Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Paediatirc Assessment Guide
Uploaded by
nipoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Paediatirc Assessment Guide
Uploaded by
nipoCopyright:
Available Formats
EXCELSIOR COMMUNITY COLLEGE
FACULTY OF PURE AND APPLIED SCIENCES
SCHOOL OF NURSING
NURS 4011 Nursing Care of Children and Adolescents
Paediatric Assessment Guide
1. Guidelines for objective data
a. name of client
b. age, date of birth
c. date of admission, medical diagnosis
d. present complaint, history of present complaint, past medical, surgical history
e. allergies, immunization status
f. social, family history
g. nutrition history
h. developmental milestones, play
i. school performance (where relevant)
j. obstetric history (for all clients 1 year and below, any client for which it is important)
k. physical examination
2. Health Promotion
a. safety (accident/injury protection)
b. nutrition
c. health management (for example- care of teeth, exercise, sleep)
d. immunization
3. Safety precautions by age group (areas to be included in age specific health promotion teaching)
a. Infants - Aspiration, Falls, Poisoning, Burns, Suffocation
b. Toddler - Burns, Poisoning, Drowning, Aspiration, Falls, Motor Vehicles
c. PreSchool Age - Community Safety, Poisoning, Falls, Motor Vehicles, Falls, Burns
d. School Age - Community Safety, Burns, Sports Injuries, Firearms, Drugs, Drowning
e. Adolescents- Motor vehicles, Firearms, Drowning, Sports
4. Psychosocial stages of development-Eric Erickson
a. Infant – 0-1yr Trust vs. Mistrust
b. Toddler - 1-3yrs Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
c. Preschooler - 3-5yrs Initiative vs. Guilt
d. School-age – 6-12yrs Industry vs. Inferiority
e. Adolescent – 13-18yrs Identity vs. Role Confusion
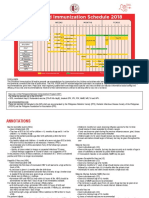
5. Immunization schedule
a. Birth to six weeks: BCG
b. Six weeks: IPV and DPT/Hep B/HIB (Pentavalent)
c. Three months: OPV and DPT/Hep B/HIB (Pentavalent)
d. Six months: OPV and DPT/Hep B/HIB (Pentavalent)
e. Twelve months: MMR
f. Eighteen months: OPV, DPT and MMR booster
g. Booster: DPT
Adapted from UWISON –USED WITH PERMISSION
For entry to Nursery and Basic School all the above vaccines are necessary
h. Four to six years: OPV and DPT booster
i. Booster: DT (over age 11years)
For entry to Primary School all the above vaccines are necessary
6. Paediatric parameters *
Pulse rate Respiratory Haemoglobin Glucose
Newborn: 70-170 (120) Newborn : 40-90 Term: 16.5 g/dL FPG < 5.6 mmol/L
1-11mnths: 80-160 (120) 1 yr: 20-40 I month: 13.9 g/dL PM < 7.8 mmol/L
2 yrs: 80-130 (110) 2 to 3 yrs: 20-30 2 months: 11.2g/dL
4yrs: 80-120 (100) 5 yrs : 20-25 6 months: 12.6g/dL
6 yrs : 75-115 (100) 10 yrs : 17-22 6-24 months: 12g/dL
8yrs: 70-110 (90) 2-6yrs: 12.5g/dL
10 yrs: 70-100 (90) 6-12yrs: 13.5g/dL
Anterior fontanel closes -18 months, Posterior fontanel -2-3months
7. Cerebrospinal fluid ranges*
Glucose Protein White blood cells
preterm 1.3-3.5mmol/L 0.65-1.50g/dl 0-25 WBC × 106 cells/L
term 1.9-6.6mmol/L 0.20-1.70g/dl 0-22 WBC × 106 cells/L
child 2.4-4.4mmol/L 0.05-0.40g/dl 0-7 WBC × 106 cells/L
8. Major Developmental milestones by age group**
Infant Toddler Preschooler
Rolls over Walks up and down stairs Uses scissors
Sits up Undresses self Rides bicycle with training
Stands Scribbles on paper wheels
Able to say 1 or 2 words Kicks a ball Throws a ball
Uses pincer grasp well Has a vocabulary of 1,000 Holds a bat
words – uses short sentences Writes a few letters
All parts of speech are well-
developed
School-age Adolescents
Possesses reading ability Fine motor skills well-
Rides a two-wheeled bike developed
Jumps rope Gross motor skills improve due
Plays organized sports to growth spurts
Mature use of language Able to apply abstract
