Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Section I Pediatrics 32: LWBK874-C02-15 - P4-64.indd 32
Uploaded by
Dain DavisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Section I Pediatrics 32: LWBK874-C02-15 - P4-64.indd 32
Uploaded by
Dain DavisCopyright:
Available Formats
32 Section I Pediatrics
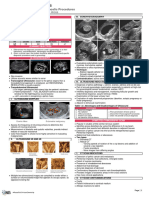
FIGURE 7.7: Ileocolic intussusception. Barium enema shows the intussusception as the f ling defect within
the hepatic f exure sur rounded by spiral mucosal folds. Signif cant distended small bow el represents distal
small bow el obstr uction. (F rom Fleisher GR, Ludwig S, and Baskin MN. Atlas of P ediatric Emergency Medicine.
Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2004.)
FIGURE 7.8: Barium enema demonstrating intussusception. Obstr uction of the colon at the hepatic f exure.
Note the characteristic coiled-spring appearance. (F rom Eisenberg RL. An Atlas of Differential Diagnosis, 4th ed.
Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2003.)
LWBK874-C02-15_p4-64.indd 32 6/20/11 5:31:21 PM
Chapter 7 Intussusception 33
Abdominal CT Scan
■ Not a f rst-line imaging modality
■ May be used to characterize a pathologic lead point pre viously detected b y ultrasound
■ May be identif ed incidentally when CT is obtained for other reasons (e.g ., appendicitis
evaluation)
■ Sensitivity and specif city for diagnosis ha ve not been w ell studied
■ Look for a round soft tissue mass with concentric rings, “target sign” representing loops of
small bow el most lik ely in the area of the ileum
TABLE 7.5: Abdominal/pelvic CT: intussusception
IV contrast Yes
PO contrast Yes
Amount of radiation 10–14 mSv*
*Approximate dose.
Classic Images
A B
FIGURE 7.9: Two images of intussusception seen on contrast CT scan: A: There is a mass within the mid
abdomen demonstrating an inter nal swir led appearance with central low attenuation lik ely representing
mesenteric fat within an ileocolic intussusception ( arrow). B: The intussusception is also captured on
longitudinal vie w (arrow). The sur rounding loops of small bow el are dilated and f lled with gas and stool lik ely
secondar y to obstr uction and reactive ileus. ( Courtesy of Children’s Hospital Boston, Boston, MA.)
FIGURE 7.10: Colonic intussusception. Axial T2-w eighted image demonstrating la yers of sigmoid colonic
intussusception with outer colon w all (arrow), pericolonic fat ( arrowhead), and inner colon w all (thin arrow). (From
Leyendecker JR and Brown JJ. Practical Guide to Abdominal and P elvic MRI. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams &
Wilkins, 2004.)
LWBK874-C02-15_p4-64.indd 33 6/20/11 5:31:22 PM
34 Section I Pediatrics
Basic Management
■ NPO
■ Intravenous h ydration
■ Pain control
■ General surger y consultation
● Surgeon present during air enema reduction in case of perforation or massive
pneumoperitoneum
■ Reduction via enema
● Barium was pre viously used, but now air is used more commonly
● Safer, cheaper, and more effective
● In the prone position, an uninf ated balloon catheter is placed into the rectum; buttocks are
taped together
● Air is introduced into the rectum with monitored pressure
● Ref ux of air from cecum into ileum conf rms complete reduction
● Patients should not be sedated for pressure reduction enemas
■ Antibiotics
● With peritoneal signs
● Prophylactically for potential perforation during pressure reduction procedure
■ Admission P ost-reduction
● There is a 10% recur rence usually within 24–48 hour s
■ Surgical treatment
● Suspected intussusception in those who are acutely ill
● Evidence of perforation
● Patients in whom nonoperative reduction is unsuccessful
● Resection of a pathologic lead point
Summary
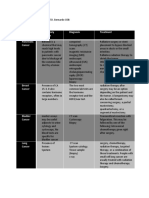
TABLE 7.6: Advantages and disadvantages of imaging modalities in intussusception
Imaging modalities Advantages Disadvantages
KUB Quick Low sensitivity ( ⬃45%)
Universally a vailable Low specif city
Low radiation High false negative rate
Ultrasound Low cost Availability
High sensitivity (98–100%) Operator-dependent
High specif city (88–100%) Body habitus limitations
Minimal patient discomfor t
No radiation
Contrast enema Gold standard Limited a vailability
Diagnostic and therapeutic Requires skilled per sonnel
Radiation exposure
Requires on-site surgeon for reduction
CT scan Used more for adult diagnosis Radiation exposure
Identif cation of lead points Not well studied in children
LWBK874-C02-15_p4-64.indd 34 6/20/11 5:31:23 PM
You might also like
- Target Volume Delineation and Field Setup: A Practical Guide for Conformal and Intensity-Modulated Radiation TherapyFrom EverandTarget Volume Delineation and Field Setup: A Practical Guide for Conformal and Intensity-Modulated Radiation TherapyNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Lesi Pra Kanker SoloDocument61 pagesManajemen Lesi Pra Kanker Solotria ayuNo ratings yet
- Trauma Tumpul Abdomen: Stase Bedah Digestif Januari 2019Document49 pagesTrauma Tumpul Abdomen: Stase Bedah Digestif Januari 2019ArifHidayatNo ratings yet
- Retroperitoneal Appendicitis: A Surgical DilemmaDocument2 pagesRetroperitoneal Appendicitis: A Surgical DilemmaputraNo ratings yet
- Walker - Explorarea Radiologica A Tubului DigestivDocument11 pagesWalker - Explorarea Radiologica A Tubului DigestivDiana AndriucNo ratings yet
- Role of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Head and Neck CancerDocument78 pagesRole of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Head and Neck CancernasimNo ratings yet
- FluorosDocument34 pagesFluorosAyman shahzadNo ratings yet
- Interventional Radiology 1Document66 pagesInterventional Radiology 1sibrahim16No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Procedures in Gynecology (2023)Document3 pagesDiagnostic Procedures in Gynecology (2023)RONALDO CUANo ratings yet
- Retroperitoneal Appendicitis: A Surgical Dilemma: Euroasian Journal of Hepato-Gastroenterology January 2013Document3 pagesRetroperitoneal Appendicitis: A Surgical Dilemma: Euroasian Journal of Hepato-Gastroenterology January 2013putraNo ratings yet
- Radiographics 20 3 G00ma12725Document25 pagesRadiographics 20 3 G00ma12725Tomografia TicomanNo ratings yet
- 161004acuteaof Gi - MadridDocument73 pages161004acuteaof Gi - MadridMAPACHE 91No ratings yet
- 1) BiopsyDocument30 pages1) BiopsySosa GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Infected Mesenteric Cyst A Rare Cause of Surgical Abdomen - September - 2022 - 6310790226 - 8312714Document2 pagesRecurrent Infected Mesenteric Cyst A Rare Cause of Surgical Abdomen - September - 2022 - 6310790226 - 8312714Motivational SpeechNo ratings yet
- Ambulatory AnaesthesiaDocument42 pagesAmbulatory Anaesthesiamealiella omarNo ratings yet
- Gutjnl 2012 303965.fullDocument11 pagesGutjnl 2012 303965.fullOngky AristianNo ratings yet
- Annular PankreasDocument3 pagesAnnular PankreasAnonymous ocfZSRrrONo ratings yet
- Clinical Scenario 10 SummaryDocument1 pageClinical Scenario 10 SummaryMarios GhobrialNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Practice Guidelines For Emergency General SurgeryDocument19 pagesDynamic Practice Guidelines For Emergency General SurgeryHarlyn MagsinoNo ratings yet
- 1618 4726 1 PB PDFDocument6 pages1618 4726 1 PB PDFDrive IyasNo ratings yet
- Review Article Aspiration: Fine Needle CytologyDocument11 pagesReview Article Aspiration: Fine Needle CytologyHakim naufaldiNo ratings yet
- EU-5 EUS DiagnosisDocument28 pagesEU-5 EUS Diagnosiskeng suttisangchanNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Radiation ProctitisDocument2 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Radiation ProctitispatNo ratings yet
- A Child With Acute Eyelid Edema and Proptosis: JAMA Ophthalmology Clinical ChallengeDocument2 pagesA Child With Acute Eyelid Edema and Proptosis: JAMA Ophthalmology Clinical ChallengePatriciaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Operation of The Liver and Techniques of Hepatic ResectionDocument17 pagesDiagnostic Operation of The Liver and Techniques of Hepatic ResectionjuaoNo ratings yet
- Europian Surgical Abstract 2 PDFDocument114 pagesEuropian Surgical Abstract 2 PDFDrAmmar MagdyNo ratings yet
- Work-Up and Management of Lung CancerDocument90 pagesWork-Up and Management of Lung Cancerrsbahia100% (2)
- Biopsy in Surgery RereDocument41 pagesBiopsy in Surgery RereRererloluwa100% (1)
- Kjtcs 47 124Document5 pagesKjtcs 47 124dalozpa23No ratings yet
