Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Installation - Instruction - UK (Flange Torque) PDF
Installation - Instruction - UK (Flange Torque) PDF
Uploaded by
rijalharunOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Installation - Instruction - UK (Flange Torque) PDF
Installation - Instruction - UK (Flange Torque) PDF
Uploaded by
rijalharunCopyright:
Available Formats
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTION
ALL FLANGED RUBBER EXPANSION JOINTS
Rubber expansion joints are available in 1. Planning included for pipe routing/support.
two ready to fit versions with standard The reaction forces, adjusting forces
connections according to DIN, ASA, instructions and friction forces must be taken into
BS, etc. account in the dimensioning of the fixed
Expansion joints must be arranged in points and plain bearings.
l Rotatable steel flanges pipes in such a way that regular
These should fit precisely and maintenance and any necessary Reaction force (N) = Effective area
burr-free in the fitting area of the replacement can take place easily. (mm²) x working pressure (N/mm²).
rubber bellow, whereby the sealing F= A x P
surface can protrude about 1 – 10 It must be ensured that the expansion
mm depending on the nominal joints do not rub against adjacent (Adjusting forces according to type data
diameter. The mating flange sealing components also when expanded to sheet)
surfaces can be smooth (Form A) or the maximum permissible limits.
with seal (Form B) according to The expansion joints must also not be Fitting example 1 (EB 1)
EN 1092 - 1: 2001. exposed to high externally radiated or
accumulated heat. Compensation of axial expansion with
l Pressure-resistant solid rubber
expansion joints without
flanges tie rods.
These flanges are delivered includ Universal expansion joints (without
ing single-piece steel backing tie rods) for absorbing
axial, lateral and angular move- The reaction forces of the expansion
flanges. The mating flanges should joint are absorbed by the fixed
have a smooth sealing surface ments.
bearing.
according to EN 1092 - 1: 2001 For an expansion joint to absorb the
(Form A). axial or lateral movements (expansion
or compression) of a pipe, it must be
Both types of expansion joints are arranged between two fixed points. In
self-sealing; additional seals are addition, plain bearings must be
unnecessary.
EB 1
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 1 / 21 www.belman.com
Fitting example 2 (EB2) joint without tie rods. The reaction bearings must be appropriately
forces of the expansion joint are supported! Adjusting forces
Compensation of lateral and axial absorbed by the fixed bearings and must be absorbed by the fixed
expansion with an expansion plain bearings. The plain points.
EB 2
Fitting example 3 (EB 3) expansion with expansion joints without are absorbed by the fixed bearings
tie rods arranged in a pipe outlet.The and plain bearings. The plain bearings
Compensation of lateral and axial reaction forces of the expansion joint must be appropriately supported!
EB 3
Lateral expansion joints (with tie rods) between two fixed points, the axial expansion joint x working pressure).
for absorbing lateral movement must be converted into a With this arrangement, only appropriate
movements. lateral movement. This makes it plain bearings may be used for correct
possible to use an expansion joint with initiation of expansion.A large selection
If an expansion joint for absorbing axial tie rods, which neutralises the occurring of rubber expansion joint tie rods can
movements cannot be fitted reaction forces (inside area of the be found in our catalogue.
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 2 / 21 www.belman.com
Fitting example (EB 4) Compensation of axial expansion by plain bearings serve only for correct
deflection into a lateral movement with initiation of movement in the
Compensation of axial expansion by expansion joints with tie rods. The expansion joint! In contrast to
deflection into a lateral movement with adjusting forces of the expansion joint fitting example 2, axial movement of
expansion joints with tie rods. are absorbed by the fixed bearings. The the vertical pipe arm is disregarded.
EB 4
Angular expansion joints (with joint tie In order to absorb significant axial combination of angular expansion joints
rods) for absorbing angular movements. movements with low adjusting forces, a with tie rods can be used.
Fitting example 5 (EB 5) expansion joints with tie rods. Advan- joint are absorbed by the joint tie rods.
tage: Significant axial expansion can be The plain bearings serve only for correct
Compensation of axial expansion by absorbed by only two expansion joints. initiation of movement in the expansion
deflection to angular movement using The reaction forces of the expansion joint!
EB 5
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 3 / 21 www.belman.com
Fitting example 6 (EB 6) sating expansion in two directions. expansion joint are absorbed by the
Advantage: High expansion joint tie rods. The plain bearings serve
Arrangement of pipe joint expansion compensation, low adjusting forces, only for correct initiation of
joints in three joint systems for compen- soft corner. The reaction forces of the movement in the expansion joint!
EB 6
Expansion joints for pump connection Where rubber expansion joints are used stresses and vibrations in order to
(with/without tie rods) for absorbing on pumps, these should prevent the decouple the pipe system from the
vibrations. transmission of forces, pump.
Fitting example 7 (EB 7) always be used for arrangement in the reaction forces. A vacuum support
pressure pipes to prevent the pump ring should be used on the suction side
Expansion joints with tie rods should support from being overloaded due to if possible.
EB 7
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 4 / 21 www.belman.com
Fitting example 8 (EB 8) as there is a risk of the expansion the pump support to the expansion
- IMPORTANT!! joints being damaged due to joint/elbow must be 1 to 1.5 x DN.
For the transport of abrasive media relatively high velocities from swirl Pump operation against a fully or partly
(liquids containing solids such as water/ and vertebration on the pump closed gate or flap valve must be
sand), the expansion joints must not be support. This applies similarly to avoided. Cavitation must also be
arranged directly on the pump support elbows and outlets. The fitting avoided as this can quickly damage
(suction/pressure side, distance from the expansion joint.
