Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Finafloxacin
Uploaded by
Rizky Amelia Kusuma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pageskhgkh
Original Title
finafloxacin
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentkhgkh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesFinafloxacin
Uploaded by
Rizky Amelia Kusumakhgkh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Features and properties of finafloxacin Alternative names BY 377; BY-377; finafloxacin
hydrochloride; gastrochinolon; gastroquinolone; XtoroTM Class Fluoroquinolone, small-
molecule Mechanism of action DNA gyrase inhibitor; DNA topoisomerase IV inhibitor
Route of administration Topical, oral, intravenous Antimicrobial activity Antimicrobial
activity enhanced in acidic versus neutral conditions against multiple species, including skin
and urinary pathogens. Superior antibacterial activity to that of other fluoroquinolones in
acidic conditions (pH 5.8) against multiple species. Longer post-antibacterial effect than
other fluoroquinolones under acidic conditions against multiple species. Resistance is less
likely in acidic than neutral conditions Pharmacodynamics Highly selective for bacterial type
II topoisomerases (i.e. DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV); broad spectrum of antibacterial
activity Pharmacokinetics After repeated topical administration (finafloxacin otic suspension
0.3 %, 4 drops each ear for 7 days), quantifiable plasma concentrations were observed in 2 of
36 healthy subjects. After oral administration, the drug is well absorbed, reaching peak
plasma levels in just under 1 h Adverse events Occasional (topical) Ear pruritus, nausea
Occasional (oral and intravenous) Diarrhoea, nausea, fatigue, headache, injection site
reactions, musculoskeletal disorders ATC codes WHO ATC code A02B-X (Other drugs for
peptic ulcer and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease), J01 M-A (Fluoroquinolones), S02A
(Anti-infectives) EphMRA ATC code A2B9 (all other anti-ulcerants), J1G1 (oral
fluoroquinolones), J1G2 (injectable fluoroquinolones), S2A (otic anti-infectives) Chemical
name (-)-8-Cyano-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-((4aS,7aS)-hexahydropyrrolo(3,4-b)-1,4-oxazin-
6(2H)-yl)- 4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid
https://sci-hub.se/10.1007/s40265-015-0384-z
Pharmacokinetics Plasma pharmacokinetics of finafloxacin was analyzed after orally
administered single doses of 25, 50, 100, 200, 400 and 800 mg. The Cmax values were: 0.24,
0.44 ± 0.16, 1.32 ± 0.62, 1.90 ± 0.73, 5.06 ± 2.09 and 11.1 ± 2.96 mg/L, respectively.
The half life-time of finafloxacin in single dose administration were as follows: 1.28,
3.8 ± 2.7, 7.2 ± 3.2, 4.6 ± 1.9, 10.0 ± 4.4 and 10.5 ± 2.2 h, respectively. The time to reach the
Cmax varied between 0.5 and 1 h. In the case of multiple doses of 150, 300, 600 and 800 mg
were administered orally once daily for seven consecutive days. The Cmax after the seventh
day showed the following concentrations: 1.50 ± 0.52, 4.15 ± 2.11, 6.76 ± 2.2 and
8.95 ± 3.11 mg/L. The corresponding halflife time was 5.3 ± 0.6, 6.5 ± 2.5, 8.8 ± 3.1 and
14 ± 5.5 h, respectively. While time to reach Cmax was between 0.5 and 1.5 h [19].
Accumulation of finafloxacin was not relevant following daily once application of doses up
to 800 mg over 7 days. Peak serum concentrations may slightly increase proportionally
compared to dose [19]. The urine recovery data show that around 30 % of oral dose can be
detected. Moreover, the urine finafloxacin concentration exceeds MIC values determined in
Mueller–Hinton broth for many pathogens of urinary tract infections e.g.,: E. coli and P.
aeruginosa. This feature makes it advantageous in treatment of several urinary tract infections
[21, 22]. The mean concentration of finafloxacin in urine was 68 mg/L in the first 4 h and
4 mg/L at the time of 12–24 h sampling following 200 mg dose. In the case of the 800 mg
dose the mean finafloxacin concentration was 112 mg/L in the first 4 h (peak of 150 mg/L
was reached in the 4–8 h interval) and 18 mg/L in the 12–24 h sampling period [23].
