Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Herons Formula
Uploaded by
ajhjfdabCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Herons Formula
Uploaded by
ajhjfdabCopyright:
Available Formats
Study Material
Downloaded from Vedantu
FREE LIVE ONLINE
MASTER CLASSES
FREE Webinars by Expert Teachers
About Vedantu
Vedantu is India’s largest LIVE online teaching platform
with best teachers from across the country.
Vedantu offers Live Interactive Classes for JEE, NEET, KVPY,
NTSE, Olympiads, CBSE, ICSE, IGCSE, IB & State Boards for
Students Studying in 6-12th Grades and Droppers. Register for FREE
Awesome Master Teachers
Anand Prakash Pulkit Jain Vamsi Krishna
B.Tech, IIT Roorkee B.Tech, IIT Roorkee B.Tech, IIT Bombay
Co-Founder, Vedantu Co-Founder, Vedantu Co-Founder, Vedantu
My mentor is approachable and guides me My son loves the sessions and I can
in my future aspirations as well. already see the change.
Student - Ayushi Parent - Sreelatha
10,04,600+ 9,49,900+ 95% 95% Students of Regular
Hours of LIVE Learning Happy Students Top Results
Tuitions on Vedantu scored
above 90% in exams!
FREE MASTER CLASS SERIES
For Grades 6-12th targeting JEE, CBSE, ICSE & much more Register for FREE
Free 60 Minutes Live Interactive classes everyday
Learn from the Master Teachers - India’s best Limited Seats!
Download
Vedantu's App & Get
All Study Material LIVE
with Solution Doubt Solving
Daily FREE Tests and
LIVE Classes Reports
DOWNLOAD THE APP
Class IX - NCERT –Maths Exercise (12.1)
Question 1:
A traffic signal board, indicating ‘SCHOOL AHEAD’, is an equilateral triangle with side ‘a’.
Find the area of the signal board, using Heron’s formula. If its perimeter is 180 cm, what will be
the area of the signal board?
Solution 1:
Side of traffic signal board = a
Perimeter of traffic signal board = 3 × a
3
2s 3a s a
2
By Heron’s formula, Area of triangle =
3 3 3 3
Area of given triangle = a a a a a a a
2 2 2 2
s(s a)(s b)(s c)
3 a a a
a
2 2 2 2
3 2
a … (1)
2
Perimeter of traffic signal board = 180 cm
180
Side of traffic signal board (a) = cm = 60 cm
3
3
Using Equation (1), area of traffic signal board (60 cm)2
2
3600
3 cm2 900 3 cm2
4
Question 2:
The triangular side walls of a flyover have been used for advertisements. The sides of the walls
are 122 m, 22 m, and 120 m (see the given figure). The advertisements yield an earning of Rs.
5000 per m2 per year. A company hired one of its walls for 3 months. How much rent did it pay?
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 1
Study Materials
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 to 12 (Math & Science)
Revision Notes for Class 6 to 12 (Math & Science)
RD Sharma Solutions for Class 6 to 12 Mathematics
RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 6, 7 & 10 Mathematics
Important Questions for Class 6 to 12 (Math & Science)
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9, 10 & 12 (Math &
Science)
Important Formula for Class 6 to 12 Math
CBSE Syllabus for Class 6 to 12
Lakhmir Singh Solutions for Class 9 & 10
Previous Year Question Paper
CBSE Class 12 Previous Year Question Paper
CBSE Class 10 Previous Year Question Paper
JEE Main & Advanced Question Paper
NEET Previous Year Question Paper
Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd.
Score high with a personal teacher, Learn LIVE Online!
www.vedantu.com
Solution 2:
The sides of the triangle (i.e., a, b, c) are of 122 m, 22 m, and 120 m respectively.
Perimeter of triangle = (122 + 22 + 120) m
2s = 264 m
s = 132 m
By Heron’s formula,
Area of triangle =
Area of given triangle = 132 132 122132 22 132 120 m2
= 132 1011012
s(sm2 s b)(s c
a)( 1320 m2 )
Rent of 1 m2 area per year = Rs. 5000
5000
Rent of 1 m2 area per month = Rs.
12
5000
Rent of 1320 m2 area for 3 months = Rs. 3 1320
12
= Rs. (5000 × 330) = Rs. 1650000
Therefore, the company had to pay Rs. 1650000.
Question 3:
The floor of a rectangular hall has a perimeter 250 m. If the cost of panting the four walls at the
rate of Rs. 10 per m2 is Rs.15000, find the height of the hall.