EB 8
Expansion joints with pressure relief for expansion joints can be used to from excess or low pressure to
absorbing axial and lateral movement. prevent the transmission of reaction adjacent fixed bearings, apparatus
Pressure-relieved forces resulting or machines.
Fitting example 9 (EB 9) the transmission of reaction forces fixed bearings, apparatus or
Expansion joints for absorbing axial resulting from excess or low machines (observe adjusting
expansion without pressure to adjacent forces).
EB 9
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 5 / 21 www.belman.com
Fitting example 10 (EB 10) on an elbow without the excess or low pressure to adjacent
Expansion joints for absorbing axial transmission of reaction forces fixed bearings (adjusting forces).
and lateral expansion resulting from
EB 10
Expansion joints (with tie rods) for To compensate for fitting inaccuracies expansion joint with tie rods can also
fitting/removal or for easy fitting or removal, an be mounted directly on a valve.
Fitting example 11 (EB 11) Tie rods prevent the transmission of of the tie rod flange, the rubber bellow
Expansion joint with tie rods for fitting/ reaction forces to a connected valve can be compressed to its maximum
removal. and by loosening the flange connection axial limits to enable removal of the
with the aid valve.
EB 11
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 6 / 21 www.belman.com
Fitting example 12 (EB 12) For rubberised pipes or valves, a blank be used to prevent a rubber-on-rubber
gasket must seal.
EB 12
2. built planning fixed or loose bearings is prevented the pipe diameter.
l suspension in self-aligning l The distance between the first and
Arrangement of pipe supports bearings is avoided; plain or second bearing can be max. 14 x
roller bearings must be used as the pipe diameter
The fixed points of the guide bearings
guide bearings l The distance between the
must be arranged in such a
remaining pipe bearings can be
way that:
max. 21 x the pipe diameter. This
l the expansion joint is not loaded by Arrangement of floating bearings distance must be reduced if
the weight of the pipe
The distance between the expansion necessary due to the inherent
l bending due to the arrangement of joint and first bearing can be max. 4 x stability of the pipe
EB 13
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 7 / 21 www.belman.com
Initial tension of expansion joints with the permanently fitted spring out of the groove of the steel
If an expansion joint is fitted with an expansion joint at an open point in the flange and this could damage the
initial tension greater than 10 mm pipe. (Fitting example EB 14 + 15) sealing bead or cause a leak.
axially or 5 mm laterally, the expansion Reason: A not yet fitted expansion For planning purposes, it must be
joint must be fitted first and then the joint with a higher initial tension ensured that the pipe can be
appropriate initial tension generated will cause the sealing bead to opened!
EB 14
EB 15
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 8 / 21 www.belman.com
3. Safet y measures Flow rate l UV protection cover: Protects
For high flow rates, it must be clarified against UV radiation and influences
Excess pressure, temperature rise, whether the expansion joints of weather in regions exposed to
vacuum must be used with or without guide extreme sunlight.
tube in order to prevent wear due l Flame-retardant protective cover:
Protect pipes against inadmissible Protects against fire up to
excess pressure, excessive temperature to excessive vertebration.
800°C for 30 minutes.
rise and uncontrolled vacuum. The limi-
ting values are shown in the data sheets Vacuum support spiral/ring
Dangerous media
of our catalogue. If the expected vacuum is higher than
0.8 bar absolute, a vacuum The expansion joints must be provided
Water hammer and vacuum drop support spiral or vacuum support ring with suitable splash protection for pipes
must be provided. used for transporting dangerous or
Draining and venting options are provi- environmentally harmful media.
ded to prevent water hammer and These prevent the bellow from collap-
vacuum drop. sing. For use directly downstream of a
pump, flap valve or elbow, a check Mating flanges/Flange connection
Resistance must be made to ensure correct posi- Mating flanges and flange connections
tioning after fitting – see Fitting must be as described in the following
The inner material of the bellow coming instructions + Fitting example Fitting example 16 (EB 16) to ensure a
into contact with the medium must be (EB 16)! reliable seal and to prevent damage to
suitable for the medium transported in the rubber expansion joints.
the pipe. External influences
If the list does not contain a specific Mating flanges with and without projec-
medium, we must be provided with Extreme external influences make it
necessary to protect the expansion tion according to EN 1092-1:2001
appropriate data from the safety data Form A or B must be used for expansi-
sheet for chemical substances and pre- joints via special measures:
l Ground protection cover: Protects
on joints with rotatable flanges. Only
parations according to DIN 52900, clau- smooth mating flanges should be used
ses 1 to 2.13 in order to enable us to against damage to bellows, fouling
and earth pressure on buried for expansion joints with solid flanges.
determine whether the inner liner of the Other types are available on request.
expansion joint is suitable. pipes.
Fitting example 16 (A - E) expansion joints with solid rubber flan- seal with an appropriately thick ring or
ges, the recess of the mating flange taken into account in rubber flange
If a smooth flange cannot be used for must be compensated with a fabrication.
EB 16 A
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 9 / 21 www.belman.com
When using backing flanges with thick both flanges must be filled with an ap- flange from tilting and thus avoids in-
bead, the gap above the bolts between propriate ring. This stops the backing correct contact with the sealing surface!
