Professional Documents
Culture Documents
K Eflp E, H : X I.si (KS Su D H, Q
Uploaded by
Fernando FanteOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
K Eflp E, H : X I.si (KS Su D H, Q
Uploaded by
Fernando FanteCopyright:
Available Formats
^0
V I -
vs =0.5
Es = c o n s ta n t w ith
d e p th
E la s tic s o il
KR = - ^ 4
R e sl 4
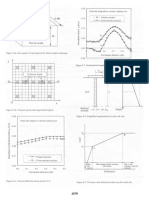
F ig u r e 5 .2 0 . E la s tic s o lu tio n s f o r u n r e s tr a i n e d f r e e - h e a d p ile in u n if o r m s o il ( lin e a r s o il m o v e m e n t p r o f il e ) ( C h e n & P o u lo s , 1 9 9 7 ).
V I -
vs = 0 .5
Es = Nh z
E la s tic s o il
0 0 .2 0 .4 0 .6 0 .8 1
z s /L z s /L _Hplp
Km= N „L 5
z , /L z , /L
F ig u r e 5 .2 1 . E la s tic s o lu tio n s f o r u n r e s tr a in e d f r e e - h e a d p ile in G ib s o n s o il ( lin e a r s o il m o v e m e n t p r o f ile ) ( C h e n & P o u lo s , 1 9 9 7 ).
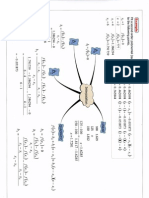
x = i.s i( K S (5.40) where su = undrained shear strength of clay; d = pile diameter; h,
= depth of clay layer; q is the applied embankment loading.
Comparisons between the bending moments computed from the
^ ' •* above equations and the design charts produced by Poulos
(1994c) suggest that these equations tend to give conservative
Kr =Eflp/ E,h* (5.42) estimates of the bending moments for relatively flexible piles.
2574
You might also like
- History of The KangaroosDocument21 pagesHistory of The KangaroosSean SikoraNo ratings yet
- Logsheets JGL - 0005Document1 pageLogsheets JGL - 0005Rahul KoppelaNo ratings yet
- FGE Electronique ESE 21-22 WDocument5 pagesFGE Electronique ESE 21-22 WSm NgNo ratings yet
- Ifilll: S /) S E/, Eu F 2 IDocument1 pageIfilll: S /) S E/, Eu F 2 IFadly ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- PA Data Viz R SolutionDocument11 pagesPA Data Viz R SolutionPriyanka RanaNo ratings yet
- Img - 0110 MCQ Ree Board Exam 213Document1 pageImg - 0110 MCQ Ree Board Exam 213Bugoy2023No ratings yet
- Antenna Temp and RadarDocument4 pagesAntenna Temp and Radarzetty_rashidNo ratings yet
- Img 0003Document3 pagesImg 0003Shayan AbagnaleNo ratings yet
- PA Data Viz RDocument8 pagesPA Data Viz RPriyanka RanaNo ratings yet
- InterpolatingDocument7 pagesInterpolatingFahmee TalibNo ratings yet
- ME Formula by Tordillo IMG - 0022Document1 pageME Formula by Tordillo IMG - 0022Arwyn BermasNo ratings yet
- ?iiril: /Q - QB S$ TDocument8 pages?iiril: /Q - QB S$ TJeremy TurnageNo ratings yet
- .5, S Eii - : Fi :H TX'&H Bo 6Document1 page.5, S Eii - : Fi :H TX'&H Bo 6Op Borang3No ratings yet
- Sssssss : SS: 5.4Tss-3Sss A TiDocument11 pagesSssssss : SS: 5.4Tss-3Sss A TiThành LêNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic TestDocument3 pagesDiagnostic TestmariaNo ratings yet
- W18Document6 pagesW18Sachin MalaviNo ratings yet
- Jadwal PATDocument2 pagesJadwal PATaisyahauliNo ratings yet
- Img 20221021 0002Document1 pageImg 20221021 0002perencanaan desa cicareuhNo ratings yet
- Don Juan Acid Rain StatementDocument1 pageDon Juan Acid Rain Statementkirsten_hallNo ratings yet
- Stress Functions ChoiceDocument4 pagesStress Functions ChoiceAnonymous JJaNDZoNo ratings yet
- The Zanzibar Leopard Between Science and CryptozoologyDocument3 pagesThe Zanzibar Leopard Between Science and CryptozoologyMartin Walsh100% (1)
- Guidelines For Style Analysis Jan LarueDocument1 pageGuidelines For Style Analysis Jan LarueExplorerNo ratings yet
- T CDocument1 pageT CKaran PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Img 0002Document1 pageImg 0002KîRäñFâtïmåNo ratings yet
- Abhirami SSLCDocument1 pageAbhirami SSLCBaiju PachikkodNo ratings yet
- Img - 0100 MCQ For Power & Ipe 187Document1 pageImg - 0100 MCQ For Power & Ipe 187rii amosNo ratings yet
- Img - 0015 MCQ Ece Board Exam 17Document1 pageImg - 0015 MCQ Ece Board Exam 17Bugoy2023No ratings yet
- Gardening Schedule 1Document1 pageGardening Schedule 1Andre AdriantoNo ratings yet
- Nytan Tetel0001Document1 pageNytan Tetel0001Konrád AndrisNo ratings yet
- Mmmlrorpnur: ImurlDocument1 pageMmmlrorpnur: Imurl范閔堯No ratings yet
- Banagher Precast Concrete - Bridge Beam Design ManualDocument49 pagesBanagher Precast Concrete - Bridge Beam Design ManualBeacher QNo ratings yet