[Hint: Area of the four walls = Lateral surface area.]
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 2
Solution 3:
Let length, breadth, and height of the rectangular hall be l m, b m, and h m respectively.
Area of four walls = 2lh + 2bh = 2(l + b) h
Perimeter of the floor of hall = 2(l + b) = 250 m
Area of four walls = 2(l + b) h = 250h m2
Cost of painting per m2 area = Rs. 10
Cost of painting 250h m2 area = Rs. (250h × 10) = Rs. 2500h
However, it is given that the cost of paining the walls is Rs. 15000.
15000 = 2500h
h=6
Therefore, the height of the hall is 6 m.
Question 4:
Find the area of a triangle two sides of which are 18 cm and 10 cm and the perimeter is 42 cm.
Solution 4:
Let the third side of the triangle be x.
Perimeter of the given triangle = 42 cm
18 cm + 10 cm + x = 42
x = 14 cm
Perimeter 42 cm
s 21 cm
2 2
By Heron’s formula, Area of triangle =
Area of given triangle = 21 21 18 21 10 21 14 cm2
21 311 7 s(cm
s 2 a)(s b)(s c)
21 11cm2
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 3
Question 5:
Sides of a triangle are in the ratio of 12:17:25 and its perimeter is 540 cm. Find its area.
Solution 5:
Let the common ratio between the sides of the given triangle be x.
Therefore, the side of the triangle will be 12x, 17x, and 25x.
Perimeter of this triangle = 540 cm
12x + 17x + 25x = 540 cm
54x = 540 cm
x = 10 cm
Sides of the triangle will be 120 cm, 170 cm, and 250 cm.
Perimeter of triangle 540 cm
s 270 cm
2 2
By Heron’s formula,
Area of triangle = s(s a)(s b)(s c)
Area of given triangle = 270 270 120 270 170 270 250 cm2
270 150100 20 cm2
9000cm2
Therefore, the area of this triangle is 9000 cm2.
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 4
Question 6:
An isosceles triangle has perimeter 30 cm and each of the equal sides is 12 cm. Find the area of
s(s a)(s b)(s c)
the triangle.
Solution 6:
Let the third side of this triangle be x.
Perimeter of triangle = 30 cm
12 cm + 12 cm + x = 30 cm
x = 6 cm
Perimeter of triangle 30 cm
s 15 cm
2 2
By Heron’s formula, Area of triangle =
Area of given triangle = 15 15 1215 1215 6 cm2
15 339 cm2
9 15 cm2
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 5
Exercise (12.2)
Question 1:
A park, in the shape of a quadrilateral ABCD, has ∠C = 90°, AB = 9 m, BC = 12 m, CD = 5 m
and AD = 8 m. How much area does it occupy?
Solution 1:
Let us join BD.
In BCD, applying Pythagoras theorem,
BD2 = BC2 + CD2
= (12)2 + (5)2
= 144 + 25
BD2 = 169
BD = 13 m
1 1
Area of BCD = BC CD 12 5 m2 30 m2
2 2
For ABD,
Perimeter (9 8 13) m
s 15 m
2 2
By Heron’s formula, Area of triangle = s(s a)(s b)(s c)
Area of ABD = 15(15 9)(15 8)(15 13) m2
15(6)(7)(2) m2
6 35 m2
(6 5.916) m2
35.496 m2
Area of the park = Area of ABD + Area of BCD
= 35.496 + 30 m2
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 6
= 65.496 m2 = 65.5 m2 (approximately).
Question 2:
Find the area of a quadrilateral ABCD in which AB = 3 cm, BC = 4 cm, CD = 4 cm, DA = 5 cm
and AC = 5 cm.
Solution 2:
For ABC,
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
(5)2 = (3)2 + (4)2
Therefore, ABC is a right-angled triangle, right-angled at point B.
1 1
Area of ABC = AB BC 3 4 6 cm2
2 2
For ADC,
Perimeter = 2s = AC + CD + DA = (5 + 4 + 5) cm = 14 cm
s = 7 cm
By Heron’s formula, Area of triangle = s(s a)(s b)(s c)
Area of ADC = 7(7 5)(7 5)(7 4) cm2
7(2)(2)(3) cm2
2 21 cm2
(2 4.583) cm2
9.166 cm2
Area of ABCD = Area of ABC + Area of ACD
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 7
= (6 + 9.166) cm2
= 15.166 cm2 = 15.2 cm2 (approximately).