EB 16 B
When using flare flanges and slip-on of the mating flange corresponds to the diameter of the mating flange is larger,
flanges, it must be ensured that the internal diameter of the bellow. a blank metal gasket and an
internal diameter of the sealing surface If this is not the case and the internal additional seal must be used!
EB 16 C
Mating flanges with groove or tongue
must not be used.
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 10 / 21 www.belman.com
EB 16 D
It must be ensured during fitting that the groove of the expansion joint flan- surface may be damaged and leaks
the rubber bead is located correctly in ge, otherwise the sealing can occur!
EB 16 E
4. Packaging without being subject to stress, l Note „TOP“ at the top and
deformation and kinking „cable or lifting hook“
l Check the packaging for external l Rubber expansion joints with steel l Steel backing rings (with bracing)
damage flanges must be stored upright and the rubber expansion joint
l Check the contents against the deli on the flanges (risk of crushing) flanges must remain fastened
very note or packing list l Store in a cool, dry, dust-free and until final fitting to avoid
l If possible, do not unpack the moderately ventilated room excessive loads on the rubber
expansion joints prior to assembly l Protect rubber parts against part!
l Only open the packaging with a draughts and cover if necessary. l Do not use any sharp-edged
blunt object Ozone-generating equipment such tools, wire ropes, chains or
l Ensure that nails or staples in as electric motors, fluorescent light lifting hooks (risk of damage
wooden crates do not come into sources, etc., must not be used at to rubber)
contact with the rubber bellow the place of storage l Always lift both steel flanges
l Do not store any solvents, fuels, simultaneously.
chemicals or similar together with Shackle at both sides or place
5. Storage the expansion joints padded tie-bars through
the expansion joint
l See DIN 7716 - Guidelines for the l For ground level transportation
storage of rubber parts. 6. Transport without means of transport,
Rubber expansion joints must be roll the expansion joint on the
stored l Leave the parts packed
flanges
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 11 / 21 www.belman.com
7. Fitting Only one expansion joint or several damage the expansion joint
expansion joints coupled to form a l The pipe flanges must be clean,
Rubber expansion joints are intended unit may be fitted between two fixed grease-free, smooth, flat and
for absorbing movements points burrfree
under certain pressure and temperature l Check the size of the fitting gap. l It must be ensured that the flange
conditions to be determined The mating flanges should be fitted connections are as described in the
in advance. To ensure that the maxi- in alignment with each other. The section “Mating flanges/flange
mum service life is reached, the maximum deviation between the fit connections – A-E” under “Safety”
following must be observed for fitting. ting gap and expansion joint can be l If an expansion joint is to be
+/-10 mm axially and +/-5 mm provided with a guide tube, this
laterally must be inserted into the expansion
Prior to fitting l Note: If the aforementioned toleran joint prior to fitting in the pipe (do
ces cannot be maintained, the pro not forget seal between guide tube
l Check the packaging of the rubber
cedure is as described in the sec and mating flange)
expansion joints and after unpac
tion “Initial tension of expansion l If the use of a vacuum support
king also the expansion joint itself
joints” Fitting example 8 (EB 8) spiral or vacuum support ring is
for damage. Damaged expansion
l The pipe flanges must not be twi necessary due to low pressure,
joints must not be fitted
sted towards each other when fit these same must be fitted in
l Check the pipe run to ensure that it
ting an expansion joint with solid advance. For a vacuum support
is straight in the area in which the
rubber flanges, as the expansion ring, the section “Vacuum support
expansion joint is to be fitted and
joint will be subject to torsion – this ring” in the following must be
that the pipe is limited by
must be avoided as torsion can observed (EB 17)!
appropriate fixed points
IMPORTANT pipe system, steel wire expansion joints It is also important to note that the
can be damaged by stray currents or expansion joint must not be insulated
Welding in the vicinity of expansion
electrical earth conduction. The anode at temperatures above 50°C, as this
joints must be avoided. If this cannot
and cathode of the electric welding will cause the rubber bellow to heat
be avoided, the expansion joint must
connection must always be located on up and harden as a result of the
be covered with a flame-retardant
the same line section. (Not separated accumulated heat.
and heat resistant material to protect
by the rubber expansion joint!) The rub-
it against welding heat and flying
ber bellow must not be painted after fit- The bellow must not be painted.
sparks. When welding the complete
ting in the pipe.
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 12 / 21 www.belman.com
Fitting an expansion joint with ised pipe flanges, valves or blank ned. Readjustment of the tie rods
flange connection gaskets – see corresponding sec subsequently takes place after fit
l Centring mandrels, rubber hammer tion above! ting the expansion joint – see fol-
and torque wrench are required for l Fix the expansion joint at both lowing description “Fitting the tie
fitting. Do not use any sharp-edged flanges using at least two bolts or rods”
tools! threaded rods. If necessary, l The remaining fixing bolts can now
l Carefully push the expansion joint the lifting device can be detached/ be inserted and tightened
into the fitting gap. Take care not to removed hand-tight
damage the sealing surfaces l When fitting expansion joints with tie l For the bolted flange connection,
l No additional seals are required. The rods, it must be ensured that the tie bolts with the strength class 8.8
rubber bead or rubber flange seals rods are loosened so that the should be used
directly against the pipe flange expansion joint is able to adjust l Do not use a washer on the expan
Attention: Exceptions for rubber itself to the fitting gap when tighte- sion joint flange
The following must be noted when l See Flange bolt torque (table 1 and be inserted with the bolt head
inserting the bolts: 2, page 20 and 21) towards the bellow to prevent
l For expansion joints with through damage to the bellow under
holes, all bolts must pressure.
