Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CS PDF
CS PDF
Uploaded by
Vikram Pratap Chauhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageOriginal Title
CS.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageCS PDF
CS PDF
Uploaded by
Vikram Pratap ChauhanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
CS: Computer Science and Information Technology
Section 1: Engineering Mathematics
Discrete Mathematics: Propositional and first order logic. Sets, relations, functions, partial orders and
lattices. Groups. Graphs: connectivity, matching, coloring. Combinatorics: counting, recurrence
relations, generating functions.
Linear Algebra: Matrices, determinants, system of linear equations, eigenvalues and eigenvectors, LU
decomposition.
Calculus: Limits, continuity and differentiability. Maxima and minima. Mean value theorem. Integration.
Probability: Random variables. Uniform, normal, exponential, poisson and binomial distributions. Mean,
median, mode and standard deviation. Conditional probability and Bayes theorem.
Section 2 – 10: Computer Science and Information Technology
Section 2: Digital Logic
Boolean algebra. Combinational and sequential circuits. Minimization. Number representations and
computer arithmetic (fixed and floating point).
Section 3: Computer Organization and Architecture
Machine instructions and addressing modes. ALU, data‐path and control unit. Instruction pipelining.
Memory hierarchy: cache, main memory and secondary storage; I/O interface (interrupt and DMA
mode).
Section 4: Programming and Data Structures
Programming in C. Recursion. Arrays, stacks, queues, linked lists, trees, binary search trees, binary
heaps, graphs.
Section 5: Algorithms
Searching, sorting, hashing. Asymptotic worst case time and space complexity. Algorithm design
techniques: greedy, dynamic programming and divide‐and‐conquer. Graph search, minimum spanning
trees, shortest paths.
Section 6: Theory of Computation
Regular expressions and finite automata. Context-free grammars and push-down automata. Regular and
contex-free languages, pumping lemma. Turing machines and undecidability.
Section 7: Compiler Design
Lexical analysis, parsing, syntax-directed translation. Runtime environments. Intermediate code
generation.
Section 8: Operating System
Processes, threads, inter‐process communication, concurrency and synchronization. Deadlock. CPU
scheduling. Memory management and virtual memory. File systems.
Section 9: Databases
ER‐model. Relational model: relational algebra, tuple calculus, SQL. Integrity constraints, normal forms.
File organization, indexing (e.g., B and B+ trees). Transactions and concurrency control.
Section 10: Computer Networks
Concept of layering. LAN technologies (Ethernet). Flow and error control techniques, switching.
IPv4/IPv6, routers and routing algorithms (distance vector, link state). TCP/UDP and sockets, congestion
control. Application layer protocols (DNS, SMTP, POP, FTP, HTTP). Basics of Wi-Fi. Network
security: authentication, basics of public key and private key cryptography, digital signatures and
certificates, firewalls.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- MAKAUT Question Paper Software EnggDocument2 pagesMAKAUT Question Paper Software EnggersayantanNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument38 pagesSeminar Reportapi-384849680% (5)
- NotesDocument185 pagesNotesersayantanNo ratings yet
- Stockreg PDFDocument1 pageStockreg PDFersayantanNo ratings yet
- HT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2012 Operating SystemDocument2 pagesHT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2012 Operating SystemersayantanNo ratings yet
- Careerpower - in Wp-Content Uploads 2016 10 NUMERICAL-ABILITY-SolutionDocument2 pagesCareerpower - in Wp-Content Uploads 2016 10 NUMERICAL-ABILITY-SolutionersayantanNo ratings yet
- Law Five YearsDocument293 pagesLaw Five YearsersayantanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Comp Test BankDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Comp Test BankRabab M AlyNo ratings yet