Question 3:
Radha made a picture of an aeroplane with coloured papers as shown in the given figure. Find
the total area of the paper used.
Solution 3:
For triangle I
This triangle is an isosceles triangle.
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 8
Perimeter = 2s = (5 + 5 + 1) cm = 11 cm
11 cm
s 5.5 cm
2
Area of the triangle = s(s a)(s b)(s c)
5.5(5.5 5)(5.5 5)(5.5 1) cm2
5.5(0.5)(0.5)(4.5) cm2
0.75 11 cm2
(0.75 3.317) cm2
2.488 cm2 (approximately)
For quadrilateral II
This quadrilateral is a rectangle.
Area = l × b = (6.5 × 1) cm2 = 6.5 cm2
For quadrilateral III
This quadrilateral is a trapezium.
Perpendicular height of parallelogram = 12 (0.5)2 cm
0.75 cm 0.866 cm
Area = Area of parallelogram + Area of equilateral triangle
3 2
(0.866)1 (1)
4
= 0.866 + 0.433 = 1.299 cm2
Area of triangle (IV) = Area of triangle in (V)
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 9
1
1.5 6 cm2 = 4.5 cm2
2
Total area of the paper used = 2.488 + 6.5 + 1.299 + 4.5 × 2
= 19.287 cm2
Question 4:
A triangle and a parallelogram have the same base and the same area. If the sides of triangle are
26 cm, 28 cm and 30 cm, and the parallelogram stands on the base 28 cm, find the height of the
parallelogram.
Solution 4:
Perimeter of triangle = (26 + 28 + 30) cm = 84 cm
2s = 84 cm
s = 42 cm
By Heron’s formula, Area of triangle = s(s a)(s b)(s c)
Area of given triangle 42(42 26)(42 28)(42 30) cm2
42(16)(14)(12) cm2 = 336 cm2
Let the height of the parallelogram be h.
Area of parallelogram = Area of triangle
h × 28 cm = 336 cm2
h = 12 cm
Therefore, the height of the parallelogram is 12 cm.
Question 5:
A rhombus shaped field has green grass for 18 cows to graze. If each side of the rhombus is 30 m
and its longer diagonal is 48 m, how much area of grass field will each cow be getting?
Solution 5:
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 10
Let ABCD be a rhombus-shaped field.
For BCD,
(48 30 30) m
Semi-perimeter, s = 54 m
2
By Heron’s formula, Area of triangle = s(s a)(s b)(s c)
Therefore, area of BCD 54(54 48)(54 30)(54 30) m2
54(6)(24)(24) 3 6 24 432 m2
Area of field = 2 × Area of BCD
= (2 × 432) m2 = 864 m2
864
Area for grazing for 1 cow = = 48 m2
18
Each cow will get 48 m2 area of grass field.
Question 6:
An umbrella is made by stitching 10 triangular pieces of cloth of two different colours (see the
given figure), each piece measuring 20 cm, 50 cm and 50 cm. How much cloth of each colour is
required for the umbrella?
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 11
Solution 6:
For each triangular piece,
(20 50 50) cm
Semi-perimeter, s 60 cm
2
By Heron’s formula,
Area of triangle = s(s a)(s b)(s c)
Area of each triangular piece = 60(60 50)(60 50)(60 20) cm2
60(10)(10)(40) 200 6 cm2
Since there are 5 triangular pieces made of two different coloured cloths,
Area of each cloth required (5 200 6) cm2 -1000√6 cm2
Question 7:
A kite in the shape of a square with a diagonal 32 cm and an isosceles triangles of base 8 cm and
sides 6 cm each is to be made of three different shades as shown in the given figure. How much
paper of each shade has been used in it?
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 12
Solution 7:
We know that
1
Area of square (diagonal)2
2
1
Area of the given kite (32 cm2 ) 512 cm2
2
Area of 1st shade = Area of 2nd shade
512 cm2
256 cm2
2
Therefore, the area of paper required in each shape is 256 cm2.
For IIIrd triangle
(6 6 8) cm
Semi-perimeter, s 10 cm
2
By Heron’s formula,
Area of triangle = s(s a)(s b)(s c)
Area of IIIrd triangle 10(10 6)(10 6)(10 8) cm2
10(4)(4)(2) (4 2 5) cm2
8 5 cm2
(8 2.24) cm2
17.92 cm2
Area of paper required for IIIrd shade = 17.92 cm2
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 13
Question 8:
A floral design on a floor is made up of 16 tiles which are triangular, the sides of the triangle
being 9 cm, 28 cm and 35 cm (see the given figure). Find the cost of polishing the tiles at the rate
of 50p per cm2.
