Professional Documents
Culture Documents
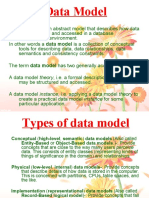
Conceptual Data Model Explained
Uploaded by
Raju kumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conceptual Data Model Explained
Uploaded by
Raju kumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Data Warehousing > Concepts > Conceptual Data Model
A conceptual data model identifies the highest-level relationships
between the different entities. Features of conceptual data model
include:
Includes the important entities and the relationships among them.
No attribute is specified.
No primary key is specified.
The figure below is an example of a conceptual data model.
Conceptual Data Model
From the figure above, we can see that the only information shown via
the conceptual data model is the entities that describe the data and the
relationships between those entities. No other information is shown
through the conceptual data model
Data Warehousing > Concepts > Logical Data Model
A logical data model describes the data in as much detail as possible,
without regard to how they will be physical implemented in the
database. Features of a logical data model include:
Includes all entities and relationships among them.
All attributes for each entity are specified.
The primary key for each entity is specified.
Foreign keys (keys identifying the relationship between different
entities) are specified.
Normalization occurs at this level.
The steps for designing the logical data model are as follows:
1. Specify primary keys for all entities.
2. Find the relationships between different entities.
3. Find all attributes for each entity.
4. Resolve many-to-many relationships.
5. Normalization.
The figure below is an example of a logical data model.
Logical Data Model
Comparing the logical data model shown above with the conceptual
data model diagram, we see the main differences between the two:
In a logical data model, primary keys are present, whereas in a
conceptual data model, no primary key is present.
In a logical data model, all attributes are specified within an entity.
No attributes are specified in a conceptual data model.
Relationships between entities are specified using primary keys
and foreign keys in a logical data model. In a conceptual data
model, the relationships are simply stated, not specified, so we
simply know that two entities are related, but we do not specify
what attributes are used for this relationship.
Data Warehousing > Concepts > Physical Data Model
Physical data model represents how the model will be built in the
database. A physical database model shows all table structures,
including column name, column data type, column constraints, primary
key, foreign key, and relationships between tables. Features of a
physical data model include:
Specification all tables and columns.
Foreign keys are used to identify relationships between tables.
Denormalization may occur based on user requirements.
Physical considerations may cause the physical data model to be
quite different from the logical data model.
Physical data model will be different for different RDBMS. For
example, data type for a column may be different between MySQL
and SQL Server.
The steps for physical data model design are as follows:
1. Convert entities into tables.
2. Convert relationships into foreign keys.
3. Convert attributes into columns.
4. Modify the physical data model based on physical constraints /
requirements.
The figure below is an example of a physical data model.
Physical Data Model
Comparing the physical data model shown above with the logical data
model diagram, we see the main differences between the two:
Entity names are now table names.
Attributes are now column names.
Data type for each column is specified. Data types can be
different depending on the actual database being used.
Secondary Key
An entity may have one or more choices for the primary key. Collectively these are
known as candidate keys. One is selected as the primary key. Those not selected are
known as secondary keys.
For example, an employee has an employee number, a National Insurance (NI) number
and an email address. If the employee number is chosen as the primary key then the NI
number and email address are secondary keys. However, it is important to note that if
any employee does not have a NI number or email address (ie: the attribute is not
mandatory) then it cannot be chosen as a primary key.
You might also like
- Ict 105 AssessmentDocument6 pagesIct 105 AssessmentNiraj ThapaNo ratings yet
- Data Structures & Algorithms Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandData Structures & Algorithms Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Harrison American Democracy Now 7eDocument6 pagesHarrison American Democracy Now 7esambabaNo ratings yet
- Database Systems Concepts 1Document12 pagesDatabase Systems Concepts 1Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Data Model, Logical Data Model, and Physical Data Model-DetailDocument4 pagesConceptual Data Model, Logical Data Model, and Physical Data Model-Detailfajarabror100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Data ModelingDocument9 pagesChapter 4 Data ModelingHildana TamratNo ratings yet
- LogicaL Data MODELDocument3 pagesLogicaL Data MODELDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science: Dual Degree Integrated Post Graduate ProgramDocument31 pagesDepartment of Computer Science: Dual Degree Integrated Post Graduate ProgramanimeshNo ratings yet
