Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handout Joint Failure Analysis Part 2
Handout Joint Failure Analysis Part 2
Uploaded by
Fran LeeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handout Joint Failure Analysis Part 2
Handout Joint Failure Analysis Part 2
Uploaded by
Fran LeeCopyright:
Available Formats
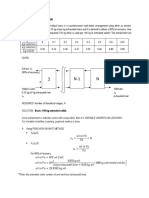
The following computation shows joint failure analysis in terms of pitch length.
Same principle applies with
a little modification on some equations.
RIVET SHEAR
𝑃 Symbol Definition
𝜏= P load
𝐴𝑠
N Refers to the number of rivets in a
𝜋 given pitch length
𝑃𝑠 = 𝜏𝐴𝑠 = 𝑁 𝑑2𝜏 As Cross sectional area of the rivet
4
shear
𝜏 Allowable shear stress for the rivet
material
d Diameter of rivet
RIVET/PLATE BEARING FAILURE
𝑃𝑏 = 𝑁(𝑑𝑡)𝜎𝑐 Symbol Definition
P load
N Refers to the number of rivets in
a given pitch length
𝜎𝑐 Allowable compressive stress of
the rivet or plate material
d Diameter of rivet
t Thickness of main plate
PLATE TEARING/ RUPTURE OF PLATE BY TENSION
𝑃𝑡𝑟𝑜𝑤 = (𝑝 ― 𝑑)𝑡𝜎𝑡 Symbol Definition
P load
𝜎𝑡 Allowable tensile stress of the
plate material
p Pitch length
d Diameter of rivet
t Thickness of main plate
STRENGTH OF THE JOINT
Strength of the riveted joint is evaluated by taking all possible failure paths in the joint into account, then determining
the largest load that can be safely applied.
EFFICIENCY OF A RIVETED JOINT
The efficiency of riveted joints is the ratio between the minimum strength of the joint against failure by tension, shear
or bearing to that of the members without a joint (or compared to the strength of the solid plate).
𝐽𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 𝑆𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑔𝑡ℎ
𝐽𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 𝑒𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦 =
𝑆𝑜𝑙𝑖𝑑 𝑃𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑆𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑔𝑡ℎ
𝑃𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑠𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑔𝑡ℎ = (𝑝𝑖𝑡𝑐ℎ)(𝑡ℎ𝑖𝑐𝑘𝑛𝑒𝑠𝑠)(𝐴𝑙𝑙𝑜𝑤𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑙𝑒 𝑠𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑠)
SAMPLE PROBLEMS:
1. A double riveted lap joint is made between 16 mm thick plate. The rivet diameter and pitch are 20 mm and 80 mm
respectively. The permissible stresses are 80 MPa in tension, 60 MPa in shear and 120 Mpa in crushing. Find the
efficiency of the joint.
2. A double riveted lap joint is made between 15 mm thick plates. The rivet diameter and pitch are 25 and 75 mm
respectively. If the ultimate stresses are 400 MPa in tension, 320 MPa in shear and 640 MPa in crushing, find the
minimum force per pitch which will rapture the joint.
If the above joint is subjected to a load such that the factor of safety is 4, find out the actual stresses developed in the
plates and the rivets.
3. Find the efficiency of the following riveted joints:
a. Single riveted lap joint of 6 mm plates with 20 mm diameter of rivets having a pitch of 50 mm.
b. Double riveted lap joint of 6 mm plates with 20 mm diameter rivets having a pitch of 65 mm. Assume:
