophic energy loss water or after exercise
spring (Aug - Oct) and in early autumn (March) Cardiac effects- endocardial
haemorrhages
Nervous involvement
Gousiektebossie- Pachystigma spp Cardiotoxicoses of ruminants characterized by Pavetamine latent period of 6-8 weeks animals
Wild Date- Fadogia homble acute heart failure approximately 6-8 weeks decreases protein synthesis of new myosin die suddenly drop dead
GOUSIEKTE
Tonnabossie- Pavetta spp following ingestion of certain plants belonging and causes a breakdown of contractile Post Mortem- heart failure and
to the Rubiaceae family proteins in the heart subendocardial pallor
Microscopy- myocardial replacement
fibrosis
Cotton- Gossypium herbaceum Specifically cultivated Gossypol Causes loss of appetite and loss of
Cottonseed oilcake Endotheliotoxic weight Poor growth and feed
Uncouples oxidative phosphorylation conversion
Hyperkalaemic heart failure.
Binds to amino acids particularly lysine,
COTTON TOXICITY
which is then unavailable for protein
synthesis, leads to hypoproteinaemia and
oedema.
Monensin These organic compounds are used for Ionophore (= carrier of ions across cell Cardiac arrhythmias,
Salinomycin the control of coccidiosis in especially membranes) Ataxia
poultry rations. Ion gradients are disturbed and Ca Weakness and recumbency
Feeding chicken litter accumulated intracellularly, accumulated
IONOPHORE TOXICITY
Cardiac and skeletal muscle
calcium releases degradative lytic enzymes degeneration and necrosis
causes the swelling of mitochondria and the Cardiomyopathy, generalized
sarcoplasmic reticulum, cell necrosis congestion
You might also like
- Arrhythmia Drugs GuideDocument3 pagesArrhythmia Drugs GuideJosa Camille BungayNo ratings yet
- Biologically Active Amines Found in Man: Their Biochemistry, Pharmacology, and Pathophysiological ImportanceFrom EverandBiologically Active Amines Found in Man: Their Biochemistry, Pharmacology, and Pathophysiological ImportanceNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument11 pagesMedical Surgical NursingMaria TagubaNo ratings yet
- Dopamine HCLDocument1 pageDopamine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- Pharmacology Important Things To RememberDocument5 pagesPharmacology Important Things To RememberHydie100% (1)
- NursingDocument4 pagesNursingadrianNo ratings yet
- Before: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott's Nursing Drug Guide, P. 407Document2 pagesBefore: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott's Nursing Drug Guide, P. 407SoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- Drugs Per SystemDocument5 pagesDrugs Per SystemLaureece Salm ApduhanNo ratings yet
- Medications at Red Zone: Sodium BicarbonateDocument13 pagesMedications at Red Zone: Sodium BicarbonateAiman ArifinNo ratings yet
- Shock: Coass Anestesi Periode 12 Desember 2017 - 13 Januari 2018Document18 pagesShock: Coass Anestesi Periode 12 Desember 2017 - 13 Januari 2018iqbalNo ratings yet
- Medication ReviewDocument2 pagesMedication ReviewJn CaducoyNo ratings yet
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewDocument7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Assignment#1Document13 pagesAssignment#1Mark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- Format in Drug StudyDocument14 pagesFormat in Drug StudyShenielyn Bartolome NapolitanoNo ratings yet
- Wuolah-Free-Topic 27Document2 pagesWuolah-Free-Topic 27Moldovan Maria TatianaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DrugsDocument6 pagesCardiovascular DrugsSilvio PerezNo ratings yet
- PHARMACILOGY SUMMryDocument16 pagesPHARMACILOGY SUMMryKathy Real VillsNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramJessica Peñamora100% (1)
- AmlodipineDocument1 pageAmlodipineMenard Tobias VelascoNo ratings yet