- What is Data Modelling and Why is it ImportantDocument8 pagesWhat is Data Modelling and Why is it ImportantShah zaibNo ratings yet
- Document 10Document3 pagesDocument 10jan janNo ratings yet
- Physical Data ModelDocument5 pagesPhysical Data Modelanimania_1989No ratings yet
- Data Modelling Conceptual, Logical, Physical Data Model TypesDocument9 pagesData Modelling Conceptual, Logical, Physical Data Model TypessrinivasNo ratings yet
- Data Modeling o-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesData Modeling o-WPS OfficeABDULAZEEZNo ratings yet
- Database Review: Conceptual, Logical & Physical Data ModelsDocument27 pagesDatabase Review: Conceptual, Logical & Physical Data ModelssdNo ratings yet
- Lesson2 Database ModelsDocument15 pagesLesson2 Database ModelsSamuel NdiranguNo ratings yet
- Databases and Data ModellingDocument53 pagesDatabases and Data ModellingVikas KaushikNo ratings yet
- Database Models and Concepts ExplainedDocument98 pagesDatabase Models and Concepts ExplainedAjaya KapaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DatabaseDocument18 pagesChapter 2 DatabaseNicho GuimbaolibotNo ratings yet
- ModelDocument17 pagesModelkhushali16No ratings yet
- What Are Entity Relationship DiagramsDocument10 pagesWhat Are Entity Relationship DiagramsELIENo ratings yet
- DBMS Important Questions With SolutionDocument20 pagesDBMS Important Questions With SolutionViney ChhillarNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument25 pagesUntitledgouvany tamerNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Database Management System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument22 pagesUnit 2 - Database Management System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inmroriginal845438No ratings yet
- Data Modeling and Database deDocument81 pagesData Modeling and Database deAdil Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Database Design: AnswerDocument14 pagesDatabase Design: AnswerRajesh BhardwajNo ratings yet
- DATA MODELING: A GUIDE TO VISUALIZING AND DESIGNING DATABASESDocument6 pagesDATA MODELING: A GUIDE TO VISUALIZING AND DESIGNING DATABASESdeezNo ratings yet
- ModelDocument2 pagesModelDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- When Not To Normalize Your Data: RelatedDocument6 pagesWhen Not To Normalize Your Data: RelatedPrerna BhandariNo ratings yet
- Logical Database ReportDocument52 pagesLogical Database ReportGlenn AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Data ModelingDocument8 pagesData ModelingShiblyNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Concepts in Relational Data ModelDocument11 pagesFundamental Concepts in Relational Data Modelsimply_coool100% (2)
- CS502 DBMS Unit-2 - 1692116698Document12 pagesCS502 DBMS Unit-2 - 1692116698Bhavika ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 03 DB Modeling Using ERDDocument44 pages03 DB Modeling Using ERDSyeda Areeba RashidNo ratings yet
- Data MedellingDocument76 pagesData MedellingMohsin ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- DataModels SlidesDocument4 pagesDataModels SlidesXen ArfeenNo ratings yet
- surv-Chapter 8Document7 pagessurv-Chapter 8Doaa RezkNo ratings yet
- Using ERwin Data ModelerDocument46 pagesUsing ERwin Data Modelerapi-3814149100% (1)
- DatamodelingDocument15 pagesDatamodelingOmkar MulekarNo ratings yet
- SYSTEMDESIGNDocument3 pagesSYSTEMDESIGNNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Database DesignDocument4 pagesDatabase DesignMichael WorkinehNo ratings yet
- 02 DB DesignDocument39 pages02 DB DesignSyeda Areeba RashidNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Data MODELDocument1 pageConceptual Data MODELDeepanshuNo ratings yet
- What Is Data Modelling - Types (Conceptual, Logical, Physical)Document10 pagesWhat Is Data Modelling - Types (Conceptual, Logical, Physical)Ajit KumarNo ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY 2 - Research: Database Models: InstructionsDocument44 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY 2 - Research: Database Models: InstructionsMarcela PasosNo ratings yet
- High-Level Conceptual Data Models For Database Design: Unit - 2 Data Modelling Using Entity-Relationship ModelDocument17 pagesHigh-Level Conceptual Data Models For Database Design: Unit - 2 Data Modelling Using Entity-Relationship Modelcp54609No ratings yet
- AikmainDocument1 pageAikmainihsanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two - Relational Model2Document5 pagesChapter Two - Relational Model2natgech624No ratings yet
- Understanding Data ModelingDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Data Modelingayodele.matthew.oluremiNo ratings yet
- Guided Questions On Database Systems Concepts and ArchitectureDocument2 pagesGuided Questions On Database Systems Concepts and Architecturecharlene.dilig.mnlNo ratings yet
- 2marks and 3marks-12.06.2020Document15 pages2marks and 3marks-12.06.2020thanigesan100% (1)
- Presentation3 ER Model GeneralisationDocument91 pagesPresentation3 ER Model GeneralisationSatyam Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- surv-ch-8Document9 pagessurv-ch-8Doaa RezkNo ratings yet
