100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views22 pagesProject Management:: Network Analysis (CPM & Pert)
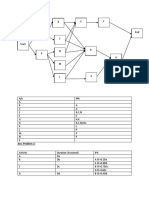
This document provides an overview of project management tools including network analysis techniques like CPM and PERT. It defines a project as a unique, time-limited undertaking requiring varied skills and resources to achieve a specific goal. Network analysis uses diagrams with activities (arrows) and events (nodes) to plan and schedule project tasks in a logical sequence. The Critical Path Method (CPM) identifies the longest path of activities in a network to determine the minimum time needed to complete the project and which activities are critical.
Uploaded by
JaythumerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views22 pagesProject Management:: Network Analysis (CPM & Pert)
This document provides an overview of project management tools including network analysis techniques like CPM and PERT. It defines a project as a unique, time-limited undertaking requiring varied skills and resources to achieve a specific goal. Network analysis uses diagrams with activities (arrows) and events (nodes) to plan and schedule project tasks in a logical sequence. The Critical Path Method (CPM) identifies the longest path of activities in a network to determine the minimum time needed to complete the project and which activities are critical.
Uploaded by
JaythumerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd