Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DMOP Homework 1 Q6
Uploaded by
khushi kumariCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DMOP Homework 1 Q6
Uploaded by
khushi kumariCopyright:
Available Formats
DMOP Homework 1
Q6- RBC Case
6-1.a RBC was currently supplying 600000 units of Tomato A and 2400000 units of Tomato B, which was
giving them a surplus of 136066 (Which is there contribution to overhead and profit). They should
explore alternatives to the current pricing scheme as increasing the proportion of grade A quality alone,
or increasing the production of B with significant higher production of grade A tomatoes would provide
RBC with more revenue and improve their financial performance
6-1.b GF’s reaction to RBC’s concern: Watson- the controller of GF responded to RBC’s concern by
putting forward the point that moving to the region RBC prefer might land them into a higher cost
production region which would entail with the reduction in profit, unless the unit price is changed to a
higher one. He also said that he will try to bring out rational from the numbers from RBC sheet with his
colleagues. The final discussion was that if both the party wins from this alteration in the product mix,
then the incremental profits needs to be shared in equal parts between them
6-2.a Win-Win Situation for the supply chain will be that when both the GF and RBC combined in the
system has increased their surplus from the current scenario. Surplus defined in the hypothetical supply
chain where RBC and GF are part of the organization will be the revenue that RBC makes from it’s
customer minus the cost that GF has to incur for the manufacturing the product. (Note that the revenue
of GF and cost of RBC gets nullified because they are part of a single supply chain where GF is supplying
to RBC internally)
Surplus (New Combined): Surplus of RBC+ Surplus of GF
6-2.b Payoff for the supply chain will be just the addition of the surplus of RBC and GF. The desired mix
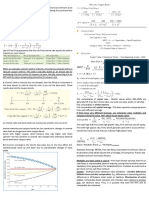
of the supply chain will be one where the payoffs gets maximized. Here, we can see from the figure
below that the payoff is maximized at Grade A= 850000 units and Grade B= 2300000
You might also like
- Starbucks: Delivering Customer ServiceDocument6 pagesStarbucks: Delivering Customer Servicegaurav90% (10)
- hw#2 PDFDocument5 pageshw#2 PDFEkta VaswaniNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Indian School of Business Homework: S B R D B K R KDocument2 pagesManagerial Economics Indian School of Business Homework: S B R D B K R KPriyanka JainNo ratings yet
- MGEC2 MidtermDocument7 pagesMGEC2 Midtermzero bubblebuttNo ratings yet
- HW 3 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesHW 3 Answer KeyHemabhimanyu MaddineniNo ratings yet
- MGFC10 Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesMGFC10 Cheat SheetĐức Hải NguyễnNo ratings yet
- MGEC HW1 Answer Key ExplainedDocument8 pagesMGEC HW1 Answer Key ExplainedAnujain JainNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document10 pagesAssignment 1AkshitaNo ratings yet
- Biocon's Phase 3 Testing and Launch Plan for Cancer Drug BIOMAbDocument4 pagesBiocon's Phase 3 Testing and Launch Plan for Cancer Drug BIOMAbMukesh SahuNo ratings yet
- PRICING EXERCISES ANALYSISDocument14 pagesPRICING EXERCISES ANALYSISvineel kumarNo ratings yet
- Maximize power plant coal output with emissions constraintsDocument2 pagesMaximize power plant coal output with emissions constraintsSaiPraneethNo ratings yet
- WAC-P16052 Dhruvkumar-West Lake Case AnalysisDocument7 pagesWAC-P16052 Dhruvkumar-West Lake Case AnalysisDHRUV SONAGARANo ratings yet
- MGECDocument8 pagesMGECSrishtiNo ratings yet
- ME - End Term Answer KeyDocument7 pagesME - End Term Answer KeyShubham Agarwal50% (2)
- BARCO Case AssignmentDocument1 pageBARCO Case AssignmentTanyaNo ratings yet
- BSB Vs Sky TelevisionDocument4 pagesBSB Vs Sky TelevisionPrabir AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Hyperlocal last mile delivery solution for groceries and fresh meatDocument11 pagesHyperlocal last mile delivery solution for groceries and fresh meatkhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Na0141 XLS EngDocument12 pagesNa0141 XLS Engkhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Avaya - 1st AnsDocument2 pagesAvaya - 1st AnsNeelu Sri100% (1)
