Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Entity Relationship Diagram - ER Diagram
Uploaded by
Mayank GoswamiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Entity Relationship Diagram - ER Diagram
Uploaded by
Mayank GoswamiCopyright:
Available Formats
ER Diagram
Entity Relationship Diagram – ER Diagram
An Entity–relationship model (ER model) describes the structure of a database with the help of
a diagram, which is known as Entity Relationship Diagram (ER Diagram). An ER model is a
design or blueprint of a database that can later be implemented as a database.
What is an Entity Relationship Diagram (ER Diagram)?
An ER diagram shows the relationship among entity sets. An entity set is a group of similar
entities and these entities can have attributes.ER diagram shows the complete logical structure of
a database.
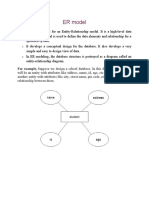
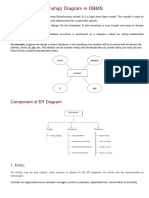
A simple ER Diagram:
In the following diagram we have two entities Student and College and their relationship. The
relationship between Student and College is many to one as a college can have many students
however a student cannot study in multiple colleges at the same time. Student entity has
attributes such as Stu_Id,Stu_Name&Stu_Addr and College entity has attributes such as
Col_ID&Col_Name.
Rectangle: Represents Entity sets.
Ellipses: Attributes
Diamonds: Relationship Set
Lines: They link attributes to Entity Sets and Entity sets to Relationship Set
Double Ellipses: Multivalued Attributes
Dashed Ellipses: Derived Attributes
Double Rectangles: Weak Entity Sets
Double Lines: Total participation of an entity in a relationship set
Ashish Chaturvedi, Dept. of CSE, LNCTE Page 1
ER Diagram
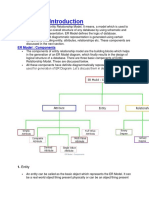
Components of a ER Diagram
1. Entity
An entity is an object or component of data. An entity is represented as rectangle in an
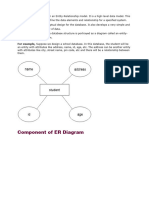
ER diagram.For example: In the following ER diagram we have two entities Student and
College and these two entities have many to one relationship as many students study in a
single college. We will read more about relationships later, for now focus on entities.
Weak Entity:
An entity that cannot be uniquely identified by its own attributes and relies on the
relationship with other entity is called weak entity. The weak entity is represented by a
double rectangle. For example – a bank account cannot be uniquely identified without
Ashish Chaturvedi, Dept. of CSE, LNCTE Page 2
ER Diagram
knowing the bank to which the account belongs, so bank account is a weak entity.
2. Attribute
An attribute describes the property of an entity. An attribute is represented as Oval in an
ER diagram. There are four types of attributes:
1. Key attribute
2. Composite attribute
3. Multivalued attribute
4. Derived attribute
1. Key attribute:
A key attribute can uniquely identify an entity from an entity set. For example, student
roll number can uniquely identify a student from a set of students. Key attribute is
represented by oval same as other attributes however the text of key attribute is
underlined.
Ashish Chaturvedi, Dept. of CSE, LNCTE Page 3
ER Diagram
2. Composite attribute:
An attribute that is a combination of other attributes is known as composite attribute. For
example, In student entity, the student address is a composite attribute as an address is
composed of other attributes such as pin code, state, country.
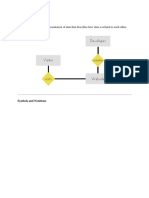
3. Multivalued attribute:
An attribute that can hold multiple values is known as multivalued attribute. It is
represented with double ovals in an ER Diagram. For example – A person can have more
than one phone numbers so the phone number attribute is multivalued.
4. Derived attribute:
A derived attribute is one whose value is dynamic and derived from another attribute. It is
represented by dashed oval in an ER Diagram. For example – Person age is a derived
attribute as it changes over time and can be derived from another attribute (Date of birth).