- PHS CVSDocument25 pagesPHS CVStewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- Clin Tox Lab 3Document6 pagesClin Tox Lab 3Czariana Cassidy MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument9 pagesDrug AnalysisKyle DapulagNo ratings yet
- HEMA IMMUNO.2Document8 pagesHEMA IMMUNO.2Marcel TabucolNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyAkira Poscablo PiranteNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmias: Table 33-13Document25 pagesDysrhythmias: Table 33-13ZeoFateXNo ratings yet
- Shock and Multi OrganDocument90 pagesShock and Multi OrganElishaNo ratings yet
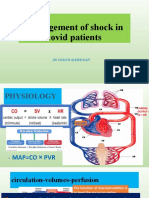
- Shock in Covid PatientDocument21 pagesShock in Covid PatientGHALEB A. AlmekhlafiNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibitors: Drug Name Clinical Use Pharmacokineti Cs Cautions Adverse Effect Interactions HyperkalemiaDocument1 pageAce Inhibitors: Drug Name Clinical Use Pharmacokineti Cs Cautions Adverse Effect Interactions HyperkalemiaSalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- Emd166 Slide Acute Coronary PDFDocument40 pagesEmd166 Slide Acute Coronary PDFlorinsyacderminnatNo ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument2 pagesAmiodaroneedemNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Antidotes: Antidote Indication Mode of ActionDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and Antidotes: Antidote Indication Mode of ActionPiny CesarNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Their AntidotesDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and Their AntidotesreynoldNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Their AntidotesDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and Their AntidotesAmirah AndresNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FurosemideDocument2 pagesDrug Study FurosemideAkira Poscablo PiranteNo ratings yet
- Flash Notes Tumor MarkersDocument22 pagesFlash Notes Tumor MarkersschxzerrydawnNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summarysechzhen96% (46)
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyJamesBond123098No ratings yet
- Anticholinesterase: PHARMACOLOGY PPT by Dr. Geraldine CorporalDocument4 pagesAnticholinesterase: PHARMACOLOGY PPT by Dr. Geraldine Corporaltaco cat100% (1)
- HNN215 Drug Diary GuideDocument10 pagesHNN215 Drug Diary GuideMaddison MitchellNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Ma'am D)Document3 pagesDRUG STUDY (Ma'am D)Angelica Mercado SirotNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology Schematic Diagrammark espirituNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology Schematic Diagrammark espirituNo ratings yet
- 9 Drugs Affecting Angina PectorisDocument3 pages9 Drugs Affecting Angina PectoristiaraNo ratings yet
- Calcium Channel Blocker Amlodipine Nursing ConsiderationsDocument1 pageCalcium Channel Blocker Amlodipine Nursing ConsiderationsElleNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - Arthritis DisordersDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Arthritis DisordersJem Son CostalesNo ratings yet
- 5-Heart FailureDocument12 pages5-Heart FailureJericho De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- KEMU Guide by Sheraz Ali SOLVEDDocument133 pagesKEMU Guide by Sheraz Ali SOLVEDdrmoazzinivyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes MellitusPearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Perinatal Asphyxia - Outline of Pathophysiology and Recent Trends in ManagementDocument31 pagesPerinatal Asphyxia - Outline of Pathophysiology and Recent Trends in Managementokwadha simionNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Manganese: AstrocytesDocument2 pagesAmmonia Manganese: AstrocytesJULIUS ART VINCENT A. PADINITNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument2 pagesAntimalarial DrugsSushmita VandariNo ratings yet