- Analysis Model, Actually A Set of Models, Is The First TechnicalDocument6 pagesAnalysis Model, Actually A Set of Models, Is The First TechnicalSaurabh ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Unit-II DBMSDocument56 pagesUnit-II DBMSSATHYABAMA MADHANKUMARNo ratings yet
- WK 1 - 2 - DATA MODELSDocument12 pagesWK 1 - 2 - DATA MODELSDORCAS GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document7 pagesTutorial 3Bishesh DangolNo ratings yet
- Usit 304 Unit 2 Dbms 2022Document32 pagesUsit 304 Unit 2 Dbms 2022sanilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data ModelingDocument59 pagesIntroduction To Data ModelingAshish ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Expert Performance Indexing in SQL Server 2019: Toward Faster Results and Lower MaintenanceFrom EverandExpert Performance Indexing in SQL Server 2019: Toward Faster Results and Lower MaintenanceNo ratings yet
- EN AU CNTNT Ebook DBMC SQL Server On Linux A Guide To Re Platforming1 PDFDocument24 pagesEN AU CNTNT Ebook DBMC SQL Server On Linux A Guide To Re Platforming1 PDFRaja PrasadNo ratings yet
- DBMS - Chapter-4Document98 pagesDBMS - Chapter-4MasterNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Structured Query Language (SQL) : E. F. CoddDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Structured Query Language (SQL) : E. F. CoddBhanvi VermaNo ratings yet
- DBMS - Chapter-4Document98 pagesDBMS - Chapter-4MasterNo ratings yet
- Top 42 Microstrategy Interview Questions & Answers PDFDocument6 pagesTop 42 Microstrategy Interview Questions & Answers PDFRaju kumarNo ratings yet
- SQL BookDocument147 pagesSQL BookRaju kumarNo ratings yet
- Top 42 Microstrategy Interview Questions & Answers PDFDocument6 pagesTop 42 Microstrategy Interview Questions & Answers PDFRaju kumarNo ratings yet
- Alter Command: Adding A ColumnDocument4 pagesAlter Command: Adding A ColumnRaju kumarNo ratings yet
- Alter Command: Adding A ColumnDocument4 pagesAlter Command: Adding A ColumnRaju kumarNo ratings yet
- Alter Command: Adding A ColumnDocument4 pagesAlter Command: Adding A ColumnRaju kumarNo ratings yet
- Fraba Absolute EncoderDocument2 pagesFraba Absolute EncoderAhmed YacoubNo ratings yet
- Microsoft SQL Server ArchitectureDocument18 pagesMicrosoft SQL Server Architectureiamsam4uNo ratings yet
- PracticaResearch-1 Q1Document63 pagesPracticaResearch-1 Q1Jyne SalvallonNo ratings yet
- Techlog 2020-2 Synchronization Tool Deployment GuideDocument17 pagesTechlog 2020-2 Synchronization Tool Deployment Guidekrackku kNo ratings yet
- CP Lab 400 Complete Systems: Learning Systems For Industry 4.0Document16 pagesCP Lab 400 Complete Systems: Learning Systems For Industry 4.0adiamiruNo ratings yet
- Custom Offering and Fact Group For OBIA 11.1.1.8.1 or 11.1.1.7.1Document8 pagesCustom Offering and Fact Group For OBIA 11.1.1.8.1 or 11.1.1.7.1Anil PatialNo ratings yet
- Editor Sfjd,+Art.+003+SFJDDocument27 pagesEditor Sfjd,+Art.+003+SFJDMLW BDNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Sales Prediction Using Machine Learning TechniquesDocument6 pagesIntelligent Sales Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniquesshabir AhmadNo ratings yet
- Analisis Tanah Longsor Desa Banaran Kecamatan Pulung Kabupaten Ponorogo 2017Document15 pagesAnalisis Tanah Longsor Desa Banaran Kecamatan Pulung Kabupaten Ponorogo 2017Kharisma FitrianiNo ratings yet
- Research Methods Information Systems andDocument4 pagesResearch Methods Information Systems andMỵ Châu LươngNo ratings yet
- FPM Search UibbDocument13 pagesFPM Search Uibbrjsoni30inNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 PythonDocument21 pagesUnit-4 PythonDivyasri JeganNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id3293275Document42 pagesSSRN Id3293275humanbody22No ratings yet
- About Preference Variables - HelpDocument51 pagesAbout Preference Variables - HelpocnogueiraNo ratings yet
- 20CS2050L Software Engineering LabmanuelDocument47 pages20CS2050L Software Engineering LabmanuelR J SHARIN URK21CS5022No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - 8Document119 pagesChapter 5 - 8humayun fanNo ratings yet
- CleeeeanDocument33 pagesCleeeeanJohn RockNo ratings yet
- High Availability With Mariadb TX: The Definitive GuideDocument20 pagesHigh Availability With Mariadb TX: The Definitive GuideAnkitJainNo ratings yet
- Clustered Data ONTAP - NFS Best Practice and Implementation GuideDocument161 pagesClustered Data ONTAP - NFS Best Practice and Implementation GuideVinay K SinghNo ratings yet
- Neptune PDFDocument34 pagesNeptune PDFFull NameNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 2.1Document2 pagesPerformance Task 2.1Vieram CasadoresNo ratings yet
- MT6739 Android ScatterDocument14 pagesMT6739 Android Scatterاسامه ايوبNo ratings yet
- Using Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse PDFDocument225 pagesUsing Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse PDFramilanezNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Lecture Notes-11Document15 pagesOperating Systems Lecture Notes-11Arun SasidharanNo ratings yet
- M30624MGA-394FP DatasheetDocument274 pagesM30624MGA-394FP Datasheetsunder punjabiNo ratings yet
- TCP Congestion Control AIMD and Adaptive RetransmissionsDocument34 pagesTCP Congestion Control AIMD and Adaptive RetransmissionsrockerptitNo ratings yet
- GIS Objective ExamDocument5 pagesGIS Objective ExamVani RajasekharNo ratings yet
- Sap BPCDocument8 pagesSap BPCAqueel MohammedaliNo ratings yet