Solution 8:
It can be observed that
(35 28 9) cm
Semi-perimeter of each triangular-shaped tile, s 36 cm
2
By Heron’s formula,
Area of triangle = s(s a)(s b)(s c)
Area of each tile 36(36 35)(36 28)(36 9) cm2
36(1)(8)(27) 36 6 cm2
= (36 × 2.45) cm2
= 88.2 cm2
Area of 16 tiles = (16 × 88.2) cm2= 1411.2 cm2
Cost of polishing per cm2 area = 50 p
Cost of polishing 1411.2 cm2 area = Rs. (1411.2 × 0.50) = Rs. 705.60
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 14
Therefore, it will cost Rs. 705.60 while polishing all the tiles.
Question 9:
A field is in the shape of a trapezium whose parallel sides are 25 m and 10 m. The non-parallel
sides are 14 m and 13 m. Find the area of the field.
Solution 9:
Draw a line BE parallel to AD and draw a perpendicular BF on CD.
It can be observed that ABED is a parallelogram.
BE = AD = 13 m
ED = AB = 10 m
EC = 25 − ED = 15 m
For BEC,
(13 14 15) m
Semi-perimeter, s 21 m
2
By Heron’s formula, Area of triangle = s(s a)(s b)(s c)
Area of BEC 21(21 13)(21 14)(2115) m2
21(8)(7)(6) m2 = 84 m2
1
Area of BEC = CE BF
2
168
BF 11.2 m
15
Area of ABED = BF × DE = 11.2 × 10 = 112 m2
Area of the field = 84 + 112 = 196 m2
12. Heron's Formula www.vedantu.com 15
Thank You
for downloading the PDF
FREE LIVE ONLINE
MASTER CLASSES
FREE Webinars by Expert Teachers
FREE MASTER CLASS SERIES
For Grades 6-12th targeting JEE, CBSE, ICSE & much more Register for FREE
Free 60 Minutes Live Interactive classes everyday
Learn from the Master Teachers - India’s best Limited Seats!
You might also like
- Math 12 ImpDocument109 pagesMath 12 ImpAkhshitaa CastellanNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument27 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SerieskaruneshnNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document32 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Ladukishore RathNo ratings yet
- The Stright LineDocument184 pagesThe Stright LineRamNagalNo ratings yet
- Mensuration TanmayDocument32 pagesMensuration TanmayTanishk MahereNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument41 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SeriesNeha MishraNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument28 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SerieskaruneshnNo ratings yet
- 10th - 2013 Exam PaperDocument27 pages10th - 2013 Exam PaperRani PranavNo ratings yet
- 5cee27be8f0817f983b8d6ee 5e9a09869e955c217f32760d 1587579041269Document23 pages5cee27be8f0817f983b8d6ee 5e9a09869e955c217f32760d 1587579041269urout783No ratings yet
- Maths Class VII Practice Test 03 Chapter 10 Perimeter and Area AnswersDocument6 pagesMaths Class VII Practice Test 03 Chapter 10 Perimeter and Area AnswersNeelamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Surface Areas and VolumesDocument105 pagesChapter 13 Surface Areas and VolumesNitish MehraNo ratings yet
- Maths Sample PaperDocument8 pagesMaths Sample PaperComedy WorldNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument29 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SeriesRohan ChandraNo ratings yet
- Maths 2013Document28 pagesMaths 2013Sahl H JamsheerNo ratings yet
- Math 2017 PDFDocument28 pagesMath 2017 PDFAVULSION RAJNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Downloaded From VedantuDocument28 pagesStudy Material: Downloaded From VedantuAneesha priyadarshiniNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument11 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SeriesJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Downloaded From VedantuDocument59 pagesStudy Material: Downloaded From VedantuRahul SaravananNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 10Document32 pagesChemistry Class 10Saran MohanNo ratings yet
- 2022 10 SP Maths S 04Document11 pages2022 10 SP Maths S 04John DoeNo ratings yet
- 7 Math Comparing QuantitiesDocument16 pages7 Math Comparing QuantitiesikramNo ratings yet
- Herons Formula for Calculating Areas of TrianglesDocument12 pagesHerons Formula for Calculating Areas of TrianglesComedy Zone of swasNo ratings yet
- Math 2014Document34 pagesMath 2014Sahl H JamsheerNo ratings yet
- CBSE Mathematics 2017 Board QuestionsDocument6 pagesCBSE Mathematics 2017 Board QuestionsHeena Maqsood AhmadNo ratings yet
