Professional Documents
Culture Documents
No. Judul Penelitian Peneliti Metode Penelitian Sasaran Dan Lokasi Hasil Penelitian Referensi 1
Uploaded by
Christie Ismael0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesResume Jurnal Kaki Diabetik
Original Title
Resume Jurnal Kaki Diabetik
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentResume Jurnal Kaki Diabetik
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesNo. Judul Penelitian Peneliti Metode Penelitian Sasaran Dan Lokasi Hasil Penelitian Referensi 1
Uploaded by
Christie IsmaelResume Jurnal Kaki Diabetik
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Nama : Christie
NIM : PO.62.20.1.16.125
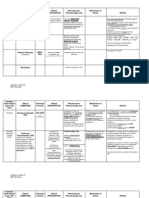
No. Judul Peneliti Metode Sasaran dan Hasil Penelitian Referensi
Penelitian Penelitian Lokasi
1 COMPARISO A.K Prospectiv Conducted in the Results: 13 wounds became pus culture Department of General
N OF Rajenderan, e Department of negative for organisms in 3rd culture sample Surgery, Stanley
EFFICACY Arun Babu, Comparati General Surgery , in study group, in control group, only 9 Medical College,
OF Kumaresan, ve Study. Stanley medical patients attained pus culture negativity in 8th Chennai – 600 001
NEGATIVE Raja College during the sample. 11 out of 20 patients,wound closure Affilated to the
PRESSURE Chandrasek period from April was attained within 2 weeks in study group. 8 Tamilnadu
WOUND ar, Gnana 2016 to September out of 20 patients, wound closure was Dr.M.G.R.Medical
THERAPY Sezhian 2016. 40 diabetic attained within 4 weeks. Complete clearance University
VS foot patients where of aerobic flora and anerobic flora was
CONVENTIO randomly divided observed much earlier in patients who l 4 | Issue 4 |October -
NAL into study group received NPWT. December | 2017
NORMAL (20 members) who Stanley Medical
SALINE received the NPWT was effective in reduction of bacterial Journal
DRESSING negative pressure flora of diabetic wounds.It was confirmed
IN DIABETIC wound therapy and with the pus culture. NPWT was effective in
FOOT control group (20 clearing aerobes and anerobic bacteria well
members) who and very effective in clearing pseudomonas
received only which was the most common organism
saline dressing. isolated from the wound. NPWT although it
Subsequently both created an anerobic atmosphere around the
group members wound,did not induce proliferation of
were assessed for anerobes. NPWT caused an increase in
wound size proliferation of granulation tissue which was
reduction and essential for wound closure especially by skin
control of grafting. Hence we found that NPWT Was
infection effective in reducing the bacterial burden of
the wound and caused proliferation of
granulation tissue needed for wound closure
and decreased the duration of wound closure
and hospital stay
2 tudy on Shareef, A cross- was carried out for A total of 122 pathogens were identified from 2018 Journal of Social
bacteriological Sandra sectional a period of eight 71 patients with male (63.38%) predominance Health and Diabetes |
profile and Sunny study months in the over females (36.61%). Out of the 71 patients, Published by Wolters
antibiotic , K. R. . Department of 38 (53.52%) patients had monomicrobial Kluwer ‑ Medknow
susceptibility Bhagavan surgery in patients infections and 33 (46.47%) patients had
pattern in with diabetic foot polymicrobial infections. Of the total 122
Shareef, et al.:
patients with ulcer at a tertiary organisms, 79(64.75%) organisms were found
Bacteriological profile
diabetic foot care teaching to be gram negative organisms and
and Antibiotic
ulcers in a hospital. Patient 43(35.24%) were gram positive.
susceptibility in
tertiary care data relevant to the Pseudomonas aeruginosa found in 22
Diabetic foot ulcer
teaching study were (18.03%) patients was the predominant
hospital collected using a pathogen isolated followed by Klebsiella
Javedh standard data pneumonia found
collection form in 18 (14.75%) patients. The gram-positive
designed as per the organisms isolated showed maximum
need of the study. susceptibility towards antibiotics Teicoplanin
Details of the and Linezolid while the gram-negative
organisms organisms showed susceptibility to Imipenem,
isolated and Meropenem, and Piperacillin/Tazobactum
susceptibility combination.
pattern were
collected from The study showed a preponderance of gram-
microbiology negative bacilli among the isolates from the
department diabetic foot ulcers. It is recommended that
antimicrobial sensitivity testing is necessary
for initiating appropriate antibiotic regimen
which will help to reduce the drug resistance
and minimize the healthcare costs.