thought and analysis
Adapted from UWISON –USED WITH PERMISSION
Adapted from UWISON –USED WITH PERMISSION
You might also like
- History - Hood Leddy & PepperDocument41 pagesHistory - Hood Leddy & PeppernipoNo ratings yet
- 3a Introduction To Drug TherapyDocument69 pages3a Introduction To Drug TherapynipoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory Systemparitosh7_886026No ratings yet
- Seizure Disorder, Spinal Injury Neural TumorDocument52 pagesSeizure Disorder, Spinal Injury Neural TumornipoNo ratings yet
- Heart and Neck VesselsDocument129 pagesHeart and Neck VesselsnipoNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Endocrine SystemDocument88 pagesDisorders of The Endocrine SystemnipoNo ratings yet
- Needs Approach 1. Oxygen (Respiratory & Cardiovascular)Document2 pagesNeeds Approach 1. Oxygen (Respiratory & Cardiovascular)nipoNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Endocrine SystemDocument88 pagesDisorders of The Endocrine SystemnipoNo ratings yet
- PregnancyDocument4 pagesPregnancynipoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Disorders GuideDocument100 pagesNervous System Disorders GuidenipoNo ratings yet
- Pricing Strategies: Additional Considerations (Chapter 11) : Lecture #11 Lecturer: Donna-Kay Smith Date: June 29, 2016Document36 pagesPricing Strategies: Additional Considerations (Chapter 11) : Lecture #11 Lecturer: Donna-Kay Smith Date: June 29, 2016nipoNo ratings yet
- Pricing Strategies: Additional Considerations (Chapter 11) : Lecture #11 Lecturer: Donna-Kay Smith Date: June 29, 2016Document36 pagesPricing Strategies: Additional Considerations (Chapter 11) : Lecture #11 Lecturer: Donna-Kay Smith Date: June 29, 2016nipoNo ratings yet
- 2 DRUG DOSAGE FORMS New - Lec 2Document18 pages2 DRUG DOSAGE FORMS New - Lec 2nipoNo ratings yet
- Nurs4015 Theory RosterDocument1 pageNurs4015 Theory RosternipoNo ratings yet
- Peds CarplanDocument10 pagesPeds CarplannipoNo ratings yet
- Analyzing The Marketing Environment (Chapter 3) : Lecture #3 Lecturer: Donna-Kay Smith Date: June 3, 2016Document39 pagesAnalyzing The Marketing Environment (Chapter 3) : Lecture #3 Lecturer: Donna-Kay Smith Date: June 3, 2016nipoNo ratings yet
- Business Markets & Business Buyer Behaviour (Chapter 6) : Lecture #6 Lecturer: Donna-Kay Smith Date: June 10, 2016Document26 pagesBusiness Markets & Business Buyer Behaviour (Chapter 6) : Lecture #6 Lecturer: Donna-Kay Smith Date: June 10, 2016nipoNo ratings yet
- 2016.06.3 - Lecture 3 - Principles of Marketing - Chapter 3Document39 pages2016.06.3 - Lecture 3 - Principles of Marketing - Chapter 3nipoNo ratings yet
- 01 NursingPharmacologyDocument171 pages01 NursingPharmacologynipoNo ratings yet
- New Product Development & Product Life-Cycle Strategies (Chapter 9)Document42 pagesNew Product Development & Product Life-Cycle Strategies (Chapter 9)nipoNo ratings yet
- 2016.06.01 - Lecture 2 - Summer School Principles of Marketing - Chapter 2Document28 pages2016.06.01 - Lecture 2 - Summer School Principles of Marketing - Chapter 2nipoNo ratings yet
- Building Customer Value Through Products, Services & BrandsDocument44 pagesBuilding Customer Value Through Products, Services & BrandsnipoNo ratings yet
- STRATEGIC PLANNING MULTIPLE CHOICEDocument30 pagesSTRATEGIC PLANNING MULTIPLE CHOICEnipoNo ratings yet
- 2 Drug Dosage Forms New - Lec 2Document18 pages2 Drug Dosage Forms New - Lec 2nipoNo ratings yet
- 1125Document7 pages1125aldiansyahraufNo ratings yet
- 2016.06.14 - Lecture 7 - Principles of Marketing - Chapter 7Document40 pages2016.06.14 - Lecture 7 - Principles of Marketing - Chapter 7nipoNo ratings yet
- Drugs That Affect The Urinary System: NURS 1950: PharmacologyDocument96 pagesDrugs That Affect The Urinary System: NURS 1950: PharmacologynipoNo ratings yet
