Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2009 Mid-Term Exam
Uploaded by
KAUSHIK TIMOTHYCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2009 Mid-Term Exam
Uploaded by
KAUSHIK TIMOTHYCopyright:
Available Formats
Project Management Mid-term Exam
2009 2nd Term, 11/16/09
ID: Name:
1. (15 points) Multiple Choice Questions
1.1. Which of the following activities is not considered a project?
a. Developing a new software program
b. Designing a space station
c. Preparing the site for the Olympic Games
d. Production of automobile tires
e. Developing a new advertising program
1.2. Which of the following constraints is not typically found in managing projects?
a. Time
b. People
c. Cost
d. Performance
e. Both B and D are not typical constraints
1.3. Which of the following characteristics is not typical of a project manager?
a. Managing a temporary activity
b. Possesses indepth technical knowledge
c. Managing a nonrepetitive activity
d. Manages independently of the formal organization
e. Provides a direct link to the customer
1.4. Which of these is not part of the "sociocultural dimension" of project management?
a. Negotiation
b. Resource allocation
c. Customer expectations
d. Leadership
e. Politics
(15 points) 2. Fill in the blanks
2.1 The ________ financial model measures the current value of all cash inflows and outflows using
management's minimum desired rate of return.
2.2. In some cases organizations will use a __________ to solicit ideas for projects when the knowledge
requirements for the project are not available in the organization.
2.3.. Two of the major disadvantages of the ________ organizational approach to project management are
that projects may lack focus and it can take longer to complete projects.
2.4. In a ________ system, there are usually two chains of command, one along functional lines and the
other along project lines.
(20 points) 3. Short Answer Question
3.1 What is meant by a work breakdown structure and how does it help manage projects?
3.2. Under what conditions would the topdown approach to estimating project times and costs be the best
choice?
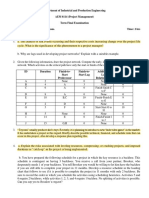
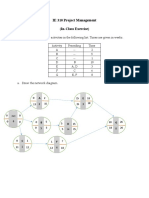
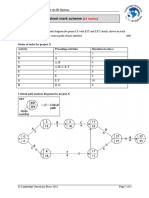
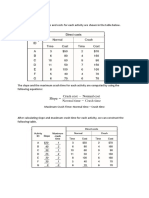
(20 points) 4. From the following information, draw the project network. Compute the early, late, and
slack times for each activity. Identify the critical path (Hint: draw the finishtostart relationships first)
ID Duration Finish-to-Start Finish-to-Start Additional Lag Relationships Lag
Predecessor Lag
A 5 None 0 None 0
B 10 A 0 None 0
C 15 A 0 Start-Finish C to D 20
D 5 B 5 Start- Start D to E 5
Finish-Finish D to E
E 20 B 0 Finish-Finish E to F 25
F 15 D 0 None 0
G 10 C 10 Finish-Finish G to F 0
H 20 F 0 None 10
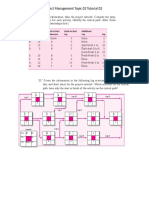
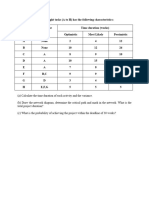
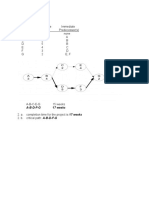
(30 points) 5. Given the network plan that follows, compute the early, late, and slack times. What is the
project duration? Using any approach you wish (e.g., trial and error), develop a loading chart for
resources Carpenters (C) and Electricians (E). Assume only one Carpenter is available and two
Electricians are available. Given your resource schedule, compute the early, late, and slack times for your
project. Which activities are now critical? What is the project duration now?
You might also like
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledgazigalibNo ratings yet
- Attempt To Answer All Questions: Assessment ExerciseDocument2 pagesAttempt To Answer All Questions: Assessment ExerciseChristila Kartika100% (1)
- Método Pert CPMDocument99 pagesMétodo Pert CPMAngie Marcela BastoNo ratings yet
- 5 Project Management SDocument7 pages5 Project Management SliamdrlnNo ratings yet
- Fall 2018 MGMT727 Project Management Assignment SolutionDocument4 pagesFall 2018 MGMT727 Project Management Assignment SolutionTaimoor SultanNo ratings yet
- PM ExampleDocument6 pagesPM ExamplejulsNo ratings yet
- BENG 405: Project Management Topic 02 Tutorial 02Document5 pagesBENG 405: Project Management Topic 02 Tutorial 02Joel Christian MascariñaNo ratings yet
- ch07 - 97 (1) PROJECT SCHEDULING, PPTDocument103 pagesch07 - 97 (1) PROJECT SCHEDULING, PPTMT TMNo ratings yet
- PERT&CPMDocument23 pagesPERT&CPMBee ParindaNo ratings yet
- Construction Management: ENCE4331Document16 pagesConstruction Management: ENCE4331Osayd SrourNo ratings yet
- CSCI380-Week 5-Lecture 1-Pert ChartDocument5 pagesCSCI380-Week 5-Lecture 1-Pert Chart12110159No ratings yet
- CEN 451 - Lecture 9 & 10Document22 pagesCEN 451 - Lecture 9 & 10Shah Md. Asik Kabir 6044No ratings yet
- Uts MpsiDocument3 pagesUts MpsiShopi Nurul HasanahNo ratings yet
- Class CPM 2023Document55 pagesClass CPM 2023Sk Nahidul Islam ShrabonNo ratings yet
- Project SchedulingDocument71 pagesProject SchedulingVEDIKA MALVIYANo ratings yet
- 154 - PM - Midterm Exam Question - MBA 2019-21 - Term IV PDFDocument2 pages154 - PM - Midterm Exam Question - MBA 2019-21 - Term IV PDFBalvinde1234No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Problem # 1Document7 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Problem # 1MELISSA WONG PAU YU -No ratings yet
- AEM 6114 (Project Management) Quiz 2 Answer The Following QuestionsDocument2 pagesAEM 6114 (Project Management) Quiz 2 Answer The Following QuestionsgazigalibNo ratings yet
- EE Exam Suplim PracticDocument11 pagesEE Exam Suplim PracticAvasiloaei IonutNo ratings yet
- IEMM 5 - Virya Wijayati - Project Management ExamDocument5 pagesIEMM 5 - Virya Wijayati - Project Management ExamfreteerNo ratings yet
- In-Class Assignment1olaDocument2 pagesIn-Class Assignment1olaOLA BAJABANo ratings yet
- Lec 02 PRM 11032023 110032amDocument39 pagesLec 02 PRM 11032023 110032amkhizar mehboobNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Project Time ManagementDocument17 pagesModule 3: Project Time ManagementEliyas BezabehNo ratings yet
- MGT 302 3rd SlideDocument14 pagesMGT 302 3rd SlideNafis Sadique SifatNo ratings yet
- In-Class Assignment1Document2 pagesIn-Class Assignment1OLA BAJABANo ratings yet
- Project Management: Brig (R) DR Masood RazaDocument48 pagesProject Management: Brig (R) DR Masood RazaMunam AliNo ratings yet
- Exam Budgeting Techniques and Project ManagementDocument2 pagesExam Budgeting Techniques and Project Managementdalinmom180No ratings yet
- Cobol Mock Test IDocument6 pagesCobol Mock Test IMilanGuptaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Group Assignment: Assignment File Naming ConventionDocument5 pagesWeek 2 Group Assignment: Assignment File Naming ConventionVaibhav MahajanNo ratings yet
- Af201 Final Exam Revision Package - S2, 2020 Face-to-Face & Blended Modes Suggested Partial SolutionsDocument9 pagesAf201 Final Exam Revision Package - S2, 2020 Face-to-Face & Blended Modes Suggested Partial SolutionsChand DivneshNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Chapter 8: Scheduling Assignment 1:: B15 E15 H35 EndDocument10 pagesAssignment For Chapter 8: Scheduling Assignment 1:: B15 E15 H35 EndPhuongNo ratings yet
- 2020-Dec CE-306 74Document3 pages2020-Dec CE-306 74Sahil ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- QuestionDocument2 pagesQuestionhab ibraNo ratings yet