E-R diagram with multivalued and derived attributes:
Ashish Chaturvedi, Dept. of CSE, LNCTE Page 4
ER Diagram
3. Relationship
A relationship is represented by diamond shape in ER diagram, it shows the relationship
among entities. There are four types of relationships:
1. One to One
2. One to Many
3.Many to One
4. Many to Many
1. One to One Relationship
When a single instance of an entity is associated with a single instance of another entity
then it is called one to one relationship. For example, a person has only one passport and
a passport is given to one person.
2. One to Many Relationship
When a single instance of an entity is associated with more than one instances of another
entity then it is called one to many relationship. For example – a customer can place
many orders but a order cannot be placed by many customers.
Ashish Chaturvedi, Dept. of CSE, LNCTE Page 5
ER Diagram
3. Many to One Relationship
When more than one instances of an entity is associated with a single instance of another
entity then it is called many to one relationship. For example – many students can study
in a single college but a student cannot study in many colleges at the same time.
4. Many to Many Relationship
When more than one instances of an entity is associated with more than one instances of
another entity then it is called many to many relationship. For example, a can be assigned
to many projects and a project can be assigned to many students.
Ashish Chaturvedi, Dept. of CSE, LNCTE Page 6
You might also like
- ER Diagram - KameshwariDocument12 pagesER Diagram - KameshwariKameshwari PurusothmanNo ratings yet
- Data ModelDocument9 pagesData ModelsuvadarshiniswainNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Data Models - ER ModelDocument9 pages5.1 Data Models - ER Model2002746.it.cecNo ratings yet
- DBMS ER DiagramDocument11 pagesDBMS ER DiagramAayushi ChowlaNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument17 pagesDBMSAngel RanaNo ratings yet
- Anish GuptaDocument14 pagesAnish GuptaSatyam MallickNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Part-2)Document15 pagesUnit-1 (Part-2)Avinash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document25 pagesUnit 2ananyamarysebastian05No ratings yet
- Entity Relationship DiagramDocument20 pagesEntity Relationship DiagramTynan SokNo ratings yet
- DBMS-lecture 4 ER-Model IntroductionDocument14 pagesDBMS-lecture 4 ER-Model IntroductionMonica TimberNo ratings yet
- A Simple ER Diagram:: 1) Explain Design of Entity Relational ModalDocument18 pagesA Simple ER Diagram:: 1) Explain Design of Entity Relational Modalchaithu goudNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 & 4 Entity Relationship Modelling: Er. Pradip KharbujaDocument68 pagesTopic 3 & 4 Entity Relationship Modelling: Er. Pradip Kharbujaniravthegreate999No ratings yet
- Entity Relationship Diagram - ER DiagramDocument10 pagesEntity Relationship Diagram - ER DiagramSwati HansNo ratings yet
- Data Models in DBMS Unit 2Document24 pagesData Models in DBMS Unit 2Shubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- E-R ModelDocument14 pagesE-R Modelkiller HackingNo ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument13 pagesER ModelManit MittalNo ratings yet
- E R DiagramDocument6 pagesE R DiagramLloyd PiscaderoNo ratings yet
- The Enity Relationship ModelDocument39 pagesThe Enity Relationship ModelcleophacerevivalNo ratings yet
- Components of ER Diagram: EntityDocument5 pagesComponents of ER Diagram: EntityAyan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- About Database Management System: Sachin Kumar Asst. Professor IIMT College of Management, Greater NoidaDocument40 pagesAbout Database Management System: Sachin Kumar Asst. Professor IIMT College of Management, Greater NoidaM10 FFNo ratings yet