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 13 / 21 www.belman.com
Exception (supporting shoulder), the bolt can way round – however the bolt must
If the expansion joint has a long collar also be inserted the other not be longer than the collar!
l For expansion joints with tapped the bolts should be flush towards the protrud ing bolts are liable to damage
holes in the flange, bellow side with the flange, as the bellow under pressure.
l The bolted flange connections
must be tightened as follows: Step 3: l If a leak should occur during
Apply
l final torque according to the subsequent pressure test,
Step 1: Step 3 in two passes crosswise the bolts must be tightened with
l Tighten all bolts by hand l The bolts do not require further the torque according to Step 3.
l Apply torque evenly according to tightening as this would ultimately If the bolted flange connection
Step 1 crosswise damage the sealing surface is still leaky, the tightening
l Check gap width on outer edge of l Throughout the entire fitting pro torque must be increased
flange cess, it must be ensured that the slightly.
l Settling time >= 30 minutes sealing bead does not tilt Before retightening the bolts,
The protruding sealing surface the pressure in the expansion
Step 2: should be compressed evenly joint must be reduced.
on all sides l Throughout the entire fitting
l Tighten all bolts crosswise accord-
l When fitting silicone rubber expan- process, it must be ensured
ing to Step 2
sion joints, the specified tightening that the expansion joint is not
l Check gap width
torques must be reduced by 30%. overexpanded or crushed.
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 14 / 21 www.belman.com
Vacuum support ring (EB 17) At high flow rates, a check must be
l Firm seating (max. 10 - 15 mm l
For vacuum support rings clearance between bellow and made to determine whether an ex-
arranged directly down- ring on one side) pansion joint with vulcanised support
stream of a pump, flap valve or l If necessary, adapter plates ring should be used in order to avoid
elbow the vacuum support should be used to obtain the fatigue failures due to strong turbu-
rings must be checked for permissible seat clearance lence (EB 17 B)
correct positioning after l The connection lock should l After fitting, check that the hexagon
fitting as follows always be in the lower flow bolts and nuts are securely locked to
(EB 17 A): area (6°) prevent loosening
EB 17 A
EB 17 B
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 15 / 21 www.belman.com
8. Final fitting clean the expansion joint If leaks should occur in the area
l Check the expansion joint for of the flange connection during
check damage the pressure test, the bolted flan-
l Check that all supports, fixed ge connection must be retighten-
l Check the expansion joints on all and plain bearings are fitted and ed according to the tightening
sides for any visible damage and in functional table Step 3.
particular clean the gap between l Check the tie rods for even loading
the steel backing flange and rub and if necessary adjust them to
ber bellow (remove foreign bodies, the prevailing conditions
sand, etc.) 11. Supplementary
l After being fitted, the expansion assembly and
joints should be provided with
suitable protection against dam- 10. Pressure test fittings
age, which must only be removed instructions
directly prior to commissioning The rubber expansion joint is not a
l The rubber parts must not be proper pressure vessel, but is for t ype 45 - 46
painted.Solvents and chemicals classified according to the
attack the surface and damage the Pressure Equipment Directive Rubber expansion joints type 46
bellow as a “pipe accessory” must be fitted stress-free.
l The expansion joints must not be (pipe component). The bolted connections should
insulated as this can cause the When fitting the expansion joint in always be made using two wrenches
bellow to overheat and dry out and piping, sealing does not take place to avoid torsion on the expansion joint
ultimately lead to damage of the via a separate seal, but directly on (EB 18).
the sealing surface of the integrated l Mount the bolting parts on the
bellow
l The best results are obtained rubber bellow. pipe and check the fitting gap!
when the expansion joint is able The fitting gap should have the
to function stress-free under ope- A one hundred per cent pressure same length as the expansion
rating conditions (initial tension test of the rubber expansion joint at joint bellow (e.g. 130 mm +/- 5 mm
must be taken into account when the manufacturer can adversely type 46 and 120, 130,140 or 155
fitting) influence the integrated rubber mm depending on the nominal
l For expansion joints with tie rods, sealing surface. diameter for type 45)
Pressure testing of the rubber l Insert the expansion joint and
check the tie rods. They should be
able to be turned hand-tight. The expansion joints at the tighten using two wrenches as
lock nuts must be tightened manufacturer therefore takes follows:
l If possible, check the support place only l DN 20/25 type 46 and
spirals/rings, if present, for correct at the special request of the DN 20–50 type 45
seating and locking customer with the utmost care. The front threaded part must be
used as a counter support and
The pressure test normally takes the sleeve nut tightened
9. Measures prior place only after the rubber (to avoid torsion on the bel-
to pressure expansion joints have been fully low)
installed in the pipe system. l DN 32–50 Type 46
test and All of the instructions contained in The rear threaded part must be
commissioning these fitting instructions should be used as a counter support and
observed prior to the the sleeve nut tightened (to avoid
l Remove the protective covers and pressure test. torsion on the bellow)
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 16 / 21 www.belman.com
EB 18 A
DN 20/25 Typ 46 und DN 20 – 50 Typ 45
DN 20/25 Typ 46 und DN 20 – 50 Typ 45
DN 32 – 50 Typ 46
EB 18 B
DN 32 – 50 Typ 46
All other fitting positions are as descri- 12. Supplementary subjected to tension, torsion or
bed in our main fitting instructions. bending
assembly and l No additional seals are required
Tightening torques for all types 100 Nm. fitting instruc- l Only hexagon head bolts
according bed in our main fitting
tions for t ype instructions to DIN 933 with
60 - WRG washer should be used
l The bolt tightening torque is 30
l The rubber-metal pipe connector Nm
type 60 WRG must be fitted
stress-free All other fitting positions are as
l The fitting gap must be 70 mm described in our main fitting instruc-
l The pipe connector must not be tions.