- PPTXDocument12 pagesPPTXkhushi kumari100% (1)
- Decision Models and Optimization: Sample-Endterm-with SolutionsDocument6 pagesDecision Models and Optimization: Sample-Endterm-with SolutionsYash NyatiNo ratings yet
- Eco 4Document5 pagesEco 4SamidhaSinghNo ratings yet
- Harrington Collection Explores Growth in Active-Wear MarketDocument13 pagesHarrington Collection Explores Growth in Active-Wear MarketPoonam Chauhan100% (2)
- Midterm PracticeDocument7 pagesMidterm PracticeDoshi VaibhavNo ratings yet
- EC2101 Practice Problems 8 SolutionDocument3 pagesEC2101 Practice Problems 8 Solutiongravity_coreNo ratings yet
- MadmDocument9 pagesMadmRuchika SinghNo ratings yet
- Atlantic ComputerDocument4 pagesAtlantic Computerrahul agarwalNo ratings yet
- Atlantic Computers: A Bundle of Pricing OptionsDocument7 pagesAtlantic Computers: A Bundle of Pricing OptionsShivaniNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems-DMOPDocument5 pagesSample Problems-DMOPChakri MunagalaNo ratings yet
- Decision Models and Optimization: Indian School of Business Assignment 4Document8 pagesDecision Models and Optimization: Indian School of Business Assignment 4NANo ratings yet
- Marketing Decision Making ConceptsDocument18 pagesMarketing Decision Making ConceptsAvi JainNo ratings yet
- GE Medical Systems International Business AssignmentDocument4 pagesGE Medical Systems International Business AssignmentMarissa BradleyNo ratings yet
- Gyaan Kosh: Global EconomicsDocument19 pagesGyaan Kosh: Global EconomicsU KUNALNo ratings yet
- The Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyDocument14 pagesThe Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyronNo ratings yet
- GLEC Assignment-Country Report (Spain)Document15 pagesGLEC Assignment-Country Report (Spain)Sohil AggarwalNo ratings yet
- MKDM Gyan KoshDocument17 pagesMKDM Gyan KoshSatwik PandaNo ratings yet
- Gyaan Kosh CSTR SummaryDocument23 pagesGyaan Kosh CSTR SummarySatwik PandaNo ratings yet
- Sample ProblemsDocument9 pagesSample ProblemsDoshi VaibhavNo ratings yet
- Victoria Project TemplateDocument15 pagesVictoria Project TemplateAbhijit KoundinyaNo ratings yet
- Gillette Indonesia Case Study: Cut Costs and Reduce Prices to Gain Market ShareDocument5 pagesGillette Indonesia Case Study: Cut Costs and Reduce Prices to Gain Market ShareMarthaRaniNo ratings yet
- How Hindalco Industries can improve its working capital managementDocument15 pagesHow Hindalco Industries can improve its working capital managementBikramdevPadhiNo ratings yet
- Berkshire Threaded Fasteners Co.: Question 1: Drop 300 As of 1/1/74?Document24 pagesBerkshire Threaded Fasteners Co.: Question 1: Drop 300 As of 1/1/74?Yousif100% (1)
- Dominion Motors and Controls Ltd. - Case AnalysisDocument7 pagesDominion Motors and Controls Ltd. - Case Analysisdhiraj agarwalNo ratings yet
- MADM - IN-CLASS QUIZ SOLUTIONSDocument11 pagesMADM - IN-CLASS QUIZ SOLUTIONSPiyush SharmaNo ratings yet
- DMUU Assignment 1 - GroupCDocument4 pagesDMUU Assignment 1 - GroupCJoyal ThomasNo ratings yet
- Emirates Airline Success Behind Solid GrowthDocument1 pageEmirates Airline Success Behind Solid GrowthChRehanAliNo ratings yet
- Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesPractice QuestionsAnyone SomeoneNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4 2021Document2 pagesProblem Set 4 2021Monodeep DuttaNo ratings yet
- TruEarth SWOT Analysis and Market Strategy for Launching Whole Grain PizzaDocument5 pagesTruEarth SWOT Analysis and Market Strategy for Launching Whole Grain Pizzadeepim4No ratings yet
- GOLFLOGIX CASE CRITIQUEDocument15 pagesGOLFLOGIX CASE CRITIQUEVikas KhannaNo ratings yet
- Technological Change Best Explains Wage InequalityDocument7 pagesTechnological Change Best Explains Wage InequalityDoshi VaibhavNo ratings yet
- Virgin Mobile USA: Pricing for the First TimeDocument5 pagesVirgin Mobile USA: Pricing for the First Timebonfument100% (1)
- Problem Sheet II - Confidence Interval, Sample SizeDocument4 pagesProblem Sheet II - Confidence Interval, Sample SizeShamil MNo ratings yet
- Natureview FarmDocument2 pagesNatureview FarmBen Hiran100% (1)
