Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Manish KR Singh BCA-1 21-8-18
Uploaded by
maanish singhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Manish KR Singh BCA-1 21-8-18
Uploaded by
maanish singhCopyright:
Available Formats
operating system (OS)
An operating system (OS) is the program that, after being initially loaded into
the computer by a boot program, manages all the other programs in a
computer. The other programs are called applications or application
programs. The application programs make use of the operating system by
making requests for services through a defined application program interface
(API). In addition, users can interact directly with the operating system through
a user interface such as a command line or a graphical user interface (GUI).
An operating system performs these services for applications:
In a multitasking operating system where multiple programs can be running
at the same time, the operating system determines which applications
should run in what order and how much time should be allowed for each
application before giving another application a turn.
It manages the sharing of internal memory among multiple applications.
It handles input and output to and from attached hardware devices, such
as hard disks, printers, and dial-up ports.
It sends messages to each application or interactive user (or to a system
operator) about the status of operation and any errors that may have
occurred.
It can offload the management of what are called batch jobs (for example,
printing) so that the initiating application is freed from this work.
On computers that can provide parallel processing, an operating system
can manage how to divide the program so that it runs on more than one
processor at a time.
All major computer platforms (hardware and software) require and sometimes
include an operating system, and operating systems must be developed with
different features to meet the specific needs of various form factors.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- CRC CardDocument5 pagesCRC Cardmaanish singhNo ratings yet
- Data Structures-I: Submitted To:-Mr. Naresh Bhutani Submitted By: - Manish Kumar Singh Bca - Iii Roll No. 4310509Document1 pageData Structures-I: Submitted To:-Mr. Naresh Bhutani Submitted By: - Manish Kumar Singh Bca - Iii Roll No. 4310509maanish singhNo ratings yet
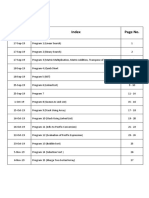
- DS File IndexDocument1 pageDS File Indexmaanish singhNo ratings yet
- Dbms File IndexDocument2 pagesDbms File Indexmaanish singhNo ratings yet
- PC Software Notes Unit-IDocument4 pagesPC Software Notes Unit-Imaanish singhNo ratings yet