- DBMS (Unit II)Document33 pagesDBMS (Unit II)Abhay KNo ratings yet
- VND - Openxmlformats Officedocument - Presentationml.presentation&rendition 1 2Document42 pagesVND - Openxmlformats Officedocument - Presentationml.presentation&rendition 1 2fashion20trendsNo ratings yet
- DBMS - Data Models and Relational Database Design NotesDocument48 pagesDBMS - Data Models and Relational Database Design NotesKomal Ramteke100% (1)
- ER DigramDocument10 pagesER DigramNDDHSADNo ratings yet
- ER Diagram RepresentationDocument9 pagesER Diagram RepresentationWhite AntNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit 1Document13 pagesDBMS Unit 1Harsh OjhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document26 pagesUnit 2laket64875No ratings yet
- Entity Relationship ModelDocument8 pagesEntity Relationship ModeltanujaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PDFDocument32 pagesUnit 2 PDFyuvrajNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 ErDocument6 pagesUnit 2 Erkalik goyalNo ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument12 pagesER Modelwaleed.khaldNo ratings yet
- DatamodelingDocument8 pagesDatamodelingRakshita NathawatNo ratings yet
- ER Model: For Example, Suppose We Design A School Database. in This Database, The StudentDocument7 pagesER Model: For Example, Suppose We Design A School Database. in This Database, The Studentpyari mohanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document33 pagesUnit 2yuvrajNo ratings yet
- Data Models in DBMSDocument12 pagesData Models in DBMSnarikitsNo ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument5 pagesER ModelHarpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship Data ModellingDocument13 pagesEntity Relationship Data ModellingSamuel NdiranguNo ratings yet
- The Entity-Relationship ModelDocument15 pagesThe Entity-Relationship ModelCherry PepitoNo ratings yet
- 5.1 (B) ER ModelDocument10 pages5.1 (B) ER Model2002746.it.cecNo ratings yet
- ER Model: Component of ER DiagramDocument9 pagesER Model: Component of ER Diagramprerana sheteNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 ER Diagram in DBMSDocument35 pagesLecture 5 ER Diagram in DBMSEichhorst AutomobilesNo ratings yet
- Data Modeling ER Model Concept: Component of ER DiagramDocument21 pagesData Modeling ER Model Concept: Component of ER DiagramAnick KhanNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship DiagramDocument20 pagesEntity Relationship DiagramHamad HRNo ratings yet
- Dbms 2Document50 pagesDbms 2VedantGonnadeNo ratings yet
- Unit-II DBMSDocument20 pagesUnit-II DBMSMsr. B. Jeyalakshmi Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit 2Document54 pagesDBMS Unit 2Nishita PandeyNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument46 pagesUnit IIomgunjal85No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - ER Diagram in DBMSDocument32 pagesLecture 5 - ER Diagram in DBMSNjemax PanasheNo ratings yet
- ER Model InfoDocument34 pagesER Model Infokiran_qaNo ratings yet
- DBMS - Unit Ii-1Document29 pagesDBMS - Unit Ii-1Bot IdNo ratings yet
- E-R DiagramDocument11 pagesE-R DiagramAaruni BattaNo ratings yet
- CS8492 - DBMS - Unit 2Document18 pagesCS8492 - DBMS - Unit 2alexb072002No ratings yet
- Unit Ii Database DesignDocument18 pagesUnit Ii Database DesignHarish SNo ratings yet
- Systems Analysis and Design - ErdDocument25 pagesSystems Analysis and Design - ErdSon NickNo ratings yet
- E-R Diagram: ER-Diagram Is A Visual Representation of Data That Describes How Data Is Related To Each OtherDocument12 pagesE-R Diagram: ER-Diagram Is A Visual Representation of Data That Describes How Data Is Related To Each OthersubhamohanNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Database Design: CS8492 /database Management Systems Department of IT 2021 - 2022Document18 pagesUnit Ii Database Design: CS8492 /database Management Systems Department of IT 2021 - 20224073 JOSEPH SAVIO PEREIRANo ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument8 pagesER ModelAhmad FakharNo ratings yet