- Adjustmen WasherDocument1 pageAdjustmen WasherSriram SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document11 pagesChapter 4Mohiminur Rahman IftyNo ratings yet
- Zrinyi 2019Document2 pagesZrinyi 2019Ecsedi Margareta100% (1)
- EF Iu: T (' A DBVDocument1 pageEF Iu: T (' A DBVRohmawatiNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0021 MCQ College Algebra 19Document1 pageIMG - 0021 MCQ College Algebra 19Hnqr584hNo ratings yet
- Tur Ies) V All Ey CH Ata LH T Ell T Ay Ina T Lis Et Ep e Ki Ne TH Öy ÜkDocument3 pagesTur Ies) V All Ey CH Ata LH T Ell T Ay Ina T Lis Et Ep e Ki Ne TH Öy ÜkMariacarmela MontesantoNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Mar 21 2023Document12 pagesAdobe Scan Mar 21 2023Wilbert MannNo ratings yet
- Tricky Maths (Arithmetic) Sunil Khurab (Sscstudy - Com)Document289 pagesTricky Maths (Arithmetic) Sunil Khurab (Sscstudy - Com)sdeepika_bNo ratings yet
- Derivatives NotesDocument7 pagesDerivatives NotesJamie TangcaNo ratings yet
- SCAN SERTIFIKAT - PNGDocument1 pageSCAN SERTIFIKAT - PNGsiti kurniyahNo ratings yet
- Sertifikat Enumerator 2018Document1 pageSertifikat Enumerator 2018Ahmad FedyaniNo ratings yet
- Flaker Aleksandar O POJMU AVANGARDEDocument6 pagesFlaker Aleksandar O POJMU AVANGARDEJovanaNo ratings yet
- TDS Certificate 2020Document1 pageTDS Certificate 2020sonam phunthsoNo ratings yet
- Fce Pratice Tests Mark Harrison PDF FreeDocument38 pagesFce Pratice Tests Mark Harrison PDF Freejiangjung2007No ratings yet
- Arc Length: Calculus BC Section 7.4: Arc Length and Surfaces of Revolution, Pg. 476Document4 pagesArc Length: Calculus BC Section 7.4: Arc Length and Surfaces of Revolution, Pg. 476Noor FarhanNo ratings yet
- FaciesDocument1 pageFaciesPrisaca CristianNo ratings yet
- Lab Enzymes BubblesDocument1 pageLab Enzymes BubblesGeeti S. SinghNo ratings yet
- Img PDFDocument1 pageImg PDFHaffi ZurindaNo ratings yet
- Img PDFDocument1 pageImg PDFHaffi ZurindaNo ratings yet
- Img PDFDocument1 pageImg PDFHaffi ZurindaNo ratings yet
- Img PDFDocument1 pageImg PDFHaffi ZurindaNo ratings yet
- TDD Routine June 16Document2 pagesTDD Routine June 16ani1167No ratings yet
- Img 20181212 0074Document1 pageImg 20181212 0074yudiNo ratings yet
- Loop Statements HandoutDocument3 pagesLoop Statements HandoutOckouri BarnesNo ratings yet
- Maths Without Use of Pen Pencil 2Document306 pagesMaths Without Use of Pen Pencil 2sameeringateNo ratings yet
- l1 IL Iql: Ç9 'A? YP PF: RT P' T:LDocument1 pagel1 IL Iql: Ç9 'A? YP PF: RT P' T:LbenNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0128 MCQ College Algebra 241Document1 pageIMG - 0128 MCQ College Algebra 241rii amosNo ratings yet
- Integration by Changing VairablesDocument7 pagesIntegration by Changing VairablesSophia MokNo ratings yet
- 1997 04 0014 PDFDocument2 pages1997 04 0014 PDFFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Crosswise-Loaded Pile Tests On Residual Soil Site: ICE Publishing: All Rights ReservedDocument5 pagesCrosswise-Loaded Pile Tests On Residual Soil Site: ICE Publishing: All Rights ReservedFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- International Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringDocument8 pagesInternational Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- 1969 03 0008 PDFDocument59 pages1969 03 0008 PDFFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- International Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringDocument7 pagesInternational Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- GTJ10676J 23315 PDFDocument8 pagesGTJ10676J 23315 PDFFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Document PDFDocument13 pagesDocument PDFFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Pile Diameter (MM) Pile Diameier (MM)Document1 pagePile Diameter (MM) Pile Diameier (MM)Fernando FanteNo ratings yet