- Barilla Spa (Hbs 9-694-046) - Case Study Submission: Executive SummaryDocument3 pagesBarilla Spa (Hbs 9-694-046) - Case Study Submission: Executive SummaryRichaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Supply Inc.Document4 pagesHospital Supply Inc.alomelo100% (2)
- Improving Operations at Synthite Through Reduced Lead Times and Inventory CostsDocument4 pagesImproving Operations at Synthite Through Reduced Lead Times and Inventory CostsrakeshNo ratings yet
- Amal EPGP10 008 Atlantic ComputersDocument5 pagesAmal EPGP10 008 Atlantic ComputersAMAL ARAVINDNo ratings yet
- SMMD: Practice Problem Set 3 Confidence IntervalsDocument2 pagesSMMD: Practice Problem Set 3 Confidence Intervalsbala sanchitNo ratings yet
- Ome Merged PDFDocument311 pagesOme Merged PDFNavya MohankaNo ratings yet
- CAN Submission-Unilever in India: Hindustan Lever's Project Shakti - Marketing FMCG To The Rural ConsumerDocument3 pagesCAN Submission-Unilever in India: Hindustan Lever's Project Shakti - Marketing FMCG To The Rural ConsumerRitik MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- TFC Scenario AnalysisDocument3 pagesTFC Scenario AnalysisAshish PatelNo ratings yet
- ME Problem Set-IX (2019)Document4 pagesME Problem Set-IX (2019)Divi KhareNo ratings yet
- Bill French Case StudyDocument1 pageBill French Case StudyAnusha BeesettiNo ratings yet
- Multi-Item Newsboy - Inv - MGMT - 2Document6 pagesMulti-Item Newsboy - Inv - MGMT - 2khushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Trial 1Document2 pagesTrial 1khushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Trial 1Document2 pagesTrial 1khushi kumariNo ratings yet
- China. Production of Wet Process Phosphoric Acid. Technical Report (16400.en)Document217 pagesChina. Production of Wet Process Phosphoric Acid. Technical Report (16400.en)khushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Free PPT Templates Click to Add TitleDocument33 pagesFree PPT Templates Click to Add TitleSetyorini SafitriNo ratings yet
- CSEM Session 2Document22 pagesCSEM Session 2khushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Dunzo Case WriteUpDocument5 pagesDunzo Case WriteUpkhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- CheatsheetDocument1 pageCheatsheetkhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- CheatsheetDocument1 pageCheatsheetkhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing StrategyDocument10 pagesDigital Marketing Strategykhushi kumari100% (1)
- Classisical Conditioning PrincipleDocument2 pagesClassisical Conditioning Principlekhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Coca Cola SalesDocument54 pagesCoca Cola Saleskhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Anuja - Chandrasekar - V2 (AD - V1)Document1 pageAnuja - Chandrasekar - V2 (AD - V1)khushi kumariNo ratings yet
- DMOP 6 Part 3Document3 pagesDMOP 6 Part 3khushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Rosewood Hotels and ResortsDocument5 pagesRosewood Hotels and Resortskhushi kumari100% (1)
- GameResult Isb3 Team002 1 1-Classic Donothing ISBDocument5 pagesGameResult Isb3 Team002 1 1-Classic Donothing ISBkhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Cost Efficiency & Revenue Upscale A&MDocument2 pagesCost Efficiency & Revenue Upscale A&Mkhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Cost Efficiency & Revenue Upscale A&MDocument2 pagesCost Efficiency & Revenue Upscale A&Mkhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Open Questions For CMR, Wesco, Zucamor and Tata Steel ECA - Version 1.01.14.20Document2 pagesOpen Questions For CMR, Wesco, Zucamor and Tata Steel ECA - Version 1.01.14.20khushi kumariNo ratings yet
- For Students Interaction PlotsDocument2 pagesFor Students Interaction Plotskhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Classisical Conditioning PrincipleDocument2 pagesClassisical Conditioning Principlekhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- The Fashion Channel NotesDocument4 pagesThe Fashion Channel Noteskhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Assignmengt 2 Question1Document22 pagesAssignmengt 2 Question1khushi kumariNo ratings yet
- Trial SimulationDocument14 pagesTrial Simulationkhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- CFIN2 CheatsheetDocument2 pagesCFIN2 Cheatsheetkhushi kumariNo ratings yet