Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fermentation
Fermentation
Uploaded by
Ronald OlacOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fermentation
Fermentation
Uploaded by
Ronald OlacCopyright:
Available Formats
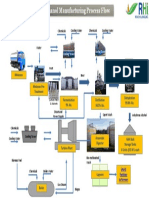
Fermentation plant consists of five fermenters with all the accessories like plate heat
exchangers for cooling, spurges, broth mixers and air blowers. The yeast is
immobilized using special media and it remains in the fermentation plant throughout
and hence it gives tremendous advantages in maintaining the yeast population and in
combating the bacterial infection. Molasses after weighing is diluted and also pre-
treated to an appropriate sugar concentration in the Molasses Treatment Plant. The
fermenters are then inoculated with culture developed from the laboratory in the
culture vessels. Dropping of culture from the laboratory was carried out in a daily
basis.
To help the fermentation sustain its viability, nitrogen are added in the medium in the
form of Urea and DAP as required. Temperature in the fermenters is maintained to
an optimum level as required for efficient reaction with the help of Plate Heat
Exchanger and recirculation pumping system. This recirculation also helps in proper
mixing of fermented wash. The retention time for the reaction is about 24 to 36
hours. Air blower is provided to supply the necessary oxygen required for the yeast
and also for agitation. After completion of reaction the fermented wash is delivered
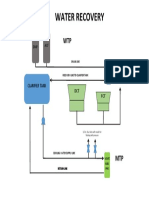
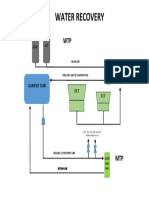
to Continuous Stabilization Tank (CST). In CST, solids are settled down. The
supernatant goes to Buffer Tank (BT) and sludge from the bottom goes to Sludge
Decanter.
The CO2 liberated in the reaction is scrubbed in water, with the help of CO2
Scrubber. This CO2 contains ethanol, which is recovered by collecting CO2
Scrubber water into Sludge Trough. The diluted sludge is pumped into Sludge
decanter. The traces of ethanol present in diluted sludge are separated at the
supernatant, which is collected into BT through overflow, and washed sludge from
bottom is drained off.
The fermented mash collected in the Buffer Tank is feed to Distillation section.
You might also like
- Productiom Target April 1-30, 2019 97.58% Deviation From TargetDocument2 pagesProductiom Target April 1-30, 2019 97.58% Deviation From TargetRonald OlacNo ratings yet
- Bernard Water RecoveryDocument1 pageBernard Water RecoveryRonald OlacNo ratings yet
- Production Material Balance: RS at 96% V/V 106,000 Liters/dayDocument1 pageProduction Material Balance: RS at 96% V/V 106,000 Liters/dayRonald OlacNo ratings yet
- Carbo Solutions: Summary of Recommendations by Dr. EspinosaDocument4 pagesCarbo Solutions: Summary of Recommendations by Dr. EspinosaRonald OlacNo ratings yet
- Quality Manual: I. Functional ObjectiveDocument7 pagesQuality Manual: I. Functional ObjectiveRonald OlacNo ratings yet
- Bioethanol Process Flow v.2Document1 pageBioethanol Process Flow v.2Ronald OlacNo ratings yet
- RBC Waste Water DiagramDocument3 pagesRBC Waste Water DiagramRonald OlacNo ratings yet
- Water Flow DiagramDocument1 pageWater Flow DiagramRonald OlacNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)