- 391 TESe PDFDocument5 pages391 TESe PDFFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- 77 2001 04 0007 PDFDocument1 page77 2001 04 0007 PDFFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Pile Groups Arc in Acircular Configuration With Spacing Between Adjacent Piles 3diametersDocument1 pagePile Groups Arc in Acircular Configuration With Spacing Between Adjacent Piles 3diametersFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- (1 - 0 - 2 1 o G Lo (1 0 0 / (L / ¿) ) (1 - 8 R - + 2 5 T - 2) (5 - 8)Document1 page(1 - 0 - 2 1 o G Lo (1 0 0 / (L / ¿) ) (1 - 8 R - + 2 5 T - 2) (5 - 8)Fernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Et Al., Deep Excavation ExampleDocument1 pageEt Al., Deep Excavation ExampleFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Et Al. Et Al.Document1 pageEt Al. Et Al.Fernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Deformation Parameters - Shear ModulusDocument1 pageDeformation Parameters - Shear ModulusFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- 2 S 0 - 2 2 5 - 2 0 0 - 1 7 S - Is O - 1 2 5 - 1 0 0 - 7 S - 5 0 - 2 5Document1 page2 S 0 - 2 2 5 - 2 0 0 - 1 7 S - Is O - 1 2 5 - 1 0 0 - 7 S - 5 0 - 2 5Fernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Soil-Structure InteractionDocument1 pageSoil-Structure InteractionFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Check Moment Equilibrium Check Force EquilibriumDocument1 pageCheck Moment Equilibrium Check Force EquilibriumFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Eraf/ExiiDocument1 pageEraf/ExiiFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- 28 2001 04 0007Document1 page28 2001 04 0007Fernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Perfect Accuracy and Reliability: Figure 4.8. Summary of Soil Conditions Near Footing 1Document1 pagePerfect Accuracy and Reliability: Figure 4.8. Summary of Soil Conditions Near Footing 1Fernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Rate o F Settlement Creep and Secondary ConsolidationDocument1 pageRate o F Settlement Creep and Secondary ConsolidationFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- 0° 5° K KP V: ProgramsDocument1 page0° 5° K KP V: ProgramsFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- A Frqrferî"?: Figure 6.11. G Rid Used For FLA C 3D Analysis o F Pile GroupsDocument1 pageA Frqrferî"?: Figure 6.11. G Rid Used For FLA C 3D Analysis o F Pile GroupsFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Piled Raft Foundations: Li H H H - °°Document1 pagePiled Raft Foundations: Li H H H - °°Fernando FanteNo ratings yet
- U Niform Loads Young'S Modul: Eso Esav EsiDocument1 pageU Niform Loads Young'S Modul: Eso Esav EsiFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Instructor Dean For Academic AffairsDocument9 pagesInstructor Dean For Academic Affairsjhen bautistaNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current PDFDocument18 pagesAlternating Current PDFVishwa MoteNo ratings yet
- NIMS PosterDocument1 pageNIMS Posterアスリアナ イブラヒムNo ratings yet
- NMR UNit 1Document22 pagesNMR UNit 1magesh06No ratings yet
- Open Channel Hydraulics: CENG 3601Document21 pagesOpen Channel Hydraulics: CENG 3601Solomon MehariNo ratings yet
- Solving Indeterminate Structures - CompatibilityDocument24 pagesSolving Indeterminate Structures - CompatibilityY SAHITHNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Part 1Document8 pagesMagnetism Part 1AnonymousNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of The EyeDocument3 pagesThe Anatomy of The EyeChezcaDionisioNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Design Manual (Moss) 205Document1 pagePressure Vessel Design Manual (Moss) 205anu radha100% (1)
- Physics Calculations For A MangonelDocument18 pagesPhysics Calculations For A MangonelMiluNo ratings yet
- Unit 358 Unit 2 The Function of Electrical and Electronic CompDocument10 pagesUnit 358 Unit 2 The Function of Electrical and Electronic CompJean Paul RousselinNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Massachusetts Institute of Technology RibologyDocument3 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Massachusetts Institute of Technology RibologyHamood Al-bahraniNo ratings yet
- What Is Short Transmission Line - Its Phasor Diagram & ABCD Parameters - Circuit GlobeDocument19 pagesWhat Is Short Transmission Line - Its Phasor Diagram & ABCD Parameters - Circuit GlobeHumayun ArshadNo ratings yet
