Professional Documents
Culture Documents
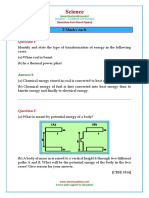
Chapter 22
Chapter 22
Uploaded by
Maruf_0070 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views27 pages[Solutions Manual by Chapters] University Physics - Sears and Zemansky's 11th Ed
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document[Solutions Manual by Chapters] University Physics - Sears and Zemansky's 11th Ed
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views27 pagesChapter 22
Chapter 22
Uploaded by
Maruf_007[Solutions Manual by Chapters] University Physics - Sears and Zemansky's 11th Ed
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
224: a)
b) As long as the sheet is fat, its shape does not matter.
ci) The maximum flux occurs at an angle between the normal and field.
cii) The minimum flux occurs at an angle between the normal and field.
In parti), the paper is oriented to “capture” the most field lines whereas in ii) the
area is oriented so that it “captures” no field lines.
b) The total flux through the cube must be zero; any flux entering the cube must also
leave it.
22.
a) Given that L, and
b) Total flux
22.4:
22.5: a)
b) We would get the same flux as in (a) ifthe cylinder’s radius was made larger—the
field lines must still pass through the surface.
©) If the length was increased to the flux would increase by a factor of
two:
22.
b)
c)
4d)
°)
a)
1) All that matters for Gauss’s law is the total amount of charge enclosed by the
surface, not its distribution within the surface.
22.7: a)
b)
©) No. All that matters is the total charge enclosed by the cube, not the details of
where the charge is located
22.8: a) No charge enclosed so
b)
°)
22!
a) Since is uniform, the flux through a closed surface must be zero. That is:
But because we can choose any volume we
want, must be zero if the integral equals zero.
b) If there is no charge in a region of space, that does NOT mean that the electric field
is uniform, Consider a closed volume close to, but not including, a point charge. The field
diverges there, but there is no charge in that region.
22.10: a) If and uniform, then inside any closed surface is greater than zero.
and so the electric field cannot be uniform, i., since an
arbitrary surface of our choice encloses a non-zero amount of charge, must depend on
position.
b) However, inside a small bubble of zero density within the material with density,
the field CAN be uniform, All that is important is that there be zero flux through the
surface of the bubble (since it encloses no charge). (See Exercise 22.61.)
2211: But the box is
symmetrical, so for one side, the flux is:
b) No change. Charge enclosed is the same.
22.12: Since the cube is empty, there is no net charge enclosed in it. The net flux,
according to Gauss’s law, must be zero.
22.13:
The flux through the sphere depends only on the charge within the sphere.
22.14: a)
b) inside of a conductor or else free charges would move under the influence of
forces, violating our electrostatic assumptions (ice, that charges aren’t moving).
22.15: a)
b) As long as we are outside the sphere, the charge enclosed is constant and the sphere
acts like a point charge.
22.16: a)
b) Double the surface area:
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- E10-Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyDocument4 pagesE10-Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyAisyah Arief100% (1)
- CN Tower - Teachers Resource Guide - Grade 3Document6 pagesCN Tower - Teachers Resource Guide - Grade 3ohsandra0% (1)
- AtwoodDocument3 pagesAtwoodBahril IlmiwanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Important Questions For Physics - Motion in A Plane PDFDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 11 Important Questions For Physics - Motion in A Plane PDFHaltz t00nNo ratings yet
- USP Chapter 41 Technical NoteDocument2 pagesUSP Chapter 41 Technical NoteAdhitya PT. SIGNo ratings yet
- Virtual SEA Mid-Frequency Structure-Borne Noise Modeling Based On Finite Element AnalysisDocument11 pagesVirtual SEA Mid-Frequency Structure-Borne Noise Modeling Based On Finite Element AnalysisKivanc SengozNo ratings yet
- Accelerometer Case StudyDocument3 pagesAccelerometer Case StudyAYESHANo ratings yet
- 9 Science Chapter 11 Board Papers 2 MarksDocument7 pages9 Science Chapter 11 Board Papers 2 MarksNiti AroraNo ratings yet
- Gravity LabDocument2 pagesGravity Labah maNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Principles - Dynamics of Rotating SystemsDocument14 pagesMechanical Principles - Dynamics of Rotating SystemsSteven GoddardNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Quiz 2 PHY11LDocument4 pagesReviewer Quiz 2 PHY11LMikaella TambisNo ratings yet
- Friction ProblemsDocument6 pagesFriction ProblemsNopmangunawanNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Modern Physics by Nurul Amin SirDocument13 pagesIntroduction of Modern Physics by Nurul Amin SirFardeen KhanNo ratings yet
- Hot Rolled Bulb Flats PDFDocument4 pagesHot Rolled Bulb Flats PDFLaurentiu GavrilaNo ratings yet
- Physics II ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics II ProblemsBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- OCR Maths M2 Topic Questions From Papers Circular MotionDocument12 pagesOCR Maths M2 Topic Questions From Papers Circular MotionDahanyakage WickramathungaNo ratings yet
- Answer PHYSIC STPM Trial Sem 1 2013Document6 pagesAnswer PHYSIC STPM Trial Sem 1 2013Zuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- JEE Mains 2024 Question Paper 1 Feb Shift 1Document3 pagesJEE Mains 2024 Question Paper 1 Feb Shift 1anunay.mishra4141No ratings yet
- Helical Engine: David M. Burns, PH.DDocument9 pagesHelical Engine: David M. Burns, PH.Dgregorbanalt1No ratings yet
- Class 9 Physics Guess Paper by HOMELANDERDocument33 pagesClass 9 Physics Guess Paper by HOMELANDERjavedroxx4No ratings yet
- Convert MefsDocument3 pagesConvert MefssaghfadNo ratings yet
- 4PH0 1P Rms 20120823 PDFDocument24 pages4PH0 1P Rms 20120823 PDFwalyatNo ratings yet
- Formulas For Phys207Document2 pagesFormulas For Phys207trantt9No ratings yet
- Recursive Newton EulerDocument7 pagesRecursive Newton EulerShubham ThakurNo ratings yet
- PHY GravationDocument10 pagesPHY GravationDaksh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Class 28: Outline: Hour 1: Displacement Current Maxwell's Equations Hour 2: Electromagnetic WavesDocument33 pagesClass 28: Outline: Hour 1: Displacement Current Maxwell's Equations Hour 2: Electromagnetic Wavesakirank1No ratings yet
- HL Paper1Document21 pagesHL Paper1Proleteriat Dictatorship of Koperia0% (1)
- Solucionario Capitulo 24 Paul E TippensDocument20 pagesSolucionario Capitulo 24 Paul E TippensLalito Lopez100% (1)
- Theory - Laws of Motion+Friction - JM+JA - Live 2Document169 pagesTheory - Laws of Motion+Friction - JM+JA - Live 2bqfhwdmdcyNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper ASAT X PDFDocument17 pagesSample Paper ASAT X PDFanurag680% (1)