- Medici Di Makati College 1061 Metropolitan Avenue, San Antonio Village, Makati City, Philippines 1200Document18 pagesMedici Di Makati College 1061 Metropolitan Avenue, San Antonio Village, Makati City, Philippines 1200Andee SalegonNo ratings yet
- PotassiumDocument2 pagesPotassiumtuffie85No ratings yet
- Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e (Campbell) : Test Bank (1) PartDocument21 pagesBiology: Concepts and Connections, 6e (Campbell) : Test Bank (1) Partluchi_babezNo ratings yet
- Central Metabolic Pathway (White - Chap8)Document32 pagesCentral Metabolic Pathway (White - Chap8)Jesrael RojeroNo ratings yet
- Biofact Sheet Nerves SynapsesDocument4 pagesBiofact Sheet Nerves SynapsesJonMortNo ratings yet
- PHYSIO ReviewerDocument3 pagesPHYSIO ReviewerPHILYP EPHRAIM PARANGALANNo ratings yet
- Gayatri Gaikwad (Biology)Document29 pagesGayatri Gaikwad (Biology)prashik vigheNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing PinoyDocument85 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing PinoyrosebaseNo ratings yet
- British J Pharmacology - 2021 - ZobdehDocument20 pagesBritish J Pharmacology - 2021 - ZobdehRenju KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- 5 Senses Detailed Lesson PlanDocument4 pages5 Senses Detailed Lesson PlanErica MonferoNo ratings yet
- Iggy - Chapter 26 - Burns - PPDocument34 pagesIggy - Chapter 26 - Burns - PPnicole pilandNo ratings yet
- Anatomi TumbuhanDocument30 pagesAnatomi TumbuhanMEISYI DSNo ratings yet
- Basic Science JSS2 Question BankDocument3 pagesBasic Science JSS2 Question BankIsaacNo ratings yet
- 2 Murthy Et Al 2014 Secondary Metabolites Review Murthy2014 PDFDocument16 pages2 Murthy Et Al 2014 Secondary Metabolites Review Murthy2014 PDFmartha glezNo ratings yet
- Intra Aortic Balloon CounterpulsationDocument39 pagesIntra Aortic Balloon Counterpulsationmerin sunilNo ratings yet
- 10k Training Program (Interval, Cruise and Long Dist)Document6 pages10k Training Program (Interval, Cruise and Long Dist)kevinalmerNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument22 pagesEnzymes: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- Canine ReproductionDocument16 pagesCanine ReproductionDr rigs100% (2)
- Laura Otis Mullers Lab 2007Document337 pagesLaura Otis Mullers Lab 2007guilhermefsantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Basic Principles of Food Fermentation 1487564123Document37 pagesLecture 1 Basic Principles of Food Fermentation 1487564123Dr. Gurumurthy D M100% (1)
- Rhinologic and Sleep Apnea Surgical Techniques 1st Ed 2007 SDocument427 pagesRhinologic and Sleep Apnea Surgical Techniques 1st Ed 2007 SKarolina RamirezNo ratings yet
- Lipids Classification and FunctionsDocument4 pagesLipids Classification and FunctionsThalia PacamalanNo ratings yet
- Biology - BiodiversityDocument0 pagesBiology - Biodiversitywww.bhawesh.com.npNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Medical Language 3rd Edition Allan Test BankDocument143 pagesEssentials of Medical Language 3rd Edition Allan Test BankDebbieCollinsokpzd100% (14)
- 515Document972 pages515solecitodelmarazul100% (6)
- Hi DzamaDocument8 pagesHi DzamaeminNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion ENGLISHDocument40 pagesBlood Transfusion ENGLISHHajrahPalembangan100% (2)
- Bioenergetics and Lipid MetabolismDocument34 pagesBioenergetics and Lipid MetabolismM Daffa Abhista ReviansyahNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma ChapterDocument32 pagesGlaucoma ChapterAhmed Omara100% (5)
- Aakash Zoology Study Package 3 SolutionsssssssDocument104 pagesAakash Zoology Study Package 3 SolutionsssssssRishika PaulNo ratings yet
- Diet Mediterania Kontrol Kadar Glukosa Darah Pada Diabetes Mellitus Tipe 2Document6 pagesDiet Mediterania Kontrol Kadar Glukosa Darah Pada Diabetes Mellitus Tipe 2krisnaNo ratings yet
- Higher Center - Dr. BarbonDocument5 pagesHigher Center - Dr. BarbonMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet