Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Serotonin Syndrome
Uploaded by
JYG0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageOriginal Title
Serotonin Syndrome.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageSerotonin Syndrome
Uploaded by
JYGCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
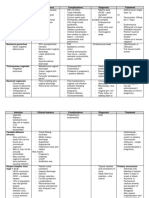
SEROTONIN SYNDROME
- Life threatening condition caused by elevated serotonin conc.
- Can occur in context of initiation or dose increase of serotonergic agent, inadvertent interactions
between serotonergic medications, overdose of serotonergic medications or use of recreational drugs
- Specific agents: antidepressants, mood stabilisers, analgesics, 5-HT1 agonists (e.g. triptans), CNS
stimulants, hallucinogens, St John’s Wort
Signs/symptoms
- Psychiatric/neurological: agitation, confusion, coma, death
- Neuromuscualr: ataxia, hyperreflexia (usually lower limb), myoclonus, rigidity, tremors
- Autonomic: GI upset (nausea, diarrhoea), hyper/hypotension, hyperthermia,mydriasis, tachycardia
Comparison between serotonin syndrome and NMS
Feature Serotonin syndrome Neuroleptic malignant
syndrome
Associated agent Serotonin agent Antipsychotic medication
Mechanism Serotonin excess Dopamine antagonism
Symptom onset Minutes to hours Days to weeks
Symptom resolution <24 hours 5-14 days
Muscle rigidity Less severe More severe
Activity Hyperkinesia Bradykinesia
Myoclonus and seizure Common Rare
Rhabdomyolysis Rare Common
Elevated transaminases Rare Common
Management
- Severe symptoms – immediate transfer to ED for supportive treatment and acute management
- Overdose – gastric lavage a/o activated charcoal
Biological
- Discontinue any serotonergic
- BZD – relieve muscular symptoms
- Serotonin receptor antagonists (e.g. cyprotheptadine)
- Beta-blockers – propranolol and pindolol
Course and prognosis
- Resolve without sequelae within 24-36 hours with adequate supportive measures
- Restart serotonergic agents slowly and @ low doses and consider using serotonergic agents from a
different class
You might also like
- Core Challenge Workout CalendarDocument1 pageCore Challenge Workout CalendarJYGNo ratings yet
- Opthalmology - Summary TableDocument4 pagesOpthalmology - Summary TableJYGNo ratings yet
- OBSGYN - Shoulder DystociaDocument6 pagesOBSGYN - Shoulder DystociaJYGNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry - TreatmentDocument19 pagesPsychiatry - TreatmentJYG100% (1)
- Background: Alpha-1 Antitrypsin DeficiencyDocument2 pagesBackground: Alpha-1 Antitrypsin DeficiencyJYGNo ratings yet
- Syncope AlgorithmDocument1 pageSyncope AlgorithmJYGNo ratings yet
- OBSGYNDocument5 pagesOBSGYNJYGNo ratings yet
- List of SymptomsDocument2 pagesList of SymptomsJYGNo ratings yet
- List of SymptomsDocument2 pagesList of SymptomsJYGNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Function Mechanism of ActionDocument1 pageDrug Name Function Mechanism of ActionJYGNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)