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 17 / 21 www.belman.com
Screw measures for
DN Flange PN 6 Flange PN 10
20 4 x M10 x 25 4 x M12 x 30
25 4 x M10 X 25 4 x M12 x 30
32 4 x M12 x 30 4 x M16 x 30
40 4 x M12 x 30 4 x M16 x 30
50 4 x M12 x 30 4 x M16 x 30
65 4 x M12 x 30 4 x M16 x 30
80 4 x M16 x 35 8 x M16 x 35
100 4 x M16 x 35 8 x M16 x 35
125 8 x M16 x 35 8 x M16 x 40
150 8 x M16 x 35 8 x M20 x 40
200 - 8 x M20 x 45
13. Supplementary 14. Supplementary
assembly and assembly and
fitting instruC- fittinginstruc-
tions for t ype tions for t ype
61 64
l Type 61 is fitted as part of the pipe The expansion joint must not be or other steel parts included in the
installation. Installation in the fitting fitted before all work on the pipes delivery should be checked and
gap is only difficult in the case of and flanges has been completed correspond to the drawings. The
very large nominal diameters and all anchors and supports bolt holes must be arranged sym-
l The pipe ends must be long enough mounted. metrical in each flange.
to reach the beginning of the shaft This is intended to prevent the l For lifting the expansion joint,
on both sides expansion joint from being it is recommended to use a sup
l Only use wide GBS clamps for fixing damaged by welding sparks, port plate or inner frame Prefer-
the expansion joint (min. 20 x 1 mm) sharp-edged objects, etc. ably, the expansion joint should
l At an operating pressure of up to 2 be pre-assembled with backing
bar, one clamp is adequate per side. Since the expansion joints type flanges and internal sleeve (if
Above 2 bar, two clamps should be 64 are made from highly flexible included in the delivery) on the
used materials, the durability depends on ground before lifting.
All other fitting positions are as careful and correct fitting.
described in our main fitting l Avoid sharp edges and folds. All other fitting positions are as
instructions. l Ducting flanges, backing flanges described in our main fitting.
Tightening torques for type 64
Material Backing flange / Bolts
40 x 10 / M10 50 x 10 / M12 60 x 10 / M12 60 x 12 / M16
NBR 60 Nm 70 Nm 80 Nm 80 Nm
EPDM 60 Nm 80 Nm 80 Nm 80 Nm
Vion - 80 Nm 80 Nm 80 Nm
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 18 / 21 www.belman.com
torque table 3, page 21)
15. Supplementary l The limiting bolts (tie rods) must
checked a single time
assembly and be adjusted to the maximum l First inspection 1 week after
fitting permissible expansion after commissioning.
assembly of the expansion joint. Further inspections after 1, 4
instructions The limiting bolts must not be and 12 months and then yearly.
for t ype 80 removed The following must be checked:
l In the course of commissioning,
The expansion joints are delivered the flange connections should
l l External damage of rubber
with protective covers. be retightened with the specified
bellow, flange and tie rods
These covers must only be torque after reaching operating
l Deformations of the rubber
removed directly prior to assem temperature
flange between the bolts
l If leaks occur, the flange connec
bly. If these covers need to be (displacement of flange
removed in advance for the pur tions must be checked for paral-
surfaces)
pose of inspection, they must be lelism of the flanges, fouling or
l Changes to the rubber bellow
screwed back into place in any damage to the sealing surfaces
(bubbles, brittleness, cracks,
event hairline cracks
l Welding, soldering and brazing on
Minor indentations or damage can be
l Check of the tie rods for
the PTFE bellow is forbidden as removed with emery cloth.
impermissible displacement and
the bellow can be damaged and misalignment
highly toxic gases can develop l Assessment of corrosion and
l The use of seals between PTFE/ 16. Maintenance wear on the entire component.
PTFE sealing surfaces is unneces
sary. It is recommended to use a and l The expansion joints can be
5 mm thick PTFE seal for connec monitoring cleaned with a weak soap solution
tions to glass, enamel and other and clear water.
components l Prior to final commissioning, the Do not use sharpedged
l The flange connection bolts must flange connection tightening tor objects, wire brushes or emery
be tightened according to the que must be cloth.