- Management of Endometrial CarcinomaDocument46 pagesManagement of Endometrial CarcinomaSapna SNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Radiologi FixDocument44 pagesJurnal Radiologi FixAfifa Prima GittaNo ratings yet
- Surgical RX of Cancer 2023 - BNS 313Document32 pagesSurgical RX of Cancer 2023 - BNS 313Kemo RakhoboNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain MARS 2.0 - Dr. Siswidiyati, SP - RadDocument34 pagesAbdominal Pain MARS 2.0 - Dr. Siswidiyati, SP - RadarifdeathsciethNo ratings yet
- Part 2 210-273Document64 pagesPart 2 210-273alrabaee92No ratings yet
- Salvagability Giant HydronephrosisDocument14 pagesSalvagability Giant HydronephrosisAndy WijayaNo ratings yet
- 30 Retained Surgical SpongesDocument8 pages30 Retained Surgical SpongesErickNo ratings yet
- 9 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Unknown Primary in The Head and NeckDocument7 pages9 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Unknown Primary in The Head and NeckjorgeaznarNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic of Cancer 1Document27 pagesDiagnostic of Cancer 1222041No ratings yet
- Ultrasound-Guided Core-Needle Biopsy of Breast Lesions: ReviewDocument8 pagesUltrasound-Guided Core-Needle Biopsy of Breast Lesions: ReviewrasminojNo ratings yet
- Surgicopath July 2017Document105 pagesSurgicopath July 2017Rendy Adhitya PratamaNo ratings yet
- 10 CR Killian Jamieson DiverticulumDocument2 pages10 CR Killian Jamieson DiverticulumUmesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Type of CancerDocument1 pageType of CancerDominic BernardoNo ratings yet
- FB:Cardiologia Siglo XXI: TABLE 264-1Document200 pagesFB:Cardiologia Siglo XXI: TABLE 264-1Fiamma LamasNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy: Videos in Clinical MedicineDocument3 pagesBone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy: Videos in Clinical MedicineAnonymous AQwxbUaNo ratings yet
- Dipilih IVA Dan Untuk Treat Dipilih Cryotherapy.: Schiller'sDocument13 pagesDipilih IVA Dan Untuk Treat Dipilih Cryotherapy.: Schiller'sBarbara YoungNo ratings yet
- Gossypiboma Case ReportDocument2 pagesGossypiboma Case ReportArvind KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Fistula Nefrocolica Por RFADocument3 pagesFistula Nefrocolica Por RFARenan DiasNo ratings yet
- New Anatomical Classification of The Axilla With Implications For Sentinel Node BiopsyDocument8 pagesNew Anatomical Classification of The Axilla With Implications For Sentinel Node BiopsyIonelia PoticaNo ratings yet
- Case-Based Discussion-6: Dian Ariningrum, DR, Mkes, SPPKDocument36 pagesCase-Based Discussion-6: Dian Ariningrum, DR, Mkes, SPPKKristianti MRPNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Management of Early Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of The Esophagus - Screening, Diagnosis, and Therapy AGA 2018Document16 pagesEndoscopic Management of Early Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of The Esophagus - Screening, Diagnosis, and Therapy AGA 2018Nishiby PhạmNo ratings yet
- Retroperitoneal Hydatid Cyst Challenging The Dia - 2024 - International JournalDocument4 pagesRetroperitoneal Hydatid Cyst Challenging The Dia - 2024 - International JournalRonald QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Mistakes in Series 06 2022 GastrosDocument5 pagesMistakes in Series 06 2022 Gastrosfahd bin haiderNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ImagingLecture DR McGintyDocument162 pagesAbdominal ImagingLecture DR McGintyBiplob EmtiazNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic of CancerDocument27 pagesDiagnostic of CancerAyoub ZeinEddinNo ratings yet
- Intraductal Biliopancreatic Imaging: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technology ReviewDocument15 pagesIntraductal Biliopancreatic Imaging: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technology ReviewMadalina StoicescuNo ratings yet
- Abdomen Agudo - Radiologic Clinics of Northamerica 2003Document254 pagesAbdomen Agudo - Radiologic Clinics of Northamerica 2003arsilbNo ratings yet
- Meredith 2010Document6 pagesMeredith 2010Ilma Kurnia SariNo ratings yet