- 2016.06.01 - Lecture 2 - Summer School Principles of Marketing - Chapter 2Document28 pages2016.06.01 - Lecture 2 - Summer School Principles of Marketing - Chapter 2nipoNo ratings yet
- Anemia-1Document35 pagesAnemia-1nipoNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- IB rHIVda PDFDocument7 pagesIB rHIVda PDFMark CervantesNo ratings yet
- Media Preparation, Isolation of Pure Culture and Bacterial GrowthDocument6 pagesMedia Preparation, Isolation of Pure Culture and Bacterial Growthhamody662002No ratings yet
- CDC Guide to Toxoplasmosis BiologyDocument2 pagesCDC Guide to Toxoplasmosis BiologyReynalth Andrew SinagaNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous TBDocument45 pagesCutaneous TBWarren Lie100% (1)
- The Anti Vaccine MovementDocument13 pagesThe Anti Vaccine MovementMariangeles PontorieroNo ratings yet
- Progress of Polio Eradication in NepalDocument49 pagesProgress of Polio Eradication in NepaladkrsauravNo ratings yet
- Vitality Atlas 3.3 FINALDocument10 pagesVitality Atlas 3.3 FINALJakarta ClinicNo ratings yet
- Digital IDs Drive Development AccessDocument3 pagesDigital IDs Drive Development AccessraymartNo ratings yet
- Preventive Veterinary MedicineDocument48 pagesPreventive Veterinary MedicineBorja Bueno Garcia100% (3)
- DRUG STUDY: Rocephin - Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY: Rocephin - Ceftriaxone SodiumYum C100% (1)
- History of Influenza Pandemics by Bruno LinaDocument13 pagesHistory of Influenza Pandemics by Bruno LinasirjsslutNo ratings yet
- Arellano University College of Nursing Legarda - Pasay - PasigDocument3 pagesArellano University College of Nursing Legarda - Pasay - PasigCharles Loriaga Cruz IINo ratings yet
- Tools Used in Community Diagnosis Demographyvital and Health Statistics EpidemiologyDocument41 pagesTools Used in Community Diagnosis Demographyvital and Health Statistics EpidemiologyFatmaIbrahim100% (1)
- Gram Positive Bacteria of Medical ImportanceDocument12 pagesGram Positive Bacteria of Medical ImportanceGeorge C. KasondaNo ratings yet
- Nutri Quiz2Document6 pagesNutri Quiz2Rosa Lynn YaunNo ratings yet
- TORCH Test Safety Data SheetDocument11 pagesTORCH Test Safety Data SheetLucian MihuNo ratings yet
- Velocity Health FormDocument2 pagesVelocity Health FormChris HansenNo ratings yet
- Adult HIV Notes On GuidelinesDocument423 pagesAdult HIV Notes On GuidelinesJokerNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Vs Viruses PPT 2019Document25 pagesBacteria Vs Viruses PPT 2019Rene Ramilo100% (1)
- Signs & Symptoms of Strep B in InfantsDocument59 pagesSigns & Symptoms of Strep B in InfantsAbdul Ghaffar AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Borregopedia 01Document82 pagesBorregopedia 01Lee Kyung Hee0% (1)
- IEL / ETM Case Study Series: Xeno Mouse Patent Portfolio AnalysisDocument83 pagesIEL / ETM Case Study Series: Xeno Mouse Patent Portfolio AnalysisGunaseelan RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Factsheet: Tacrolimus Ointment (Protopic®)Document4 pagesFactsheet: Tacrolimus Ointment (Protopic®)Ivan LinNo ratings yet
- Cis 2018 PDFDocument3 pagesCis 2018 PDFTara Oliveros Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- FilariasisDocument2 pagesFilariasismariaNo ratings yet
- Quarantine and Isolation GuidelinesDocument1 pageQuarantine and Isolation GuidelinesGlendaNo ratings yet
- Ifu PDFDocument33 pagesIfu PDFCeline LingNo ratings yet
- Saifur Rahman Sabbir Tika Card - Masum BestDocument1 pageSaifur Rahman Sabbir Tika Card - Masum BestTowhidul Azam BabuNo ratings yet
- Needlestick and Sharps Injuries in Diabetes: R U FIT4Safety?Document8 pagesNeedlestick and Sharps Injuries in Diabetes: R U FIT4Safety?yusuf BakhtiarNo ratings yet
- The Immune SystemDocument19 pagesThe Immune Systemmay esteban100% (2)