- CS Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesCS Cheat SheetSyed Farhan FaroghNo ratings yet
- Cs2307-Computer Networks Lab Viva QuestionsDocument2 pagesCs2307-Computer Networks Lab Viva QuestionsersayantanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (Computer Networking)Document1 pageQuestion Bank (Computer Networking)ersayantanNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematics 30 Formula SheetDocument1 pageApplied Mathematics 30 Formula SheetersayantanNo ratings yet
- ENGO 431: Chapter 1: Principles of PhotogrammetryDocument42 pagesENGO 431: Chapter 1: Principles of PhotogrammetryDelasdriana WiharjaNo ratings yet
- Ora 04031Document3 pagesOra 04031api-257220146No ratings yet
- ConsensusDocument77 pagesConsensusPhạm Huy HoàngNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Freecom Dual Drive Network Center enDocument2 pagesDatasheet Freecom Dual Drive Network Center enPaynal SethNo ratings yet
- SrsDocument11 pagesSrsNiraj ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Oracle PL SQLDocument153 pagesOracle PL SQLsuman8361No ratings yet
- ControlLogix® Redundancy System Revision 11Document12 pagesControlLogix® Redundancy System Revision 11l1f3b00kNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AutoCADDocument16 pagesIntroduction To AutoCADAzman SyafriNo ratings yet
- Oracle 10G Run Report From FormsDocument4 pagesOracle 10G Run Report From FormsaanandkumaarNo ratings yet
- DBMS Final ReportDocument5 pagesDBMS Final ReportShaniRulzzNo ratings yet
- Steps To Create Authorization FieldDocument2 pagesSteps To Create Authorization FieldPiyushkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Bjarnason TrampolinesDocument8 pagesBjarnason TrampolinesfaxecoNo ratings yet
- JMETERDocument12 pagesJMETERSimona PitamNo ratings yet
- Web Scripting With PHP, Mysql & Apache: Afrosp (African Open Source Project)Document18 pagesWeb Scripting With PHP, Mysql & Apache: Afrosp (African Open Source Project)Greg KawereNo ratings yet
- VPN Configuration Guide: Zywall (4.X Firmware)Document19 pagesVPN Configuration Guide: Zywall (4.X Firmware)Santiago PlazaNo ratings yet
- Frank Warmerdam, Even Rouault, and OthersDocument970 pagesFrank Warmerdam, Even Rouault, and OthersDavidDuqueNo ratings yet
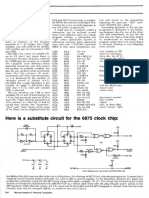
- Here Is A Substitute Circuit For The 6875 Clock Chip:: Dream 6800 ComputerDocument1 pageHere Is A Substitute Circuit For The 6875 Clock Chip:: Dream 6800 ComputerHernan BenitesNo ratings yet
- ExP1-9 FINALDocument68 pagesExP1-9 FINALkarthiNo ratings yet
- COMP2102 Unit #4 - Working With Windows Server Storage ServicesDocument7 pagesCOMP2102 Unit #4 - Working With Windows Server Storage ServicesSrikanth SiddareddyNo ratings yet
- ICS Telecom v9 - Install InstructionsDocument2 pagesICS Telecom v9 - Install InstructionstariktarikovNo ratings yet
- MPLAB Getting Started 51281hDocument44 pagesMPLAB Getting Started 51281hSimona AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Configuration of SAP SMTPDocument8 pagesConfiguration of SAP SMTPRobbin PintoNo ratings yet
- Theory of Computation Prof. Kamala Krithivasan Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDocument31 pagesTheory of Computation Prof. Kamala Krithivasan Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasSunil ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Capstone Manuscript OutlineDocument4 pagesCapstone Manuscript OutlineAlou Camille B. Sabado100% (2)
- Chapter 5: Information Representation Method-HTML-I SolutionsDocument15 pagesChapter 5: Information Representation Method-HTML-I SolutionsAman Singh75% (4)
- An FBI Backdoor in OpenBSDDocument3 pagesAn FBI Backdoor in OpenBSDpazminopNo ratings yet
- Enterprise System Concepts - HandoutsDocument20 pagesEnterprise System Concepts - HandoutsThotapalli PravallikaNo ratings yet
- MCA Bus OperationsDocument10 pagesMCA Bus OperationsDrift GeeNo ratings yet
- Oracle Forms Developer 9i TutorialDocument37 pagesOracle Forms Developer 9i Tutorialmani@pfizerNo ratings yet