- Physics: Chapterwise Practise Problems (CPP) For JEE (Main & Advanced) Chapter - Units and MeasurementDocument4 pagesPhysics: Chapterwise Practise Problems (CPP) For JEE (Main & Advanced) Chapter - Units and MeasurementKripa mariam JosephNo ratings yet
- Weather InstrumentsDocument6 pagesWeather InstrumentskirkemmanNo ratings yet
- Schaum S Theory and Problems of State Space and Linear Systems PDFDocument246 pagesSchaum S Theory and Problems of State Space and Linear Systems PDFRajesh Gangwar100% (2)
- Welding PDFDocument18 pagesWelding PDFsatymu3No ratings yet
- Purlin & GirtDocument96 pagesPurlin & GirtudayvadapalliNo ratings yet
- Helical Antenna PDFDocument20 pagesHelical Antenna PDFOmar F'KassarNo ratings yet
- Motion - Worksheet 2Document4 pagesMotion - Worksheet 2Shrijeet SomaniNo ratings yet
- 4-1 / 6-1 Energy - Physics and Trilogy: 1.0 A Weightlifter Picks Up A BarbellDocument11 pages4-1 / 6-1 Energy - Physics and Trilogy: 1.0 A Weightlifter Picks Up A BarbellHaleemahNo ratings yet
- UlabyISMCh03Document58 pagesUlabyISMCh03taulanberishaNo ratings yet
- 3 Surface Roughness SymbolsDocument7 pages3 Surface Roughness SymbolsAMIRHUSAIN MOMINNo ratings yet
- CFD Simulation of Human Coughs and Sneezes: A Study in Droplet Dispersion, Heat, and Mass TransferDocument11 pagesCFD Simulation of Human Coughs and Sneezes: A Study in Droplet Dispersion, Heat, and Mass TransferNishant VermaNo ratings yet
- C. de Koninck - Random Reflections On Science & CalculationDocument37 pagesC. de Koninck - Random Reflections On Science & CalculationJoseph TrabbicNo ratings yet
- Conservation of MomentumDocument17 pagesConservation of MomentumWilma Y. VillasanNo ratings yet
- Audio Reality Bruce Rozenblit PDFDocument124 pagesAudio Reality Bruce Rozenblit PDFmehdi_mohebi2009100% (7)
- Refraction of Light (01!11!2023)Document5 pagesRefraction of Light (01!11!2023)navrosepreetsingh8a4hhps14No ratings yet
- Ex03 05 WorksheetDocument4 pagesEx03 05 Worksheetdrag600No ratings yet
- Electrostatics: Assignment IITJEE - 2023Document5 pagesElectrostatics: Assignment IITJEE - 2023Udharav KesarNo ratings yet
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsFrom EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNo ratings yet
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda Cans (Father's Day Gift for Science and Engineering Curious Dads)From EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda Cans (Father's Day Gift for Science and Engineering Curious Dads)No ratings yet
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansFrom EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Troubleshooting and Repair of Diesel EnginesFrom EverandTroubleshooting and Repair of Diesel EnginesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Rocks and Minerals of The World: Geology for Kids - Minerology and SedimentologyFrom EverandRocks and Minerals of The World: Geology for Kids - Minerology and SedimentologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignFrom EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (138)
- Crossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetFrom EverandCrossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- The Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeFrom EverandThe Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (59)
- Skyway: The True Story of Tampa Bay's Signature Bridge and the Man Who Brought It DownFrom EverandSkyway: The True Story of Tampa Bay's Signature Bridge and the Man Who Brought It DownNo ratings yet
- Structural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignFrom EverandStructural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Compendium of Best Practices in Road Asset ManagementFrom EverandCompendium of Best Practices in Road Asset ManagementNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Finite Element Analysis and Design of Steel and Steel–Concrete Composite BridgesFrom EverandFinite Element Analysis and Design of Steel and Steel–Concrete Composite BridgesNo ratings yet
- Summary of Taiichi Ohno's Taiichi Ohno's Workplace ManagementFrom EverandSummary of Taiichi Ohno's Taiichi Ohno's Workplace ManagementNo ratings yet