- B Scan Ultrasonography01Document54 pagesB Scan Ultrasonography01dr samreen arif50% (2)
- Axillary Clearance in MRMDocument58 pagesAxillary Clearance in MRMGanesh VlNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ImagingDocument45 pagesAbdominal ImagingFahriansyah Mp Tmc100% (1)
- Hepatic ParagangliomaDocument2 pagesHepatic ParagangliomaDain DavisNo ratings yet
- Pandya HistoryDocument4 pagesPandya HistoryDain DavisNo ratings yet
- Nutrition HandoutDocument9 pagesNutrition HandoutMukul KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Bethlehem: Statement of Textbook Account For The Year 2011-2012Document1 pageBethlehem: Statement of Textbook Account For The Year 2011-2012Dain DavisNo ratings yet
- English Class Vii PDFDocument101 pagesEnglish Class Vii PDFpannapurohitNo ratings yet
- Eco JetDocument15 pagesEco JetJustin CoyNo ratings yet
- Practice For Mounting Buses & Joints-374561Document11 pagesPractice For Mounting Buses & Joints-374561a_sengar1No ratings yet
- Coffee Quality Manual by Abra Rand Nig Use IDocument25 pagesCoffee Quality Manual by Abra Rand Nig Use IIpungNo ratings yet
- PANASONIC - WebCam-TQZJ402 - TY-CC20W PDFDocument188 pagesPANASONIC - WebCam-TQZJ402 - TY-CC20W PDF123anthonyNo ratings yet
- Gaffin, Biblical Theology and Westminster StandardsDocument16 pagesGaffin, Biblical Theology and Westminster StandardstheoarticlesNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Avances de AcesoriosDocument3 pagesTabla de Avances de AcesoriosPedro Diaz UzcateguiNo ratings yet
- Integration ConceptDocument34 pagesIntegration ConceptJANELLA ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- The Working of KarmaDocument74 pagesThe Working of KarmaSuhas KulhalliNo ratings yet
- Iso 8033 2016Document9 pagesIso 8033 2016Eric ChuNo ratings yet
- Anderson, Poul - Flandry 02 - A Circus of HellsDocument110 pagesAnderson, Poul - Flandry 02 - A Circus of Hellsgosai83No ratings yet
- Carrefour-SA Shopping Center TurkeyDocument2 pagesCarrefour-SA Shopping Center TurkeyVineet JogalekarNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Essential Learning Competencies 2020Document5 pagesEarth Science Essential Learning Competencies 2020Charry CervantesNo ratings yet
- Iec60227-3 (Ed2.1) en DDocument6 pagesIec60227-3 (Ed2.1) en Duntuk donlod aaaNo ratings yet
- PH & TemperatureDocument8 pagesPH & TemperatureNanaNo ratings yet
- Manual GA 55 VSD Atlas CompresorDocument114 pagesManual GA 55 VSD Atlas Compresormondaxa_mme50% (4)
- Terminals of Ecm: E3 E4 E5 E6Document2 pagesTerminals of Ecm: E3 E4 E5 E6jeremih alhegn100% (1)
- Child DevelopmentDocument15 pagesChild Development4AndreeaNo ratings yet
- 3M Novec 1230 Fire Protection Fluid FAQDocument8 pages3M Novec 1230 Fire Protection Fluid FAQEden CansonNo ratings yet
- ACR39U-U1: (USB Type A) Smart Card ReaderDocument8 pagesACR39U-U1: (USB Type A) Smart Card Readersuraj18in4uNo ratings yet
- RepaHeel Beeswax-Based Gel For Treating Heel Spurs Has Been Produced in EUDocument2 pagesRepaHeel Beeswax-Based Gel For Treating Heel Spurs Has Been Produced in EUPR.comNo ratings yet
- Homeo Treatment of Eye Diseases and AllergiesDocument17 pagesHomeo Treatment of Eye Diseases and AllergiesZia AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Emergency and Critical CareDocument14 pagesWildlife Emergency and Critical CareRayssa PereiraNo ratings yet
- MMW ReviewerDocument3 pagesMMW ReviewerMarcSaloj NeryNo ratings yet
- Ecological Quality RatioDocument24 pagesEcological Quality RatiofoocheehungNo ratings yet
- Quartile1 PDFDocument2 pagesQuartile1 PDFHanifah Edres DalumaNo ratings yet
- Arts Class: Lesson 01Document24 pagesArts Class: Lesson 01Lianne BryNo ratings yet
- F24 60manual (New)Document14 pagesF24 60manual (New)Robert CumpaNo ratings yet
- The Manufacture and Uses of Expanded Clay Aggregate: Thursday 15 November 2012 SCI HQ, LondonDocument36 pagesThe Manufacture and Uses of Expanded Clay Aggregate: Thursday 15 November 2012 SCI HQ, LondonVibhuti JainNo ratings yet
- Notes Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument12 pagesNotes Transfer of Thermal Energymahrosh mamoon100% (2)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyFrom EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)