Bismillah hayuukk
https://www.merlionpharma.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/F1-2036_Wohlert.pdf
https://www.merlionpharma.com/news-publications/presentations-and-posters/
10.1128/AAC.00082-17
formula :
https://patents.google.com/patent/US8536167B2/en
sintetis
https://sci-hub.tw/10.1021/op100229b
You might also like
- FORM REVIEW - Jurnal VENESYADocument6 pagesFORM REVIEW - Jurnal VENESYARizky Amelia KusumaNo ratings yet
- Hammars Trom 1975Document5 pagesHammars Trom 1975Rizky Amelia KusumaNo ratings yet
- Water-Cyclohexane-"Span 80"-"Tween 80" Systems: Solution Properties and Water/Oil Emulsion FormationDocument12 pagesWater-Cyclohexane-"Span 80"-"Tween 80" Systems: Solution Properties and Water/Oil Emulsion FormationRizky Amelia KusumaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Evaluasi Penggunaan Obat "Drug Utilization Evaluation of Anti Epileptics Used in Guntur City Hospital"Document8 pagesTugas Evaluasi Penggunaan Obat "Drug Utilization Evaluation of Anti Epileptics Used in Guntur City Hospital"siti fatmahNo ratings yet
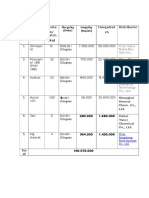
- No. Bahan Jumla H/ Batch (KG) Harga/kg (Dolar) Harga/kg (Rupiah) Harga/bat CH DistributorDocument10 pagesNo. Bahan Jumla H/ Batch (KG) Harga/kg (Dolar) Harga/kg (Rupiah) Harga/bat CH DistributorRizky Amelia KusumaNo ratings yet
- Data PreDocument11 pagesData PreRizky Amelia KusumaNo ratings yet
- BcsDocument10 pagesBcsRizky Amelia KusumaNo ratings yet
- No. Bahan Jumlah/batch (KG) Harga/kg Harga/batch DistributorDocument7 pagesNo. Bahan Jumlah/batch (KG) Harga/kg Harga/batch DistributorRizky Amelia KusumaNo ratings yet
- Us 8697122Document9 pagesUs 8697122Rizky Amelia KusumaNo ratings yet
- Abdul Karim - 2Document8 pagesAbdul Karim - 2Yuliet SusantoNo ratings yet
- No Bahasa Inggris Artinya: Behind DibelakangDocument6 pagesNo Bahasa Inggris Artinya: Behind DibelakangSandyNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- P 398Document1 pageP 398Arup Ratan PaulNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument24 pagesNotesriann leigh TrangiaNo ratings yet
- Extravasations DiagramDocument1 pageExtravasations DiagramJohnNo ratings yet
- Vasquez, Julianne Gabrielle G. Pharmacology BSN 2-A-7 Course Task #1Document6 pagesVasquez, Julianne Gabrielle G. Pharmacology BSN 2-A-7 Course Task #1PagodNo ratings yet
- Clin Experimental Derm - 2021 - Pradhan - Treatment Options For LeishmaniasisDocument6 pagesClin Experimental Derm - 2021 - Pradhan - Treatment Options For LeishmaniasisVOOGLS PUBLICATIONNo ratings yet
- On W.D Ross and His Ethics of DutyDocument2 pagesOn W.D Ross and His Ethics of DutyAbegail Ada QuiselNo ratings yet
- Notes On Cdi 7 Drug Education and Vice ControlDocument11 pagesNotes On Cdi 7 Drug Education and Vice ControlDr.MontañoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper VIII - Elective Pharmaceutical Chemistry: SyllabusDocument38 pagesChemistry Paper VIII - Elective Pharmaceutical Chemistry: SyllabusC123No ratings yet
- Official Website of Pharmacy CouncilDocument1 pageOfficial Website of Pharmacy CouncilRatna DeepakNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity PcolDocument15 pagesLab Activity PcolHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Kalium DuruleDocument2 pagesDrug Study Kalium DuruleMva AgueroNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain Low RiskDocument2 pagesChest Pain Low RiskWills Consulting LLCNo ratings yet
- Audit-Carmona MedDocument2 pagesAudit-Carmona MedMa. Jennifer MapanooNo ratings yet
- 2021 Updated Pricelist of All Products of AltomedDocument98 pages2021 Updated Pricelist of All Products of Altomednoel caduaNo ratings yet
- Section 3: Vision 3.1 Vision: K'PACORA LAB INC - Pharmaceutical TechnologiesDocument9 pagesSection 3: Vision 3.1 Vision: K'PACORA LAB INC - Pharmaceutical TechnologiesAzwanie AliNo ratings yet
- Terazosin Hytrin Drug CardDocument1 pageTerazosin Hytrin Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Richard Gerster: 19-Ganesh Kale 29-Sachin Naik 39-Amol Patel 49 - Vivek SargaonkarDocument21 pagesRichard Gerster: 19-Ganesh Kale 29-Sachin Naik 39-Amol Patel 49 - Vivek SargaonkarSachin NaikNo ratings yet
- Del Rosario v. BengzonDocument7 pagesDel Rosario v. BengzonLee YuNo ratings yet
- Drug Design Training Program: Elrazi UniversityDocument3 pagesDrug Design Training Program: Elrazi UniversityTalal Ahmed Awad MohammedNo ratings yet
- FDA AcetominofenDocument2 pagesFDA AcetominofensindirdekNo ratings yet
- Aspen Guidelines Parenteral NutritionDocument34 pagesAspen Guidelines Parenteral NutritionKamilo ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- PINK PACOP PHARM CALCULATIONS Answer KeyDocument32 pagesPINK PACOP PHARM CALCULATIONS Answer Keyesther samonteNo ratings yet
- MKT 6080 Final Project Milestone 2 WorksheetDocument12 pagesMKT 6080 Final Project Milestone 2 WorksheetDEENo ratings yet
- PediamedsDocument9 pagesPediamedssven stantonNo ratings yet
- 867-Article Text-4548-1-10-20220428 2Document8 pages867-Article Text-4548-1-10-20220428 2Nelly MarwatiNo ratings yet
- Rybelsus Product MedicalDocument58 pagesRybelsus Product MedicalNovo NORDISK BalajiNo ratings yet
- General Drug CategoriesDocument3 pagesGeneral Drug CategoriesUswatun HasanahNo ratings yet
- Sales Bill Jan20Document74 pagesSales Bill Jan20Mansoor TheenNo ratings yet
- 7346 843 CderDocument18 pages7346 843 Cderdepardieu1973No ratings yet
- Inspection,,Hospital AssignmentDocument4 pagesInspection,,Hospital Assignmentamazing BoyNo ratings yet