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 19 / 21 www.belman.com
Table 1: Flange bolt torque for type 40, 42, 58 and 59
Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
DN Pre-assembly PN 6 PN 10 PN 16 ASA 150 PN 6 PN 10 ASA 150
Nm Nm Nm Nm Nm Nm Nm Nm
200 100 160 200 160 200 200 250 250
250 100 160 160 200 200 200 200 250
300 150 160 160 240 280 200 200 350
350 150 200 160 200 360 250 200 450
400 150 160 240 280 320 200 300 400
450 150 200 160 280 360 250 200 450
500 150 160 240 360 360 200 300 450
550 200 400 500
600 200 240 320 520 480 300 400 600
650 200 440 550
700 200 240 320 440 440 300 400 550
750 250 480 600
800 250 320 440 560 640 400 550 800
850 250 600 750
900 250 360 440 520 640 450 550 800
950 250 720 900
1000 250 360 560 720 680 450 700 850
1050 250 720 900
1100 250 720 900
1150 250 720 900
1200 250 440 680 960 720 550 850 900
1250 250 880 1100
1300 250 920 1150
1350 250 1000 1250
1400 250 560 840 1000 960 700 1050 1200
1450 250 1040 1300
1500 250 1000 1250
1600 250 600 1120 1360 920 750 1400 1150
1650 250 1160 1450
1800 250 680 1120 1360 1120 850 1400 1400
1950 250 1320 1650
2000 250 840 1160 1560 1480 1050 1450 1850
2100 250 1520 1900
2200 250 880 1480 1640 1100 1850 2050
2250 250 1840 2300
2400 250 920 1520 2040 1150 1900 2550
2550 250 2320 2900
2600 250 1120 1560 2560 1400 1950 3200
2700 250 2560 3200
2800 250 2680 1450 2050 3350
2850 250 2960 3700
3000 250 1160 1880 3200 1450 2350 4000
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 20 / 21 www.belman.com
Table 2 Flange bolt torque for type 48, 49, 50, 51, 53, 55, 56 and 65
Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
DN for all for all PN 6 PN 10 PN 16 PN 25 ASA 150
Nm Nm Nm Nm Nm Nm Nm
25 by hand 50 60 80 80 80 80
32 by hand 50 60 80 80 80 80
40 by hand 50 60 80 80 80 80
50 by hand 50 60 80 80 80 80
65 by hand 50 60 80 80 80 80
80 by hand 50 60 80 80 80 80
100 by hand 50 80 100 100 100 100
125 by hand 50 80 100 100 100 100
150 by hand 50 80 100 100 100 100
175 by hand 50 90 100 100 100 100
200 by hand 50 90 100 100 100 100
250 by hand 50 90 100 100 110 100
300 by hand 50 100 110 110 110 100
350 by hand 50 120 130 135 165 110
400 by hand 50 120 140 155 200 140
450 by hand 50 140 145 165 200 145
500 by hand 50 120 145 170 200 145
600 by hand 100 185 210 255 280 210
700 by hand 100 200 225 300 300 230
800 by hand 100 235 300 360 410 300
900 by hand 100 235 300 360 415 300
1000 by hand 100 300 360 425 525 360
Table 3: Flange connection dimensions according to DIN 2501
PN 10 PN 25
Screws Bolt torque Screws Bolt torque
DN Quantity Thread Nm Quantity Thread Nm
20 4 M12 10 4 M12 10
25 4 M12 20 4 M12 20
32 4 M16 30 4 M16 30
40 4 M16 40 4 M16 40
50 4 M16 50 4 M16 50
65 8 M16 70 8 M16 40
80 8 M16 40 8 M16 40
100 8 M16 40 8 M20 50
125 8 M16 50 8 M24 80
150 8 M20 60 8 M24 90
200 8 M20 90 12 M24 100
250 12 M20 60 12 M27 120
300 12 M20 70 - - -
350 16 M20 110 - - -
400 16 M24 160 - - -
500 20 M24 180 - - -
600 20 M27 240 - - -
700 24 M27 260 - - -
BG08/2013 – Subject to alterations and eventual misprints 21 / 21 www.belman.com
You might also like
- SJV Ep Ia 011 VP 002 - DWG - 190117Document7 pagesSJV Ep Ia 011 VP 002 - DWG - 190117Jahangir AlamNo ratings yet
- A10 Steam Turb - CC Plant Webnar (Rev 4-1-16)Document121 pagesA10 Steam Turb - CC Plant Webnar (Rev 4-1-16)FlamingorosadoNo ratings yet
- Quantum Field Theory and Condensed MatterDocument454 pagesQuantum Field Theory and Condensed MatterJunior Lima100% (2)
- Rubber BellowDocument20 pagesRubber BellowPrateek100% (1)
- DeZURIK KCG Knife Gate ValvesDocument12 pagesDeZURIK KCG Knife Gate ValvesKithkarnonNo ratings yet
- Nordtec ProposalDocument15 pagesNordtec Proposaluzair khan100% (1)
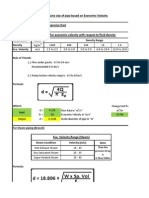
- Line Size of Pipe Based On Economic VelocityDocument19 pagesLine Size of Pipe Based On Economic Velocitymabrouk2013No ratings yet
- Standard Hook-Up Wires & Cables For ElectronicsDocument124 pagesStandard Hook-Up Wires & Cables For ElectronicsdlstoneNo ratings yet
- Thermax Evaporative CondenserDocument2 pagesThermax Evaporative CondenserShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- P&ID @chem - Eng - WorldDocument157 pagesP&ID @chem - Eng - WorldMuhamad Ali Nur RohmanNo ratings yet
- Product Key Autodesk 2016Document5 pagesProduct Key Autodesk 2016mila beusesNo ratings yet
- Piping Codes ListingDocument42 pagesPiping Codes ListingSamuel AnemeNo ratings yet
- SAN Radiators-Manufacturing Process PDFDocument6 pagesSAN Radiators-Manufacturing Process PDFAdhavan ThamizhanNo ratings yet
