0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views17 pagesGeometric Tolerancing Symbols Explained
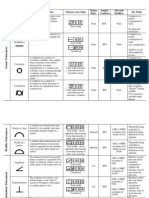
The document describes various geometric dimensioning and tolerancing symbols used in engineering drawings. It provides definitions, tolerance zones, required datums, material condition modifiers, and rules for conformance for each of the following symbols: flatness, circularity, cylindricity, straightness of a surface and axis, parallelism, perpendicularity, angularity, position, concentricity, symmetry, circular runout, total runout, and line profile. Examples are given with diagrams to illustrate how each tolerance is applied. Links are provided for more information on tolerancing floating fastener assembly parts.
Uploaded by
dramiltCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views17 pagesGeometric Tolerancing Symbols Explained
The document describes various geometric dimensioning and tolerancing symbols used in engineering drawings. It provides definitions, tolerance zones, required datums, material condition modifiers, and rules for conformance for each of the following symbols: flatness, circularity, cylindricity, straightness of a surface and axis, parallelism, perpendicularity, angularity, position, concentricity, symmetry, circular runout, total runout, and line profile. Examples are given with diagrams to illustrate how each tolerance is applied. Links are provided for more information on tolerancing floating fastener assembly parts.
Uploaded by
dramiltCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd