Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Python Cheat Sheet: Basic Data Types in 40 Characters
Uploaded by
Dario ROriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Python Cheat Sheet: Basic Data Types in 40 Characters
Uploaded by
Dario RCopyright:
Available Formats
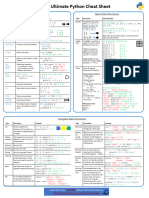
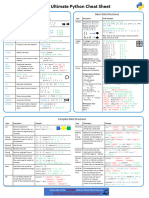
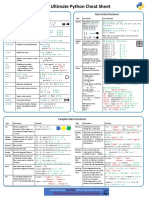
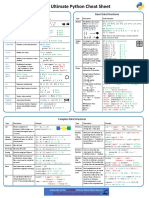
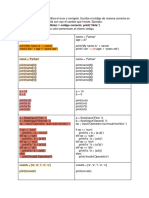
Python Cheat Sheet: Basic Data Types
“A puzzle a day to learn, code, and play” → Visit finxter.com
Description Example
Boolean The Boolean data type is a truth value, either ## 1. Boolean Operations
True or F alse. x, y = True, False
print(x and not y) # True
The Boolean operators ordered by priority: print(not x and y or x) # True
not x → “if x is False, then x, else y”
x and y → “if x is False, then x, else y” ## 2. If condition evaluates to False
x or y → “if x is False, then y, else x” if None or 0 or 0.0 or '' or [] or {} or set():
# None, 0, 0.0, empty strings, or empty
These comparison operators evaluate to True: # container types are evaluated to False
1 < 2 and 0 <= 1 and 3 > 2 and 2 >=2 and
print("Dead code") # Not reached
1 == 1 and 1 != 0 # True
Integer, An integer is a positive or negative number ## 3. Arithmetic Operations
Float without floating point (e.g. 3). A float is a x, y = 3, 2
positive or negative number with floating point print(x + y) # = 5
precision (e.g. 3.14159265359). print(x - y) # = 1
print(x * y) # = 6
The ‘//’ operator performs integer division. print(x / y) # = 1.5
The result is an integer value that is rounded print(x // y) # = 1
toward the smaller integer number print(x % y) # = 1s
(e.g. 3 // 2 == 1). print(-x) # = -3
print(abs(-x)) # = 3
print(int(3.9)) # = 3
print(float(3)) # = 3.0
print(x ** y) # = 9
String Python Strings are sequences of characters. ## 4. Indexing and Slicing
s = "The youngest pope was 11 years old"
The four main ways to create strings are the print(s[0]) # 'T'
following. print(s[1:3]) # 'he'
print(s[-3:-1]) # 'ol'
1. Single quotes print(s[-3:]) # 'old'
'Yes' x = s.split() # creates string array of words
2. Double quotes print(x[-3] + " " + x[-1] + " " + x[2] + "s")
"Yes"
# '11 old popes'
3. Triple quotes (multi-line)
"""Yes
## 5. Most Important String Methods
We Can"""
y = " This is lazy\t\n "
4. String method
print(y.strip()) # Remove Whitespace: 'This is lazy'
str(5) == '5' # True
print("DrDre".lower()) # Lowercase: 'drdre'
5. Concatenation
print("attention".upper()) # Uppercase: 'ATTENTION'
"Ma" + "hatma" # 'Mahatma'
print("smartphone".startswith("smart")) # True
print("smartphone".endswith("phone")) # True
print("another".find("other")) # Match index: 2
These are whitespace characters in strings.
print("cheat".replace("ch", "m")) # 'meat'
● Newline \ n
print(','.join(["F", "B", "I"])) # 'F,B,I'
● Space s
\
print(len("Rumpelstiltskin")) # String length: 15
● Tab t
\ print("ear" in "earth") # Contains: True
You might also like
- CheatSheet Python 2 Data StructuresDocument1 pageCheatSheet Python 2 Data StructuresSATYAJEET SARFARE (Alumni)No ratings yet
- CheatSheet Python 2 - Data StructuresDocument1 pageCheatSheet Python 2 - Data StructuresERICH PINZONNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Merged Programming PythonDocument9 pages1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Merged Programming PythonA HNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument1 pagePythonmepade9551No ratings yet
- Finxter WorldsMostDensePythonCheatSheetDocument1 pageFinxter WorldsMostDensePythonCheatSheetmachnik1486624No ratings yet
- Basic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseDocument8 pagesBasic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseJorge LuisNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Python Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesThe Ultimate Python Cheat Sheettrung_tien_datNo ratings yet
- Basic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseDocument7 pagesBasic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To Falseang_chang_1No ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Lab Manual# 1Document9 pagesDigital Image Processing Lab Manual# 1Washakh Ali Muhammad WaseemNo ratings yet
- Python Advance CheatsheetDocument11 pagesPython Advance Cheatsheetibrahimelothmani98No ratings yet
- Import: Numpy As NPDocument5 pagesImport: Numpy As NPstaffanyNo ratings yet
- PYTHON3 BASICS, INTERMEDIATE & ADVANCEDocument40 pagesPYTHON3 BASICS, INTERMEDIATE & ADVANCEtomtang77No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document8 pagesTutorial 1POEASONo ratings yet
- Find Second Largest Number List PythonDocument8 pagesFind Second Largest Number List PythonVinay SinghNo ratings yet
- Math and Python quick reference guide under 40 charactersDocument1 pageMath and Python quick reference guide under 40 charactersleeNo ratings yet
- Python BasicsDocument18 pagesPython BasicsMalli Naidu KarpurapuNo ratings yet
- perseprep1'Document5 pagesperseprep1'con.audrey1No ratings yet
- Python Example ProgramsDocument5 pagesPython Example Programsesmani84100% (1)
- Practical Assignment Xi SC (CS) - 2022-23Document8 pagesPractical Assignment Xi SC (CS) - 2022-23Adarsh Kumar PadhanNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument6 pagesPythonfarzad shaloNo ratings yet
- Pythin LearningsDocument51 pagesPythin LearningsNeha KhatriNo ratings yet
- Python BasicDocument18 pagesPython BasicAman UdyogNo ratings yet
- Python Notes and Cheat SheetsDocument10 pagesPython Notes and Cheat SheetsPRAFULL PATELNo ratings yet
- DanyDocument3 pagesDanydaNyNo ratings yet
- CheatSheet Python 1 Keywords 1 PDFDocument1 pageCheatSheet Python 1 Keywords 1 PDFRoberto Suarez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Week 8Document24 pagesWeek 8divya.kapoor04No ratings yet
- Mis 211Document17 pagesMis 211Reem MajedNo ratings yet
- Strings CheatsheetDocument7 pagesStrings CheatsheetAlice WNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument157 pagesPythonSRINIDHINo ratings yet
- Python Control Struct - VerboseDocument2 pagesPython Control Struct - VerbosemansourNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Journal ProgramsDocument34 pagesComputer Science Journal ProgramsABHI CODMNo ratings yet
- Latihan PythonDocument4 pagesLatihan Pythonrozita100% (1)
- TDTU Lab Guide for Python BasicsDocument8 pagesTDTU Lab Guide for Python Basicshuy phanNo ratings yet
- Phytoncodesxx 2Document12 pagesPhytoncodesxx 2Jennifer VeronaNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat Sheet EssentialsDocument2 pagesPython Cheat Sheet EssentialsAlexNo ratings yet
- Python Programming ExamplesDocument23 pagesPython Programming ExamplesAbu Al SaidNo ratings yet
- Kenny-230723-Python Super Cheat SheetDocument14 pagesKenny-230723-Python Super Cheat SheetvanjchaoNo ratings yet
- Finxter CheatSheets PythonDocument6 pagesFinxter CheatSheets PythonToldo94No ratings yet
- Practice On If ConditionDocument2 pagesPractice On If ConditionManohar DattNo ratings yet
- Acs Lab Record 21 OriginalDocument64 pagesAcs Lab Record 21 OriginalBomma DineshNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat Sheet & Quick ReferenceDocument35 pagesPython Cheat Sheet & Quick ReferenceMostafa MirbabaieNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesPython Cheat SheetVamshidhar Reddy100% (1)
- Flow of ControlDocument26 pagesFlow of ControlSudesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Code2pdf 65ced7de9de3bDocument10 pagesCode2pdf 65ced7de9de3bGenNo ratings yet
- 02 - Introduction To PythonDocument23 pages02 - Introduction To PythoniknowthissabrinaNo ratings yet
- CHEATSHEETDocument23 pagesCHEATSHEETNehemiah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Programming Cheatsheets All Aug2021Document37 pagesProgramming Cheatsheets All Aug2021Rini SandeepNo ratings yet
- 1012 Quick ReferenceDocument2 pages1012 Quick ReferenceCoffee And teaNo ratings yet
- Python 02 ExpressionDocument41 pagesPython 02 ExpressionYI-LIN CHANGNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat Sheet KeywordsDocument1 pagePython Cheat Sheet KeywordsDario RNo ratings yet
- Python Lab: Introduction to VariablesDocument15 pagesPython Lab: Introduction to Variablestala massadNo ratings yet
- CheatSheet Python BWSDocument9 pagesCheatSheet Python BWStanuja shihareNo ratings yet
- PYTHON 3 BEGINNER'S CHEATSHEET FOR PRINTING, VARIABLES, DATA TYPESDocument1 pagePYTHON 3 BEGINNER'S CHEATSHEET FOR PRINTING, VARIABLES, DATA TYPES?✨Me ✨?No ratings yet
- What Is PythonDocument10 pagesWhat Is Pythonskylarzhang66No ratings yet
- Summary in PythonDocument23 pagesSummary in PythonMd Himel HossainNo ratings yet
- Python Learning Made EasyDocument18 pagesPython Learning Made Easyb dNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat Sheet - Essential Python Syntax and ConceptsDocument25 pagesPython Cheat Sheet - Essential Python Syntax and ConceptsAbhisekh NayakNo ratings yet
- List of Foxy Videos 1-186Document5 pagesList of Foxy Videos 1-186Dario RNo ratings yet
- Chess Life Magazine 2021 - 02Document56 pagesChess Life Magazine 2021 - 02Dario RNo ratings yet
- Sergei Tkachenko - Bishop and Knight Save The DayDocument126 pagesSergei Tkachenko - Bishop and Knight Save The DayDario R100% (1)
- Learn Chess Fun WayDocument10 pagesLearn Chess Fun WayDario RNo ratings yet
- Dorfman MethodDocument2 pagesDorfman MethodDario RNo ratings yet
- Understanding GPRS TechnologyDocument27 pagesUnderstanding GPRS TechnologyDario RNo ratings yet
- Introduction to GSM Networks and Intelligent Network StandardsDocument6 pagesIntroduction to GSM Networks and Intelligent Network StandardsDario RNo ratings yet
- ChessBase 16 InstructionsDocument4 pagesChessBase 16 InstructionsDario RNo ratings yet
- FIDE Formular 100 PotezaDocument1 pageFIDE Formular 100 PotezaDario RNo ratings yet
- Learn Chess Fun WayDocument10 pagesLearn Chess Fun WayDario RNo ratings yet
- R2-200xxxx Clarification On PDSCH Rate-Matching Capabilities - v1Document10 pagesR2-200xxxx Clarification On PDSCH Rate-Matching Capabilities - v1Dario RNo ratings yet
- How to Think in Chess - Free Chess Ebook DownloadDocument288 pagesHow to Think in Chess - Free Chess Ebook DownloadDario RNo ratings yet
- IEEE - GSM-GPRS Architecture ProtocolsDocument13 pagesIEEE - GSM-GPRS Architecture Protocolscatalinxxx2003No ratings yet
- Eric Schiller - 639 Essential Endgame PositionsDocument402 pagesEric Schiller - 639 Essential Endgame PositionsDario R75% (4)
- Hanan W Russell - Russian For ChessplayersDocument53 pagesHanan W Russell - Russian For ChessplayersDario RNo ratings yet
- R2-200xxxx Clarification On PDSCH Rate-Matching Capabilities - v1Document10 pagesR2-200xxxx Clarification On PDSCH Rate-Matching Capabilities - v1Dario RNo ratings yet
- ChessBase 16 InstructionsDocument4 pagesChessBase 16 InstructionsDario RNo ratings yet
- Mobility Management in LTE Heterogeneous NetworksDocument111 pagesMobility Management in LTE Heterogeneous NetworksKkkkNo ratings yet
- Learn Chess Fun WayDocument10 pagesLearn Chess Fun WayDario RNo ratings yet
- Shashin MethodDocument11 pagesShashin MethodDario RNo ratings yet
- Chu Zhak in S SystemDocument75 pagesChu Zhak in S SystemSharif Mohd ZakiNo ratings yet
- Lev Polugaevsky - Hug-Polugaevsky - Biel 1986Document4 pagesLev Polugaevsky - Hug-Polugaevsky - Biel 1986Dario RNo ratings yet
- Isaac Lipnitsky - Reshevsky-Ragozin - Semmering 1937Document6 pagesIsaac Lipnitsky - Reshevsky-Ragozin - Semmering 1937Dario RNo ratings yet
- Roman's Chess Lab CollectionDocument6 pagesRoman's Chess Lab CollectionDario RNo ratings yet
- Enhancements of Narrowband IoT in 3GPP Rel-14 and Rel-15Document6 pagesEnhancements of Narrowband IoT in 3GPP Rel-14 and Rel-15Dario RNo ratings yet
- Tal vs Timman provides a concise titleDocument3 pagesTal vs Timman provides a concise titleDario RNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning With PythonDocument137 pagesMachine Learning With Pythontimirkanta100% (1)
- Survey On Energy Efficient NB-IoTDocument38 pagesSurvey On Energy Efficient NB-IoTDario RNo ratings yet
- Ben Graham Calculations Template - FinboxDocument8 pagesBen Graham Calculations Template - FinboxDario RNo ratings yet
- Learning Chess Workbook Step 1 (gnv64) PDFDocument57 pagesLearning Chess Workbook Step 1 (gnv64) PDFtariqNo ratings yet
- Case 11aDocument3 pagesCase 11aJesseNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Civil 3D 2011 TutorialsDocument22 pagesAutoCAD Civil 3D 2011 TutorialsAmy TuckerNo ratings yet
- StuffIt Deluxe Users GuideDocument100 pagesStuffIt Deluxe Users Guidesergio vieiraNo ratings yet
- KX-TA824: Programming ManualDocument236 pagesKX-TA824: Programming ManualFARHAN MEMONNo ratings yet
- 500 Word Summary CombinedDocument11 pages500 Word Summary Combinedapi-281492552No ratings yet
- 101 Mechanical Engineering Interview QuestionsDocument16 pages101 Mechanical Engineering Interview Questionsamr yosry100% (2)
- Context Analysis and Source EvaluationDocument97 pagesContext Analysis and Source EvaluationAnali BarbonNo ratings yet
- Oracle Session Traffic LightsDocument13 pagesOracle Session Traffic Lightspiciul7001No ratings yet
- About These Lesson Plans and ResourcesDocument8 pagesAbout These Lesson Plans and ResourcesAhmer TariqNo ratings yet
- CST 2410 Intro to Computer SecurityDocument3 pagesCST 2410 Intro to Computer SecurityMichael ZeroNo ratings yet
- Atomic Molecular Optical Physics by Hertel C Schulz, Volume 1Document710 pagesAtomic Molecular Optical Physics by Hertel C Schulz, Volume 1anon_user-p100% (3)
- How To Create InhumanityDocument13 pagesHow To Create InhumanityViolette Yi-Chin Lee100% (1)
- NewsNWSARReportWEB PDFDocument117 pagesNewsNWSARReportWEB PDFAnonymous NbMQ9YmqNo ratings yet
- Ayuda Swordfish CompilerDocument227 pagesAyuda Swordfish Compilerafgr1990No ratings yet
- GR 10 Economics P1 (English) November 2022 Possible AnswersDocument20 pagesGR 10 Economics P1 (English) November 2022 Possible Answerskabelomollo793No ratings yet
- Mortgage Credit Loss DistributionDocument25 pagesMortgage Credit Loss DistributionSwayambhu MandalNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics - Chapter 8 Notes: Estimating With Confidence 8.1 - Confidence Interval BasicsDocument2 pagesAP Statistics - Chapter 8 Notes: Estimating With Confidence 8.1 - Confidence Interval BasicsRhivia LoratNo ratings yet
- DLPDocument10 pagesDLPPalaming Jerico MelegritoNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and Algorithms in C++ Oleh Krisna AdiyartaDocument68 pagesData Structures and Algorithms in C++ Oleh Krisna Adiyartaindra nugrohoNo ratings yet
- Getting Started: Part One: IntroductionDocument13 pagesGetting Started: Part One: IntroductionibijbjibNo ratings yet
- 이산수학 유석인 pptDocument29 pages이산수학 유석인 ppt최규민100% (1)
- JUST Safety Audit ReportDocument3 pagesJUST Safety Audit ReportMohammad LiftawiNo ratings yet
- Assignement 11.57 Residual PlotDocument11 pagesAssignement 11.57 Residual PlotMridul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Building A Basic Low Poly Character Rig in Blender - Tuts+ 3D & Motion Graphics TutorialDocument70 pagesBuilding A Basic Low Poly Character Rig in Blender - Tuts+ 3D & Motion Graphics TutorialSergej TaneyevNo ratings yet
- Clark W Edwin Elementary Number TheoryDocument129 pagesClark W Edwin Elementary Number TheoryDireshan Pillay100% (1)
- Quiz Chapter 4 Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesQuiz Chapter 4 Questions and AnswersHữu100% (2)
- CV - Reza Kurnia Ardani - Project EngineerDocument2 pagesCV - Reza Kurnia Ardani - Project Engineerreza39No ratings yet
- Measures of Impact of Science and Technology on Indian AgricultureDocument318 pagesMeasures of Impact of Science and Technology on Indian AgricultureVikrant RaghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- DirectX TutorialDocument128 pagesDirectX Tutorialsilly_rabbitzNo ratings yet
- Ielts Writing Strategies and TechniquesDocument3 pagesIelts Writing Strategies and TechniquesBobNo ratings yet