- SRI Jigger Steam ManualDocument23 pagesSRI Jigger Steam ManualzalabiNo ratings yet
- Gas Filter Separators 4Document8 pagesGas Filter Separators 4Anonymous bHh1L1No ratings yet
- FL1627Document2 pagesFL1627Isaac Montero BarreraNo ratings yet
- Knock Out Drum: Wiring DiagramsDocument8 pagesKnock Out Drum: Wiring DiagramsAlinaIordacheNo ratings yet
- LASTlifting Pump PDSDocument3 pagesLASTlifting Pump PDSsunii19847908No ratings yet
- Module 1 PipingsDocument47 pagesModule 1 PipingsMaynard Trinidad Mendoza0% (1)
- Shell Data:: Input Echo, Tubesheet Number 1, Description: Main ShellDocument8 pagesShell Data:: Input Echo, Tubesheet Number 1, Description: Main ShellAbhishek LadNo ratings yet
- Cage Trim ValvesDocument57 pagesCage Trim ValveslinhphamNo ratings yet
- Flow and CV Calculation ToolDocument3 pagesFlow and CV Calculation Toolmohan babuNo ratings yet
- Filtration / Separation Products & Services: Making The World Safer, Healthier and More ProductiveDocument16 pagesFiltration / Separation Products & Services: Making The World Safer, Healthier and More Productivesuraj pandeyNo ratings yet
- F-4 Ik Fluid FlowDocument52 pagesF-4 Ik Fluid FlowAbdul NaeemNo ratings yet
- Behringer CatalogDocument36 pagesBehringer Catalogyazanof4No ratings yet
- Cone Design ToolDocument1 pageCone Design ToolPramod KumarNo ratings yet
- JAC 12th Result 2018, Jharkhand Intermediate Result 2018, Jac - Nic.inDocument3 pagesJAC 12th Result 2018, Jharkhand Intermediate Result 2018, Jac - Nic.inExam ResultsNo ratings yet
- TR - 75.04.01 Control Valve Position Stability PDFDocument20 pagesTR - 75.04.01 Control Valve Position Stability PDFmilecsaNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Specification Sheet US Units: 47,5 InchDocument1 pageHeat Exchanger Specification Sheet US Units: 47,5 InchGreisly MarrugoNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchange Equipment: Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument43 pagesHeat Exchange Equipment: Department of Chemical EngineeringHarshadeepthi.GNo ratings yet
- Weekly Visit PlanDocument1 pageWeekly Visit PlanSunil JoshiNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Products 2009 CompletDocument62 pagesTechnical Data Products 2009 CompletRobert NedelcuNo ratings yet
- 30 MW Power Generation ProcessDocument11 pages30 MW Power Generation ProcessMohan PNo ratings yet
- Sentry Tech BullDocument3 pagesSentry Tech BullFilipNo ratings yet
- Basco Type 500Document12 pagesBasco Type 500Sebastian OviedoNo ratings yet
- Cone Layout ToolDocument1 pageCone Layout ToolSaravanan ManiNo ratings yet
- Api 54Document1 pageApi 54keyur1109No ratings yet
- Work Methodology For Pressure Vessel and PRV InspectionDocument36 pagesWork Methodology For Pressure Vessel and PRV InspectionUmese AbrahamNo ratings yet
- M Series Actuator-RMP-23 - DEMBLADocument7 pagesM Series Actuator-RMP-23 - DEMBLAKamitkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- 2017 Babu R Et Al - Refereed Paper - POWDERED ACTIVATED CARBON (PAC) WITH MEMBRANE FILTER PRESS PDFDocument7 pages2017 Babu R Et Al - Refereed Paper - POWDERED ACTIVATED CARBON (PAC) WITH MEMBRANE FILTER PRESS PDFnghiNo ratings yet
- Materials Comparison DIN / EN / ASTM: Finished PartsDocument6 pagesMaterials Comparison DIN / EN / ASTM: Finished PartsBittuNo ratings yet
- Valve QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesValve Questionnaireprnsh_k100% (2)
- Tolerance Clarification 720029483 PDFDocument1 pageTolerance Clarification 720029483 PDFQualitysm MicrotechprecisionengineeringNo ratings yet
- CPD 190811Document61 pagesCPD 190811Raktima Majumdar0% (1)
- Processing Guides Partially Oriented Yarn PDFDocument7 pagesProcessing Guides Partially Oriented Yarn PDFviren199008No ratings yet
- ASME Flange & PN RatingDocument7 pagesASME Flange & PN Ratinggetz_meNo ratings yet
- Design of Shell & Tube HX (Unprotected For Expert Excel Users)Document31 pagesDesign of Shell & Tube HX (Unprotected For Expert Excel Users)Sameer ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Bellow Seal ValvesDocument36 pagesBellow Seal ValvesJake SparrowNo ratings yet
- Forged Steel ValvesDocument23 pagesForged Steel ValvesElderMartinsNo ratings yet
- Shell MESC Number 774133.010.1 (NEAREST)Document2 pagesShell MESC Number 774133.010.1 (NEAREST)Ehsan Ur Rehman100% (1)
- AIT & IIT Construction (Carbon & Stainless Steel) : 3 Way Ball Valves PN 16Document4 pagesAIT & IIT Construction (Carbon & Stainless Steel) : 3 Way Ball Valves PN 16Jefferson OliveiraNo ratings yet