- Ce 515 (Lec) Final ExamDocument2 pagesCe 515 (Lec) Final ExamHilton D. CalawenNo ratings yet
- EDBM - Assignment100619-20Document3 pagesEDBM - Assignment100619-20yyantie100% (1)
- Pert Ex1Document1 pagePert Ex1Ahmed mohamedNo ratings yet
- Critical Path AnalysisDocument4 pagesCritical Path AnalysisMarusaha MP SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Coursework ME-271 Project Management and Engineering EconomicsDocument2 pagesCoursework ME-271 Project Management and Engineering EconomicsHafiz AbdulRehmanNo ratings yet
- Sasmita PiliangDocument2 pagesSasmita PiliangSasmiita PiliangNo ratings yet
- Project Scheduling & Tracking (Week 3)Document35 pagesProject Scheduling & Tracking (Week 3)Gulshan MittalNo ratings yet
- Terminologies U S e D I N CPM: Activity: An Activity Carries The Arrow Symbol - This Represent A TaskDocument16 pagesTerminologies U S e D I N CPM: Activity: An Activity Carries The Arrow Symbol - This Represent A TaskVarsha PraburamNo ratings yet
- FE Review - ConstructionDocument64 pagesFE Review - ConstructionlonerstarNo ratings yet
- PMD913 Proj Prog & Cost CTRL - Coursework Apr2015Document13 pagesPMD913 Proj Prog & Cost CTRL - Coursework Apr2015tarekyehia009No ratings yet
- HW 2Document3 pagesHW 2Saif QasemNo ratings yet
- G2-Written Report - Chapter 3Document5 pagesG2-Written Report - Chapter 3John Michael BolocNo ratings yet
- Crashing Numerical SolutionDocument2 pagesCrashing Numerical SolutionSalman EjazNo ratings yet
- UNIT-III SEPM Objective QuestionsDocument5 pagesUNIT-III SEPM Objective QuestionsRajNo ratings yet
- Sesi 4-7 PenjadwalanDocument74 pagesSesi 4-7 Penjadwalanm hulaimiNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document21 pagesWeek 2Raksa MaNo ratings yet
- Critical Path Analysis 1Document5 pagesCritical Path Analysis 1cliffordpradamoyoNo ratings yet
- Project Management2Document68 pagesProject Management2panghal13No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 F2F PDF PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 3 F2F PDF PDFGarethNgNo ratings yet
- Homework2 220302251Document9 pagesHomework2 220302251StatebrigaNo ratings yet
- IB BusMan 37 Assessment Wsmark37Document3 pagesIB BusMan 37 Assessment Wsmark37Gabriel FungNo ratings yet
- Project Management With Cpm/PertDocument33 pagesProject Management With Cpm/PertAvanishNo ratings yet
- What Is The Critical Path? 2. What Is The Expected Duration For The Whole Project?Document2 pagesWhat Is The Critical Path? 2. What Is The Expected Duration For The Whole Project?Christine Niones100% (1)
- Critical Path Method: Construction of A GarageDocument12 pagesCritical Path Method: Construction of A GarageKSHITIJ PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Module 2.0 - Pert-CpmDocument9 pagesModule 2.0 - Pert-CpmTyron TayloNo ratings yet
- AHP TutorialDocument14 pagesAHP TutorialSree NivasNo ratings yet
- Challenges of Measuring Performance of The Sales and Operations Planning ProcessDocument13 pagesChallenges of Measuring Performance of The Sales and Operations Planning ProcessKAUSHIK TIMOTHYNo ratings yet
- Selection of Cricket Players Using Analytical Hierarchy ProcessDocument6 pagesSelection of Cricket Players Using Analytical Hierarchy ProcessKAUSHIK TIMOTHYNo ratings yet
- Artigo Saaty 2008 AHPDocument16 pagesArtigo Saaty 2008 AHPSeema DeviNo ratings yet
- Data PDFDocument5 pagesData PDFKAUSHIK TIMOTHYNo ratings yet
- Projeto de Implementação Do Processo Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) - Caso de EstudoDocument101 pagesProjeto de Implementação Do Processo Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) - Caso de EstudoKAUSHIK TIMOTHYNo ratings yet
- Challenges of Measuring Performance of The Sales and Operations Planning ProcessDocument13 pagesChallenges of Measuring Performance of The Sales and Operations Planning ProcessKAUSHIK TIMOTHYNo ratings yet
- Snop4 PDFDocument4 pagesSnop4 PDFKAUSHIK TIMOTHYNo ratings yet
