Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Proximal Convoluted Tubule 65
Uploaded by
Lance Jardiolin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageProximal Convoluted Tubule
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProximal Convoluted Tubule
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageProximal Convoluted Tubule 65
Uploaded by
Lance JardiolinProximal Convoluted Tubule
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Proximal Convoluted Tubule 65%
o Primary site for reabsorption of solutes and water
o Cuboidal cells with numerous microvilli and mitochondria
o Well adapted to transport molecules and ions across the nephron wall by active
transport and cotransport
o Substances transported are:
Proteins
Amino acids
Glucose
Fructose
Na, K, Ca, HCO3, Cl
o Permeable to water
As solute molecules are transported out of the proximal convoluted tubule into
the interstitial fluid, water moves by osmosis in the same direction
These solutes and water then enter the peritubular capillaries
Descending Limb of the Loop of Henle 15%
o Critical site for water reabsorption
o The walls are highly permeable to water
As filtrate moves through the medulla containing highly concentrated interstitial
fluid, water moves out of the nephron by osmosis
Ascending Limb of the Loop of Henle
o Dilutes the filtrate by removing solutes
o Thin segment
Not permeable to water
Permeable to solutes
o Thick segment
Actively transport Na out of the nephron
K and Cl are cotransported with Na
Not permeable to water
Distal Convoluted Tubule 19%
o Filtrate is more dilute than the interstitial fluid
o Only 20% of the original filtrate volume remains
o Removes water and additional solutes from the filtrate
o Na and Cl are the principal reabsorbed solutes
Sodium ions are actively transported out of the filtrate
Chloride ions are cotransported out of the filtrate with Na
o The osmosis of water accounts for the reabsorption of 19% of the original filtrate
volume
1% is then left
You might also like
- Functions of Body FluidsDocument6 pagesFunctions of Body FluidsLance JardiolinNo ratings yet
- Life and Works ofDocument26 pagesLife and Works ofLance JardiolinNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Case Study On Malignant MelanomaDocument7 pagesGroup 4 Case Study On Malignant MelanomaLance JardiolinNo ratings yet
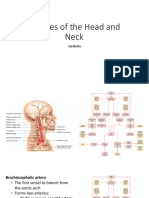
- Arteries of The Head and NeckDocument5 pagesArteries of The Head and NeckLance JardiolinNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Group 2 Written ReportDocument23 pagesAnaPhy Group 2 Written ReportLance JardiolinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Man As Embodied SubjectDocument25 pagesLecture 3 Man As Embodied SubjectLance JardiolinNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Group 2 Written ReportDocument23 pagesAnaPhy Group 2 Written ReportLance JardiolinNo ratings yet
- RA 9163 National Service Training ProgramDocument5 pagesRA 9163 National Service Training ProgramLance JardiolinNo ratings yet
- Activity 1, 2, 3Document3 pagesActivity 1, 2, 3Lance JardiolinNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)