- ER Model - Basic ConceptsDocument12 pagesER Model - Basic ConceptsGwelambertNo ratings yet
- 206-Manasi Bonde-EXPERIMENT NO 1Document10 pages206-Manasi Bonde-EXPERIMENT NO 1Manasi BondeNo ratings yet
- Locating ContourDocument13 pagesLocating ContourWendell David ParasNo ratings yet
- Practice Final Questions 1Document26 pagesPractice Final Questions 1Corn eliusNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document18 pagesAssignment 1Siddharth ShahNo ratings yet
- Object-Oriented Modeling and DesignDocument98 pagesObject-Oriented Modeling and DesignViji GopalNo ratings yet
- Lab: Box-Jenkins Methodology - Test Data Set 1: Time Series and ForecastDocument8 pagesLab: Box-Jenkins Methodology - Test Data Set 1: Time Series and ForecastzamirNo ratings yet
- Cave PDFDocument28 pagesCave PDFOlufemi SotundeNo ratings yet
- PhpMyAdmin SQL DumpDocument8 pagesPhpMyAdmin SQL DumpMuhammad NazirNo ratings yet
- Inequality Restricted Maximum Entropy Estimation in STATDocument26 pagesInequality Restricted Maximum Entropy Estimation in STATMohamed JasemNo ratings yet
- 7 - Hypothesis Testing (Compatibility Mode) PDFDocument9 pages7 - Hypothesis Testing (Compatibility Mode) PDFKenneth HicksNo ratings yet
- OOAD-Ali BahramiDocument122 pagesOOAD-Ali BahramiAndrew Walls75% (8)
- 2013 SolidWorks - File TypesDocument31 pages2013 SolidWorks - File TypesrcaletaNo ratings yet
- Business Process ModelingDocument89 pagesBusiness Process ModelingAhsan Zaman100% (2)
- Charts & Infographics: Data-Driven Charts and Editable Shapes For PowerpointDocument54 pagesCharts & Infographics: Data-Driven Charts and Editable Shapes For PowerpointJosh Ndoky SantosNo ratings yet
- AIS Lec2Document48 pagesAIS Lec2Monique del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Data Constraints FinalDocument6 pagesData Constraints FinalAjak OmarNo ratings yet
- Detecting and Measuring Circular Objects in An ImageDocument11 pagesDetecting and Measuring Circular Objects in An ImagePedroSoucasauxNo ratings yet
- Bach Cantata BWV - 82a - Score PDFDocument39 pagesBach Cantata BWV - 82a - Score PDFXavier SmithNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Entity-Relationship ModelDocument60 pagesEnhanced Entity-Relationship Modelminhtama7No ratings yet
- Guide To SQL 9th Edition Pratt Solutions ManualDocument21 pagesGuide To SQL 9th Edition Pratt Solutions Manuala87802798767% (6)
- Elec 303 HW10 ProbabilityDocument2 pagesElec 303 HW10 ProbabilityXuyang Sean LuNo ratings yet
- Classes and Objects Classes and ObjectsDocument46 pagesClasses and Objects Classes and ObjectsMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Surveying TopoDocument6 pagesSurveying TopoJelena Kilić-GrgićNo ratings yet
- Univox U-4100 Amplifier SchematicDocument1 pageUnivox U-4100 Amplifier SchematicdodNo ratings yet
- Part II Operations Management PDFDocument178 pagesPart II Operations Management PDFandrapradeshsse100% (1)
- DBMS Technical Publications Chapter 1Document24 pagesDBMS Technical Publications Chapter 1kishore5783100% (1)
- Hovel Papercraft For Rpgs PDFDocument5 pagesHovel Papercraft For Rpgs PDFCarlos MendozaNo ratings yet
- Bim Case Study Rics HQDocument11 pagesBim Case Study Rics HQPuneet Arora100% (1)
- Understanding of A Convolutional Neural NetworkDocument6 pagesUnderstanding of A Convolutional Neural NetworkJavier BushNo ratings yet
- Quiz 6 L1-L4Document117 pagesQuiz 6 L1-L4Rio Ardayana100% (6)
- Histogram Adjustments in MATLABDocument9 pagesHistogram Adjustments in MATLABĐỗ Văn TânNo ratings yet