- M Quadratic EquationsDocument73 pagesM Quadratic EquationsPoonthalirNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument21 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class Seriesparamarthasom1974No ratings yet
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument27 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SerieskaruneshnNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument62 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SeriessarojsainiNo ratings yet
- Crash Course: ProgramDocument42 pagesCrash Course: ProgramAkshit SinghNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 - MensurationDocument16 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 11 - Mensurationsanjay marumudiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 10.1 Page No: 212Document14 pagesExercise 10.1 Page No: 212Mask Man LifeNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 9 Perimeter & AreaDocument124 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 9 Perimeter & Areaat2lk22No ratings yet
- Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocument61 pagesLinear Equations in Two VariablesNoel SabuNo ratings yet
- SSC Maths Quiz for Mixed Quant QuestionsDocument10 pagesSSC Maths Quiz for Mixed Quant QuestionsTarun PandeyNo ratings yet
- Heron's Formula for Calculating Areas of Triangles and Other ShapesDocument21 pagesHeron's Formula for Calculating Areas of Triangles and Other ShapesRishabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- M2015 PDFDocument28 pagesM2015 PDFSahl H JamsheerNo ratings yet
- SMT - Sridevi Awasiyavidyapeeth: Q-1 Tick The Correct OptionsDocument2 pagesSMT - Sridevi Awasiyavidyapeeth: Q-1 Tick The Correct OptionsAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Volume and Surface Area Question BankDocument105 pagesVolume and Surface Area Question BankRathna ChalamNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Downloaded From VedantuDocument35 pagesStudy Material: Downloaded From VedantuElon Tesla MuskyashNo ratings yet
- Last Year Paper Mains (2019)Document52 pagesLast Year Paper Mains (2019)Shyamalavannan Tom100% (1)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 MensurationDocument22 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 MensurationRåvî RøyNo ratings yet
- Vibrant Academy Mathematics Class IX Full Course TestDocument5 pagesVibrant Academy Mathematics Class IX Full Course TestANGAD YADAVNo ratings yet
- HCV SolutionsDocument18 pagesHCV SolutionsKunal LuniaNo ratings yet
- Class IX Chapter 12 - Heron's Formula Maths: Exercise 12.1 Question 1Document21 pagesClass IX Chapter 12 - Heron's Formula Maths: Exercise 12.1 Question 1DurgeshNo ratings yet
- Heron's Formula Maths Area ProblemsDocument21 pagesHeron's Formula Maths Area ProblemsAshokNo ratings yet
- WWW - Bankingcareers.In Jobs Help Free EbookDocument32 pagesWWW - Bankingcareers.In Jobs Help Free EbookMadhan Karthik PrakashNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Q PDFDocument44 pagesPolynomial Q PDFnareshganeshNo ratings yet
- Study Material Downloaded from VedantuDocument26 pagesStudy Material Downloaded from VedantuRahul BoruahNo ratings yet
- Mensuration PDFDocument19 pagesMensuration PDFRakesh PradhanNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument28 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SerieskaruneshnNo ratings yet
- Eron S Ormula: WWW - Tiwariacademy. inDocument3 pagesEron S Ormula: WWW - Tiwariacademy. inSunny BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument22 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SeriesPratham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation in One Variable Important QuestionsDocument13 pagesLinear Equation in One Variable Important QuestionsSujay BharadhwajNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Area of A Triangle - by Heron's FormulaDocument6 pages10.1 Area of A Triangle - by Heron's FormulaOm BombleNo ratings yet