Permissible tensile stress in plate = 120 MPa
Permissible shearing stress in rivets = 90 MPa
Permissible crushing stress in rivets = 180 Mpa
4. A double riveted double cover butt joint in plates 20 mm thick is made with 25 mm diameter rivets at 100 mm pitch.
The permissible stresses are:
𝜏 = 100 𝑀𝑃𝑎 𝜎𝜏 = 120 𝑀𝑝𝑎 𝜎𝑐 = 150 𝑀𝑃𝑎
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Constant Underflow Leaching SolutionDocument8 pagesConstant Underflow Leaching SolutionFran LeeNo ratings yet
- 25 0 ChE MOCK BOARD 4 4may2016 ANS KEY and SolnDocument6 pages25 0 ChE MOCK BOARD 4 4may2016 ANS KEY and SolnFran LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Materials of Construction Che 515 Chemical Process Equipment DesignDocument7 pagesChapter 7: Materials of Construction Che 515 Chemical Process Equipment DesignFran LeeNo ratings yet
- Acctg For Business Combination - Second Lesson PDFDocument21 pagesAcctg For Business Combination - Second Lesson PDFDebbie Grace Latiban Linaza100% (3)
- Movement For TelanganaDocument5 pagesMovement For TelanganaTanu RdNo ratings yet
- MNGT 6301 Final ExamDocument9 pagesMNGT 6301 Final Examdale huevo100% (1)
- Problem #34 - #35 (Notes On Roasting of Pyrites) PDFDocument10 pagesProblem #34 - #35 (Notes On Roasting of Pyrites) PDFFran LeeNo ratings yet
- Qu. All - NDocument28 pagesQu. All - NArima KouseiNo ratings yet
- Sedimentation Questions and ProblemsDocument1 pageSedimentation Questions and ProblemsFran LeeNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document5 pagesProblem Set 2Fran LeeNo ratings yet
- Plant Design MODocument21 pagesPlant Design MOFran LeeNo ratings yet
- Plant Design Prelims 1Document5 pagesPlant Design Prelims 1Fran LeeNo ratings yet
- Stripping With Direct Steam InjectionDocument1 pageStripping With Direct Steam InjectionFran LeeNo ratings yet
- 100 Questions On EvaporationDocument43 pages100 Questions On EvaporationFran Lee83% (6)
- D 42. 1053 Kmol/hr B 157. 8947 Kmol/hrDocument2 pagesD 42. 1053 Kmol/hr B 157. 8947 Kmol/hrFran LeeNo ratings yet
- Variable Leaching Solution 1Document6 pagesVariable Leaching Solution 1Fran LeeNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Unit OperationsDocument5 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Unit OperationsFran LeeNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessels Intro - CPEDDocument3 pagesPressure Vessels Intro - CPEDFran LeeNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Unit OperationsDocument5 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Unit OperationsFran LeeNo ratings yet
- Physical ChemistryDocument5 pagesPhysical ChemistryFran LeeNo ratings yet
- Humidification - Leaching PDFDocument5 pagesHumidification - Leaching PDFFran LeeNo ratings yet
- FiltrationDocument20 pagesFiltrationFran LeeNo ratings yet
- MathCast SRS DocumentationDocument49 pagesMathCast SRS DocumentationRamu BanothNo ratings yet
- Building Design ReportDocument6 pagesBuilding Design ReportJohn Rhey Almojallas BenedictoNo ratings yet
- MOVE: Journal of Community Service and Engagement: AbstrakDocument5 pagesMOVE: Journal of Community Service and Engagement: AbstrakSarah RondillaNo ratings yet
- QSC rmx850 rmx1450 rmx1850hd rmx2450Document56 pagesQSC rmx850 rmx1450 rmx1850hd rmx2450JRPB ASCOPENo ratings yet
- Macro Sessions 2-5 GDP PDFDocument129 pagesMacro Sessions 2-5 GDP PDFTarun Sai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Are We All Producers NowDocument16 pagesAre We All Producers NowAAliNo ratings yet
- How To Create AStripe AccountDocument5 pagesHow To Create AStripe AccountJarrod GlandtNo ratings yet
- Sample Research Paper Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesSample Research Paper Literature Reviewfyt3rftv100% (1)
- Kavikuyil G: Clinical Research - Clinical Data Management - Pharmacovigilance - Medical Chart ReviewDocument3 pagesKavikuyil G: Clinical Research - Clinical Data Management - Pharmacovigilance - Medical Chart Reviewmubarak patelNo ratings yet
- Mil-Hdbk-338b Electronic Reliability Design HandbookDocument1,046 pagesMil-Hdbk-338b Electronic Reliability Design HandbookDan AguNo ratings yet
- Going Green QuizDocument3 pagesGoing Green QuizDubravka CrnicNo ratings yet
- Annex VI - Final Narrative ReportDocument4 pagesAnnex VI - Final Narrative ReporttijanagruNo ratings yet
- Calculate Size of ContactorDocument3 pagesCalculate Size of ContactordhruvNo ratings yet
- The JIS Z 2801 & ISO 22196Document4 pagesThe JIS Z 2801 & ISO 22196anjaleeNo ratings yet
- TPH (Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons) : Immunoassay Method 10050Document10 pagesTPH (Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons) : Immunoassay Method 10050Cindy Valenzuela RuedaNo ratings yet
- HW2Document3 pagesHW2jaijailycNo ratings yet
- SEC 12 SDMS 02 - Rev04Document21 pagesSEC 12 SDMS 02 - Rev04heshamNo ratings yet
- BisoprololDocument10 pagesBisoprololSherif KamalNo ratings yet
- An Overview of IEEE Software Engineering Standards and Knowledge ProductsDocument46 pagesAn Overview of IEEE Software Engineering Standards and Knowledge ProductsNava GrahazNo ratings yet
- Cavite Mutiny Written ReportDocument6 pagesCavite Mutiny Written ReportDaisy KetchNo ratings yet
- Connecting Loop Units: Interactive Fire Detection SystemsDocument64 pagesConnecting Loop Units: Interactive Fire Detection SystemsProduktif TetapNo ratings yet
- Emergency ManagementDocument6 pagesEmergency ManagementAdult DemonNo ratings yet
- Table 1 - Tax Table 01Document182 pagesTable 1 - Tax Table 01wellawalalasithNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggeris (Penulisan) 014 UPPM 1/ 2018 Tahun 6 1 Jam 15 MinitDocument8 pagesBahasa Inggeris (Penulisan) 014 UPPM 1/ 2018 Tahun 6 1 Jam 15 MinitAli KhanNo ratings yet
- 2 To 8 Zone Sigma A-CP Apollo-1Document2 pages2 To 8 Zone Sigma A-CP Apollo-1EngTyranNo ratings yet
- Template Robot / I.O.TDocument32 pagesTemplate Robot / I.O.TIndah Permoni SuciNo ratings yet
- 03 Standards of Professional ... Egrity of Capital MarketsDocument14 pages03 Standards of Professional ... Egrity of Capital MarketsIves LeeNo ratings yet