- OperationsDocument15 pagesOperationsKAUSHIK TIMOTHYNo ratings yet
- SnopDocument17 pagesSnopKAUSHIK TIMOTHYNo ratings yet
- Activity Time Immediate Activity (Weeks) Predecessor(s) A 3 None B 4 A C 2 B D 5 B E 4 C F 3 D G 2 E, FDocument3 pagesActivity Time Immediate Activity (Weeks) Predecessor(s) A 3 None B 4 A C 2 B D 5 B E 4 C F 3 D G 2 E, FKAUSHIK TIMOTHYNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Chapter 13 ExercisesDocument7 pagesRunning Head: Chapter 13 ExercisesluluNo ratings yet
- Crashing ProblemsDocument8 pagesCrashing ProblemsHn LeeNo ratings yet
- Part Numbers For ISIMDocument2 pagesPart Numbers For ISIMThomas SimmonsNo ratings yet
- Shriram Liberty Square - 99acresDocument24 pagesShriram Liberty Square - 99acresKayjay2050No ratings yet
- Ilana Organics Sales Report MonthlyDocument3 pagesIlana Organics Sales Report MonthlyRAVI KUMARNo ratings yet
- Postal Services HistoryDocument13 pagesPostal Services HistoryAnonymous Ndp7rXNo ratings yet
- XHarbour End-User License AgreementDocument7 pagesXHarbour End-User License AgreementPalatNo ratings yet
- FEIGENBAUM + Ishikawa + TaguchiDocument7 pagesFEIGENBAUM + Ishikawa + Taguchiaulia rakhmawatiNo ratings yet
- Help Desk Tips TricksDocument46 pagesHelp Desk Tips TricksGenaro Quispe BallascoNo ratings yet
- 05Document16 pages05juliokohutNo ratings yet
- Eticket: Hyderabad Wednesday, April 10, 2019Document2 pagesEticket: Hyderabad Wednesday, April 10, 2019Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Retail Scenario in India Cii ReportDocument21 pagesRetail Scenario in India Cii Reportapi-3823513100% (1)
- Taxation Deduction QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesTaxation Deduction QuestionnaireJanaela100% (1)
- Project Report On PVC Pipe Manufacturing Plant PDFDocument11 pagesProject Report On PVC Pipe Manufacturing Plant PDFjayson100% (1)
- Computer Notes OBJECTIVE Chapter #4 Class XI IncompleteDocument3 pagesComputer Notes OBJECTIVE Chapter #4 Class XI IncompleteNabil Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Motor CertificateDocument1 pageMotor CertificateNeil VickeryNo ratings yet
- Approaches For Enterpreneurship DevelopmentDocument3 pagesApproaches For Enterpreneurship DevelopmentSubha ThilothamanNo ratings yet
- Rights of The HolderDocument6 pagesRights of The HolderVan OpenianoNo ratings yet
- Final Individual ProjectDocument46 pagesFinal Individual ProjectSurbhi SinghalNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Area Process Name InputsDocument19 pagesKnowledge Area Process Name Inputsk_Dashy8465No ratings yet
- Presentation On Human Resource AccountingDocument14 pagesPresentation On Human Resource AccountingPrateek MishraNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Supply Base Management PDFDocument16 pagesAn Introduction To Supply Base Management PDFAmrin Diba100% (1)
- PCIB V CADocument1 pagePCIB V CAVener Angelo MargalloNo ratings yet
- 3.10 XMR Chart InvoicesDocument22 pages3.10 XMR Chart Invoicesاندر احمد اولدينNo ratings yet
- Construction Management (CENG 260) : Lecturer: Raed T. Jarrah Lecture 11a - Cost ControlDocument19 pagesConstruction Management (CENG 260) : Lecturer: Raed T. Jarrah Lecture 11a - Cost ControlHusseinNo ratings yet
- Filipino Value System2Document2 pagesFilipino Value System2Florante De LeonNo ratings yet
- UCV Session 1 Introduction IMDocument29 pagesUCV Session 1 Introduction IMLuis GarciaNo ratings yet
- Valuation of Marine VesselsDocument41 pagesValuation of Marine VesselsReza Babakhani100% (1)
- D L Packers & Movers: S.No ParticularsDocument9 pagesD L Packers & Movers: S.No ParticularsSahil SiwachNo ratings yet
- ERPDocument36 pagesERPDharmendra Thakur100% (1)
- Apple'S Profitable But Risky StrategyDocument5 pagesApple'S Profitable But Risky StrategyKelechi Alexandra IwuorieNo ratings yet
- Assignment (Esbm)Document13 pagesAssignment (Esbm)Jai KumarNo ratings yet