You might also like
- Paediatric Emergency Drug DosesDocument1 pagePaediatric Emergency Drug DosesGloriaaaNo ratings yet
- Anabolic Steroid Guide Part 1Document9 pagesAnabolic Steroid Guide Part 1Dan InsignaresNo ratings yet
- Code Conduct Annual Report 2007Document162 pagesCode Conduct Annual Report 2007noordin01No ratings yet
- Calgevax BSG Bugarska EngDocument10 pagesCalgevax BSG Bugarska EngAnonymous idBsC1No ratings yet
- List of Indus of Pithampur ExcelDocument32 pagesList of Indus of Pithampur ExcelWHATSAPP VIRAL & FUNNY COMEDY MAST WALE VIDEOS100% (1)
- Evaluation of Prescribing Patterns of Antibiotics in General Medicine Ward in A Tertiary Care HospitalDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Prescribing Patterns of Antibiotics in General Medicine Ward in A Tertiary Care HospitalEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Contamination On Used Face Masks in Healthcare PersonnelDocument2 pagesBacterial Contamination On Used Face Masks in Healthcare PersonnelMaryam birmahNo ratings yet
- Artículo 14Document5 pagesArtículo 14Yeid EsquivelNo ratings yet
- A Study On Resistance Pattern of Bacteria Isolated From Diabetic and Non - Diabetic UlcersDocument7 pagesA Study On Resistance Pattern of Bacteria Isolated From Diabetic and Non - Diabetic UlcersBIOMEDSCIDIRECT PUBLICATIONSNo ratings yet
- Efficacy and Safety of Oral Administration of A Mixture of Probiotic Strains in Patients With Psoriasis: A Randomized Controlled Clinical TrialDocument7 pagesEfficacy and Safety of Oral Administration of A Mixture of Probiotic Strains in Patients With Psoriasis: A Randomized Controlled Clinical TrialHafid Adi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- DISSEMINATIONDocument8 pagesDISSEMINATIONAbbireddy SairamNo ratings yet
- Wound DehiscenceDocument4 pagesWound DehiscenceMario AbdiwijoyoNo ratings yet
- Efficacy and Safety of Rezafungin and Caspofungin in Candidaemia and Invasive CandidiasisDocument10 pagesEfficacy and Safety of Rezafungin and Caspofungin in Candidaemia and Invasive Candidiasisluis sanchezNo ratings yet
- Bacterial and Fungal Coinfections in Covid 19 Patients Hospitalized During The New York City Pandemic SurgeDocument5 pagesBacterial and Fungal Coinfections in Covid 19 Patients Hospitalized During The New York City Pandemic SurgeReynaldo CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Articulo Original DengueDocument10 pagesArticulo Original DengueMelany Juarez LuceroNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa 2030243Document10 pagesNejmoa 2030243Suit TeeNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionDocument7 pagesJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors and The Resistance Mechanisms Involved in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Mutation in Critically Ill PatientsDocument9 pagesRisk Factors and The Resistance Mechanisms Involved in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Mutation in Critically Ill PatientsElsiana LaurenciaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: A Prospective Study in A Tertiary Care HospitalDocument4 pagesMicrobiology of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: A Prospective Study in A Tertiary Care HospitalAde Yurga TonaraNo ratings yet
- Candidiasis in PICUDocument6 pagesCandidiasis in PICUMeirinda HidayantiNo ratings yet
- Research On Pathogenic Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance of Enterobacteriaceae in Hospitalized Elderly PatientsDocument5 pagesResearch On Pathogenic Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance of Enterobacteriaceae in Hospitalized Elderly PatientsVishwas gargNo ratings yet
- Articulo Klebsiella Pneumoniae PDFDocument5 pagesArticulo Klebsiella Pneumoniae PDFOscarEduardoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Bacteremia Between Community-Acquired and NosocomialDocument7 pagesCharacteristics of Bacteremia Between Community-Acquired and NosocomialKarla MéndezNo ratings yet
- Tabrizi An 2009Document4 pagesTabrizi An 2009Dung Tran HoangNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Flora in Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes and Their Sensitivity To Commonly Used AntibioticsDocument3 pagesVaginal Flora in Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes and Their Sensitivity To Commonly Used AntibioticsginNo ratings yet
- Paul 2018Document10 pagesPaul 2018Ricardo UchuyaNo ratings yet
- Articulo 3Document12 pagesArticulo 3JOSE MONTERONo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument10 pagesResearch ArticleEka ZulyaNo ratings yet
- Eclinicalmedicine: Research PaperDocument8 pagesEclinicalmedicine: Research PaperEl LitoralNo ratings yet
- Immunopathogenesis and Treatment of The Guillain-Barré Syndrome - Part IDocument11 pagesImmunopathogenesis and Treatment of The Guillain-Barré Syndrome - Part ISAMUEL ESCARESNo ratings yet
- CREMJHIDDocument9 pagesCREMJHIDAnggy de RinconNo ratings yet
- Prescription Patterns For TigecyclineDocument13 pagesPrescription Patterns For TigecyclineSamaa Al TabbahNo ratings yet
- Catater Ventriuclar Impregndados en Ab Sep 2010Document6 pagesCatater Ventriuclar Impregndados en Ab Sep 2010Felipe Anduquia GarayNo ratings yet
- Of Vaginal Candidosis With Econazole Nitrate and Nystatin: TreatmentDocument4 pagesOf Vaginal Candidosis With Econazole Nitrate and Nystatin: TreatmentMuthanna Lo'ayNo ratings yet
- Bacteriological Profile and Antibiotic Sensitivity Pattern of Clinical Isolates in A Tertiary Cancer Care Center in The Northeast IndiaDocument5 pagesBacteriological Profile and Antibiotic Sensitivity Pattern of Clinical Isolates in A Tertiary Cancer Care Center in The Northeast IndiaAtul Kumar GoyalNo ratings yet
- LSHTM Research Online: Usage GuidlinesDocument11 pagesLSHTM Research Online: Usage GuidlinesnomdeplumNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Infectious Diseases: SciencedirectDocument10 pagesInternational Journal of Infectious Diseases: Sciencedirectbe a doctor for you Medical studentNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia In+childrenDocument4 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia In+childrendai shujuanNo ratings yet
- Multidrug Resistant Uropathogens in Urinary Tract Infections and Their Antibiotic Susceptibility PatternsDocument4 pagesMultidrug Resistant Uropathogens in Urinary Tract Infections and Their Antibiotic Susceptibility PatternsCERCEL ALESIA IOANANo ratings yet
- Viral Oncolytic Immune TherapyDocument8 pagesViral Oncolytic Immune TherapyKingNo ratings yet
- Re 10Document2 pagesRe 10HArdik NegiNo ratings yet
- ElalfyEtal210213 TrmtCovid-IVM+Zn+Ribavirin+NitazoxanideDocument8 pagesElalfyEtal210213 TrmtCovid-IVM+Zn+Ribavirin+NitazoxanideR NobleNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Microbial Drug Resistance and Its Correlates in Chronic Diabetic Foot Ulcer InfectionsDocument9 pagesCharacteristics of Microbial Drug Resistance and Its Correlates in Chronic Diabetic Foot Ulcer InfectionsPutri Alif PermatasariNo ratings yet
- (M299) RL3Document11 pages(M299) RL3Jessa Louise TurredaNo ratings yet
- Efficacy and Safety of Baricitinib PDFDocument12 pagesEfficacy and Safety of Baricitinib PDFHoracioArizaNo ratings yet
- RRESEARCHDocument24 pagesRRESEARCHSABA YOUNASNo ratings yet
- MastitisDocument5 pagesMastitisAnonymous Kv0sHqFNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Ureaplasma Parvum Meningitis: A Case Report and Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesNeonatal Ureaplasma Parvum Meningitis: A Case Report and Literature ReviewVidya VidyutNo ratings yet
- S104 Abstracts, 5th DICIDDocument2 pagesS104 Abstracts, 5th DICIDAlex HydronNo ratings yet
- Deelder Et Al. - 2019 - Machine Learning Predicts Accurately Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Drug Resistance From Whole Genome Sequencing DataDocument9 pagesDeelder Et Al. - 2019 - Machine Learning Predicts Accurately Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Drug Resistance From Whole Genome Sequencing DatafdasffdNo ratings yet
- Espondilodiscitis Infecciosa Por Patógenos Poco ComunesDocument5 pagesEspondilodiscitis Infecciosa Por Patógenos Poco ComunesOthoniel RamirezNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Pengobatan Empiris Keratitis BakterialDocument16 pagesJurnal Pengobatan Empiris Keratitis BakterialimuhammadfahmiNo ratings yet
- Ruxolitinib For Glucocorticoid-Refractory Acute Graft-versus-Host DiseaseDocument11 pagesRuxolitinib For Glucocorticoid-Refractory Acute Graft-versus-Host DiseasemrboredguyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Spectrum and Antibiogram of Acinetobacter Infections in Children Study From A Tertiary Care Centre, IndiaDocument12 pagesClinical Spectrum and Antibiogram of Acinetobacter Infections in Children Study From A Tertiary Care Centre, IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A Hospital Based Prospective Study of Prevalence of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in Dermatology Indoor Patients by Phenotypic MethodDocument9 pagesA Hospital Based Prospective Study of Prevalence of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in Dermatology Indoor Patients by Phenotypic MethodIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- (M299) RL4Document9 pages(M299) RL4Jessa Louise TurredaNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryDocument10 pagesJournal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Risk Factors Associated With Rise of Non Albicans Candidemia at Nicu of A Tertiary Care InstituteDocument6 pagesEpidemiology and Risk Factors Associated With Rise of Non Albicans Candidemia at Nicu of A Tertiary Care InstituteIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Idr 14 1517Document10 pagesIdr 14 1517Sherwan HusseinNo ratings yet