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- SAT Math Level 2 Subject Test Practice Problems 2013 EditionFrom EverandSAT Math Level 2 Subject Test Practice Problems 2013 EditionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Bergen County Academies Entrance Practice Tests: Five Full-Length Math and English Essay Tests with Detailed Answer ExplanationsFrom EverandBergen County Academies Entrance Practice Tests: Five Full-Length Math and English Essay Tests with Detailed Answer ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 5No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Division Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesDivision Lesson Plan000768311No ratings yet
- Shana Tova From BBYO!Document2 pagesShana Tova From BBYO!Bbyo TzevetNo ratings yet
- Filipino ChemistDocument2 pagesFilipino ChemistcutefeiNo ratings yet
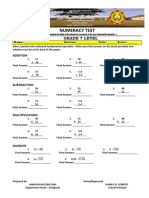
- Numeracy TestDocument5 pagesNumeracy Testrex arnold irincoNo ratings yet
- 2.abstract AcknowledgementDocument3 pages2.abstract AcknowledgementGene Narune GaronitaNo ratings yet
- Dualtech Training Center Presentation RVSADocument17 pagesDualtech Training Center Presentation RVSADennis SalongaNo ratings yet
- What Are Phrasal Verbs?: TypesDocument2 pagesWhat Are Phrasal Verbs?: TypesHeidy Teresa MoralesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan WorksheetDocument4 pagesLesson Plan WorksheetMichael UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Panel FormatDocument22 pagesPanel FormatbalakaleesNo ratings yet
- Quick and Helpful Advice Intended For Doing Better in CollegeDocument2 pagesQuick and Helpful Advice Intended For Doing Better in CollegeWiggins41DuelundNo ratings yet
- Codes StandardsDocument3 pagesCodes Standardsakshaf10No ratings yet
- MatchingDocument8 pagesMatchingJeon KookieNo ratings yet
- Rucha Joshi CV 6 July 2023 RVJSTDocument11 pagesRucha Joshi CV 6 July 2023 RVJSTapi-266430454No ratings yet
- 2021 2022 Spring HRM Assessment Brief 5Document6 pages2021 2022 Spring HRM Assessment Brief 5TrangNo ratings yet
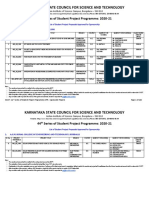
- 44S SPP Sanctioned Projects ListDocument240 pages44S SPP Sanctioned Projects ListM. Sadiq. A. PachapuriNo ratings yet
- Solving Math Problems Step-by-StepDocument7 pagesSolving Math Problems Step-by-StepnopriansyahNo ratings yet
- BHU - The School For ScandalDocument2 pagesBHU - The School For ScandalPeoples' Vigilance Committee on Human rightsNo ratings yet
- Deming 14 Point Almost DoneDocument13 pagesDeming 14 Point Almost DoneAda Ler100% (1)
- Services Marketing - A Practical Approach - Unit 6 - Week 4Document5 pagesServices Marketing - A Practical Approach - Unit 6 - Week 4Sapna RaiNo ratings yet
- Clothing - Female - Stays - English & AmericanDocument220 pagesClothing - Female - Stays - English & AmericanThe 18th Century Material Culture Resource Center100% (28)
- Item-Based Collaborative Filtering Recommendation AlgorithmsDocument11 pagesItem-Based Collaborative Filtering Recommendation AlgorithmsMirna MilicNo ratings yet
- The Delighted Customer Experience Maturity AssessmentDocument16 pagesThe Delighted Customer Experience Maturity AssessmentFadi Zaid AlkilaniNo ratings yet
- Class Activities For Teaching Speaking, Listening and ReadingDocument6 pagesClass Activities For Teaching Speaking, Listening and ReadingPablo CastroNo ratings yet
- Training and Development Program On Banking Sector Comparative Analysis Between DBBL & BRAC Bank LTDDocument8 pagesTraining and Development Program On Banking Sector Comparative Analysis Between DBBL & BRAC Bank LTDSharifMahmudNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Industrial and Organizational PsychologyDocument4 pagesReviewer in Industrial and Organizational PsychologyAirra May MedranoNo ratings yet
- Rosa ResumeDocument2 pagesRosa Resumeapi-402940629No ratings yet
- 03 Goal-Use Analysis Worksheet-V2.0 (Excel)Document8 pages03 Goal-Use Analysis Worksheet-V2.0 (Excel)Alfredo FloresNo ratings yet
- Httpsinfoday - Cuhk.edu - hkstoragefilesCUHK Infoday Booklet Output 20220930 PDFDocument15 pagesHttpsinfoday - Cuhk.edu - hkstoragefilesCUHK Infoday Booklet Output 20220930 PDFIP TSZ KIU 葉芷翹 5A 7No ratings yet
- Tuition Fee UPH Graduate Admissions Intake August 2022 - MMDocument1 pageTuition Fee UPH Graduate Admissions Intake August 2022 - MMRini WulandariNo ratings yet
- Communication Comprehension CheckDocument27 pagesCommunication Comprehension CheckMonica MarticioNo ratings yet