Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHP +14+review
Uploaded by
Crista Evans0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesThe cardiovascular system consists of the heart, arteries, veins and capillaries but not the lungs. The heart has three layers and two upper chambers called atria that receive blood and two lower chambers called ventricles that pump blood out of the heart. Blood flows through the heart into the lungs then back to the left atrium and ventricle before being pumped through the aorta to the rest of the body. The cardiovascular system is regulated by electrical impulses generated in the sinoatrial node that trigger contractions of the atria and ventricles during the cardiac cycle. Common cardiovascular pathologies include diseases of the heart valves, inflammation of the heart layers, myocardial infarction, and abnormalities in heart rate and blood pressure.
Original Description:
review
Original Title
Chp.+14+Review
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe cardiovascular system consists of the heart, arteries, veins and capillaries but not the lungs. The heart has three layers and two upper chambers called atria that receive blood and two lower chambers called ventricles that pump blood out of the heart. Blood flows through the heart into the lungs then back to the left atrium and ventricle before being pumped through the aorta to the rest of the body. The cardiovascular system is regulated by electrical impulses generated in the sinoatrial node that trigger contractions of the atria and ventricles during the cardiac cycle. Common cardiovascular pathologies include diseases of the heart valves, inflammation of the heart layers, myocardial infarction, and abnormalities in heart rate and blood pressure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesCHP +14+review
Uploaded by
Crista EvansThe cardiovascular system consists of the heart, arteries, veins and capillaries but not the lungs. The heart has three layers and two upper chambers called atria that receive blood and two lower chambers called ventricles that pump blood out of the heart. Blood flows through the heart into the lungs then back to the left atrium and ventricle before being pumped through the aorta to the rest of the body. The cardiovascular system is regulated by electrical impulses generated in the sinoatrial node that trigger contractions of the atria and ventricles during the cardiac cycle. Common cardiovascular pathologies include diseases of the heart valves, inflammation of the heart layers, myocardial infarction, and abnormalities in heart rate and blood pressure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Chp.
14 Cardiovascular System
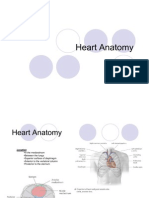
Componentsheart, arteries, veins, capillaries, venules, arterioles **not the lungs**
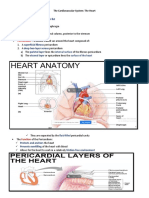
Layers of the heart
Pericardiumoutermost layer (fibrous capsule), parietal and visceral layers
Myocardiummiddle layer (muscle)
Endocardiuminnermost layer
Chambers of the heart
Atriasuperior, smaller, receive blood from the body
Ventriclesinferior, larger, pump blood away from the heart
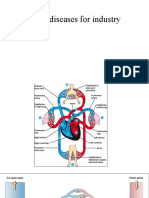
Blood flow through the heart
Superior vena cava/inferior vena cava/coronary sinusright atriumtricuspid
valveright ventriclepulmonary semilunar valvepulmonary trunkright/left
pulmonary arterieslungsright/left pulmonary veinsleft atriumbicuspid/mitral
valveleft ventricleaortic semilunar valveaorta
Cardiac Impulses
Sinoatrial node (SA)atrioventricular node (AV)AV bundle/bundle of HisPurkinje
fibers
Cardiac Cycle
Atrial contraction/systole=ventricular relaxation/diastole
Ventricular contraction/systole=atrial relaxation/diastole
Electrocardiogram
P waveatrial depolarization
QRS complexventricular depolarization
T waveventricular repolarization
Sinus rhythmnormal rhythm and heart rate
Arrhythmiaabnormal rhythm
Murmurabnormal sounds of the heart
Blood Vessels
Arterycarries blood away from the heart, thicker, more flexible
Veincarries blood back to the heart, thinner, has valves, less flexible
Layers of blood vessels
Tunica intimaendothelium, smooth
Tunica mediamuscle
Tunica adventitiaconnective tissue
Blood flow through vessels
Arteriesarteriolescapillariesvenulesveins
Pathologies
Rheumatic feverresult of streptococcus infection, damages valves of the heart
Endocarditisdamage/inflammation of the endocardium
Myocarditisinflammation of the myocardium
Pericarditisinflammation of the pericardium (very painful)
Myocardial infarction”heart attack”, tissue death as a result of lack of blood flow
Bradycardiaheart rate < 60bpm @ rest
Tachycardiaheart rate > 100bpm @ rest
Angina pectorischest pain as a result of restricted blood flow to the myocardium
Hypertensionhigh blood pressure (>140/90)
Hypotensionblood pressure (<110/60)
Cardiac output
CO=SV * HR cardiac output=stroke volume * heart rate
You might also like
- Heart Arrhythmias, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHeart Arrhythmias, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Med SurgDocument62 pagesMed SurgJean Soriano98% (65)
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cardiovascular Physical TherapyDocument204 pagesCardiovascular Physical Therapydivyam2008No ratings yet
- Heart Anatomy: LocationDocument45 pagesHeart Anatomy: LocationZaira100% (1)
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cardionursing 110207023802 Phpapp01Document18 pagesCardionursing 110207023802 Phpapp01LudwigJayBarayuga100% (5)
- Medical Terminology Cardiovascular SystemDocument35 pagesMedical Terminology Cardiovascular Systemapi-26819951486% (7)
- Heart Anatomy and Physiology PDFDocument100 pagesHeart Anatomy and Physiology PDFAndrés Menéndez Rojas100% (1)
- Cardionursing 110207023802 Phpapp01Document18 pagesCardionursing 110207023802 Phpapp01arvinnnnNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument8 pagesCongestive Heart Failureiancel_038893% (27)
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument73 pagesValvular Heart Diseaseindia2puppy100% (4)
- Chapter 19 Heart Marie BDocument29 pagesChapter 19 Heart Marie BomarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermDocument11 pagesChapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermJœnríčk AzueloNo ratings yet
- Döş TopografiDocument56 pagesDöş TopografiMahammad UsbaliyevNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument51 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystemAdeMumungNo ratings yet
- Sistem Kardiovaskular: Cardiac Output Dan Otot JantungDocument46 pagesSistem Kardiovaskular: Cardiac Output Dan Otot JantungSusanna Arie KNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument75 pagesCirculatory SystemSETH VILORIANo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Cardiovascular SystemDocument43 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Cardiovascular Systemsarah morleyNo ratings yet
- Arrythmia Heart Valves Cardiac FailureDocument52 pagesArrythmia Heart Valves Cardiac FailureCarlo MaxiaNo ratings yet
- Examinarea Clinică in Afecţiuni Ale Aparatului CardiovascularDocument49 pagesExaminarea Clinică in Afecţiuni Ale Aparatului CardiovascularFranceska LtkNo ratings yet
- Dr. I Gusti Ayu Widianti, M.Biomed: Anatomy Department, Faculty of Medicine Udayana UniversityDocument65 pagesDr. I Gusti Ayu Widianti, M.Biomed: Anatomy Department, Faculty of Medicine Udayana UniversitygedesuryawanNo ratings yet
- 19 Cardiac DisordersDocument51 pages19 Cardiac DisordersChessie Garcia100% (1)
- Cardiovascular System-Heart: Miss Wheeler Unit 8Document29 pagesCardiovascular System-Heart: Miss Wheeler Unit 8Ngatchou GaelleNo ratings yet
- Lect 8. Cardiovascular SystemDocument35 pagesLect 8. Cardiovascular Systemrukhsanatariq299No ratings yet
- Cardiac SystemDocument5 pagesCardiac SystemTanya TuckerNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCardiovascular SystemJeminah Fae CalmaNo ratings yet
- PulseDocument43 pagesPulseAngelo LacisteNo ratings yet
- Heart DiseasesDocument27 pagesHeart DiseasesHabib FrostNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Anatomy and Physiology: Iris Ken R. Rico, OTRPDocument90 pagesCardiac Anatomy and Physiology: Iris Ken R. Rico, OTRPAndra HijratulNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: The HeartDocument16 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: The HeartNicoleTrishiaDeparineNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument17 pagesCardiovascular SystemIbrahem SayedNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument101 pagesCardiovascular SystemBanessa Mae GarcianoNo ratings yet
- The HeartDocument65 pagesThe HeartMichael SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Heart AnatomyDocument7 pagesHeart AnatomyArjon BalaNo ratings yet
- CHD Fetal CirculationDocument31 pagesCHD Fetal CirculationNandita ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- CVS 2Document153 pagesCVS 2khalidtalal8000No ratings yet
- Physiology in CirculationDocument54 pagesPhysiology in CirculationPrincess CabilesNo ratings yet
- 3 CVSDocument10 pages3 CVSzabdullahstud1No ratings yet
- Pulse 160311110553Document43 pagesPulse 160311110553forever studentNo ratings yet
- Y2 Week 2 Aortic StenosisDocument4 pagesY2 Week 2 Aortic Stenosissurreal_blankNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular TermsDocument1 pageCardiovascular TermsTorio Kristine Anne P.No ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Heart and Neck VesselsDocument10 pagesChapter 20 Heart and Neck Vesselsannoja selvaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology NotesDocument56 pagesAnatomy & Physiology NotesChristina Gonez100% (2)
- Approach To Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument23 pagesApproach To Cardiovascular DiseasesanjivdasNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument35 pagesRheumatic Heart DiseaseSAYMABANUNo ratings yet
- اشرف بيركارديوم اند هارتDocument35 pagesاشرف بيركارديوم اند هارتبيلسان 'نNo ratings yet
- Mediastinal Anatomy: Superior Mediastin Um Middle Mediastin Um PericardiumDocument2 pagesMediastinal Anatomy: Superior Mediastin Um Middle Mediastin Um PericardiumBenjamin ChosichNo ratings yet
- 1-ch 20 - CardiovascularDocument142 pages1-ch 20 - Cardiovascularlouise navorNo ratings yet
- Left-Sided and Right Sided Heart FailureDocument40 pagesLeft-Sided and Right Sided Heart FailureDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- TM 8 TM 8only Clinical Exam of Heart and Circulatory System AGWEnglishDocument66 pagesTM 8 TM 8only Clinical Exam of Heart and Circulatory System AGWEnglishcellin rubianti azzharaNo ratings yet
- Cardio PathDocument6 pagesCardio PathPranay ManiarNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Heart f2f-s1b2-23Document36 pages5.4 Heart f2f-s1b2-23shlokNo ratings yet
- Hambers of The Heart: Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument1 pageHambers of The Heart: Coronary Artery DiseaseJOHNNY YNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Blood VesselsDocument12 pagesCardiovascular System: Blood VesselsSoniyaJI84100% (1)
- Ila College of Health Kuje: Cardiovascular SystemDocument24 pagesIla College of Health Kuje: Cardiovascular SystemDaniel DendaNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Cardiovascular Disease Complications: A Textbook for Medical StudentsFrom EverandPharmacotherapeutic Management of Cardiovascular Disease Complications: A Textbook for Medical StudentsNo ratings yet