- UveitisDocument10 pagesUveitisUtomo FemtomNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of A Double Carbapenem Combinations Again 2022 Saudi PharmaceuDocument7 pagesEffectiveness of A Double Carbapenem Combinations Again 2022 Saudi Pharmaceucfy28722psNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Profile of Corneal Ulcer in A Tertiary Eye Care CentreDocument6 pagesReview Article: Profile of Corneal Ulcer in A Tertiary Eye Care CentreNadhila ByantNo ratings yet
- Nebulized Colistin in The Treatment of Pneumonia Due To Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii and Pseudomonas AeruginosaDocument4 pagesNebulized Colistin in The Treatment of Pneumonia Due To Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii and Pseudomonas AeruginosaPhan Tấn TàiNo ratings yet
- Immunochromatography Candida SPPDocument5 pagesImmunochromatography Candida SPPMunawwar AweNo ratings yet
- Infections in Cancer Chemotherapy: A Symposium Held at the Institute Jules Bordet, Brussels, BelgiumFrom EverandInfections in Cancer Chemotherapy: A Symposium Held at the Institute Jules Bordet, Brussels, BelgiumNo ratings yet
- Sales Organization DesignDocument21 pagesSales Organization DesignakshayNo ratings yet
- OIntments (3) UplaodDocument27 pagesOIntments (3) UplaodFahad RasheedNo ratings yet
- What Is FDADocument10 pagesWhat Is FDAAchuthanand MukundanNo ratings yet
- Nigella Sativa Oil Lotion 20% vs. Benzoyl Peroxide Lotion 5% in The Treatment of Mild To Moderate Acne VulgarisDocument6 pagesNigella Sativa Oil Lotion 20% vs. Benzoyl Peroxide Lotion 5% in The Treatment of Mild To Moderate Acne VulgarisDita Rahmaika ANo ratings yet
- Biogenics & BiosimilarsDocument239 pagesBiogenics & BiosimilarsSooraj Rajasekharan Kartha100% (1)
- UNIT-3 2. Role of RADocument5 pagesUNIT-3 2. Role of RADheeraj JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 27 3 2014 - MWDDocument26 pages27 3 2014 - MWDTheMyawadyDailyNo ratings yet
- Validation Guide July2013Document37 pagesValidation Guide July2013Herdiwan NovindraNo ratings yet
- Ich GuidelinesDocument6 pagesIch GuidelinesVijay RavindranathNo ratings yet
- Indian Drug Manufacturers: Browse The Diseases AlphabeticallyDocument4 pagesIndian Drug Manufacturers: Browse The Diseases AlphabeticallyUday kumarNo ratings yet
- Jamu Indonesian Traditional Herbal Medicine TowardDocument24 pagesJamu Indonesian Traditional Herbal Medicine Towardseevalee BandaraNo ratings yet
- 20 Questions For Your Oncologist PDFDocument29 pages20 Questions For Your Oncologist PDFJoão JesusNo ratings yet
- Abdullahi V Pfizer PaperDocument2 pagesAbdullahi V Pfizer PaperTeam2KissNo ratings yet
- Development and Validation of RP - HPLC Method For The Estimation of Tylosin Tartrate in Pure and Pharmaceutical FormulationDocument8 pagesDevelopment and Validation of RP - HPLC Method For The Estimation of Tylosin Tartrate in Pure and Pharmaceutical FormulationSriram NagarajanNo ratings yet
- 261410761Document101 pages261410761ERNA KRISTINANo ratings yet
- Viburnum Opulus Materia Medica HerbsDocument3 pagesViburnum Opulus Materia Medica HerbsAlejandra Guerrero100% (1)
- HoxseyDocument7 pagesHoxseyuncoveringconsciousNo ratings yet
- What Is Route of Administration?Document4 pagesWhat Is Route of Administration?Quách Việt HoàngNo ratings yet
- Notification-SRO 412I - 2014-Dated-29 05 2014Document45 pagesNotification-SRO 412I - 2014-Dated-29 05 2014Naveed MahmudiNo ratings yet
- Eu GMP Annex 15 PDFDocument2 pagesEu GMP Annex 15 PDFBrian0% (1)
- Risk-Based Methodology For Validation of Pharmaceutical Batch Processes.Document14 pagesRisk-Based Methodology For Validation of Pharmaceutical Batch Processes.zombiecorpNo ratings yet
- Revco BrochureDocument24 pagesRevco BrochuremarcosfactoryNo ratings yet
- Rle TransesDocument29 pagesRle TransesElgen B. AgravanteNo ratings yet
- Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical SciencesDocument5 pagesResearch Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical SciencesDessy Erlyani Mugita SariNo ratings yet
- Group3 ElementsDocument7 pagesGroup3 ElementsPeter JimenezNo ratings yet