- ITB-spc For Tape Coating For UG Piping PDFDocument15 pagesITB-spc For Tape Coating For UG Piping PDFShyam Sundar GayenNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air Dryer: Industrial Ammonia SystemsDocument8 pagesCompressed Air Dryer: Industrial Ammonia Systemsfernando_tkm_65065No ratings yet
- Durco Plug Valve Dimensions PDFDocument28 pagesDurco Plug Valve Dimensions PDFjtai1983No ratings yet
- Eccentric Pipe Reducer DesignDocument1 pageEccentric Pipe Reducer DesignbdamitaNo ratings yet
- Securaseal Metal-Seated Ball Valves: ASME Classes: 150 - 4500 Sizes: - 24" (15 - 600 MM)Document28 pagesSecuraseal Metal-Seated Ball Valves: ASME Classes: 150 - 4500 Sizes: - 24" (15 - 600 MM)ANILNo ratings yet
- Conexiones de AceroDocument8 pagesConexiones de AceroRenzo Xavier Chavez HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Design Guide 7 Errata PDFDocument10 pagesDesign Guide 7 Errata PDFelidstone@hotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Ke Series Bearings En1337 PDFDocument16 pagesKe Series Bearings En1337 PDFShaheenHossainNo ratings yet
- Prelim Lecture Chapter 3Document72 pagesPrelim Lecture Chapter 3Herwinn Ruiz ReyesNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (4)
- Prediction of Tower FailureDocument7 pagesPrediction of Tower FailureDawood khanNo ratings yet
- Model 40D MT Triple Mast: Parts ManualDocument108 pagesModel 40D MT Triple Mast: Parts ManualChristian BedoyaNo ratings yet
- All-Terrain Crane AT-Kran Grue Tout Terrain Grúa Todo TerrenoDocument30 pagesAll-Terrain Crane AT-Kran Grue Tout Terrain Grúa Todo TerrenoMatias CarrizoNo ratings yet
- Assignment #1-Soil Exploration and Stress DistributionDocument2 pagesAssignment #1-Soil Exploration and Stress Distributionanurag shakyaNo ratings yet
- 2009 Wartsila 34DF Technology ReviewDocument16 pages2009 Wartsila 34DF Technology ReviewFlo MarineNo ratings yet
- F5OHQ1 F5OHQ2: Code 61 Connector Code 61 / SAE-ORB Code 62 Connector Code 62 / SAE-ORBDocument5 pagesF5OHQ1 F5OHQ2: Code 61 Connector Code 61 / SAE-ORB Code 62 Connector Code 62 / SAE-ORBHuy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Service Manual XW150 - Version02Document60 pagesService Manual XW150 - Version02demonhipNo ratings yet
- Proforma Invoice BMW Spare PartsDocument4 pagesProforma Invoice BMW Spare PartshatemcfmNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Grade LineDocument0 pagesHydraulic Grade LinemuazeemKNo ratings yet
- MN 28000 Ms Varilog Appendix Gea32917 EnglishDocument8 pagesMN 28000 Ms Varilog Appendix Gea32917 EnglishRodrigo ObregonNo ratings yet
- Terex PT-60 02662Document43 pagesTerex PT-60 02662Criselda PillayNo ratings yet
- Handling Qualites of CanardDocument49 pagesHandling Qualites of CanardUsman GhummanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of MaterialsDocument16 pagesThermodynamics of MaterialsAnthony AbelNo ratings yet
- High Temperature Deformation Behaviors of Hot Dip 55 WT% Al-Zn Coated SteelDocument11 pagesHigh Temperature Deformation Behaviors of Hot Dip 55 WT% Al-Zn Coated Steel張竣凱No ratings yet
- Long Test 8 September 2022Document5 pagesLong Test 8 September 2022Abigail Guzman VinuyaNo ratings yet
- Boom Lift - Man Lift Inspection ChecklistsDocument3 pagesBoom Lift - Man Lift Inspection ChecklistsAgung Tri SugihartoNo ratings yet
- Respuestos para El AutomovilDocument4 pagesRespuestos para El AutomovilMarcos CarrazcoNo ratings yet
- ECCM16 Paper IRC-Technologie UcsnikDocument8 pagesECCM16 Paper IRC-Technologie UcsnikgugugagaNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki PL PDFDocument20 pagesKawasaki PL PDFVictor Hemz100% (2)
- A-LOK Wallchart - SP3 - Parker FittingsDocument1 pageA-LOK Wallchart - SP3 - Parker FittingssanthoshkumarplNo ratings yet
- HWCH 12 BDocument3 pagesHWCH 12 BfcordNo ratings yet
- Subject - Machine Design - : Topic - Bevel GearsDocument12 pagesSubject - Machine Design - : Topic - Bevel GearsRohit GhulanavarNo ratings yet
- Towbar FORESTER - 292Document20 pagesTowbar FORESTER - 292Malakas Den Eimai100% (1)
- NTQ Electric ActuatorDocument19 pagesNTQ Electric ActuatorJennerousNo ratings yet
- WC-477 - Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) Modes of Transfer PDFDocument1 pageWC-477 - Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) Modes of Transfer PDFNathanLaertePiaiNo ratings yet
- Background On DSGDocument12 pagesBackground On DSGAhmed ElkadyNo ratings yet
- Bentone ST 120 KADocument40 pagesBentone ST 120 KAAsron Ferdian FalaahNo ratings yet
- 11R2 #OkayDocument24 pages11R2 #OkayEdilson AlvesNo ratings yet