Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Goods and Services Tax
Uploaded by
nirankush rathore0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageGoods and Services Tax (GST) is an indirect tax introduced in India on July 1, 2017 that replaced multiple taxes imposed by central and state governments. GST is governed by a GST Council led by India's Finance Minister and taxes goods and services at rates from 0% to 50%, with special rates of 0.25% for rough precious stones and 3% for gold. The goal of GST was to replace indirect taxes with a unified tax to reshape India's $2 trillion economy.
Original Description:
Original Title
Goods and Services Tax.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGoods and Services Tax (GST) is an indirect tax introduced in India on July 1, 2017 that replaced multiple taxes imposed by central and state governments. GST is governed by a GST Council led by India's Finance Minister and taxes goods and services at rates from 0% to 50%, with special rates of 0.25% for rough precious stones and 3% for gold. The goal of GST was to replace indirect taxes with a unified tax to reshape India's $2 trillion economy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageGoods and Services Tax
Uploaded by
nirankush rathoreGoods and Services Tax (GST) is an indirect tax introduced in India on July 1, 2017 that replaced multiple taxes imposed by central and state governments. GST is governed by a GST Council led by India's Finance Minister and taxes goods and services at rates from 0% to 50%, with special rates of 0.25% for rough precious stones and 3% for gold. The goal of GST was to replace indirect taxes with a unified tax to reshape India's $2 trillion economy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
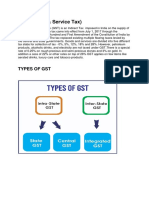
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an indirect tax which was introduced on 1 July 2017 and was
applicable throughout India, replacing multiple cascading taxes levied by the
central and state governments. It was introduced as The Constitution (One Hundred and First
Amendment) Act 2017,[1] following the passage of Constitution 122nd Amendment Act Bill. Under
GST, goods and services are taxed at the following rates, 0%, 0.25%, 3%, 5%, 12%, 18%, 28%,
29%, 31%, 43%, 45%, 48%, 50%
The GST is governed by a GST Council and its Chairman is the Finance Minister of India. [2]There is
a special rate of 0.25% on rough precious and semi-precious stones and 3% on gold.[3] In addition
a cess of upto 22% or other rates on top of 28% GST applies on few items like aerated drinks, luxury
cars and tobacco products.[4] GST was initially proposed to replace a slew of indirect taxes with a
unified tax and was therefore set to dramatically reshape the country's 2 trillion dollar economy.[5] It is
to be noted that France was the first country to implement GST.
You might also like
- How to Handle Goods and Service Tax (GST)From EverandHow to Handle Goods and Service Tax (GST)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Oods and Services Tax (GST) Is AnDocument1 pageOods and Services Tax (GST) Is AnArunPatilNo ratings yet
- Indirect Tax Central State: " ," Narendra Modi Said On Independence DayDocument1 pageIndirect Tax Central State: " ," Narendra Modi Said On Independence DayAnandan RanganadanNo ratings yet
- History: FormationDocument6 pagesHistory: FormationIshpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services TaxDocument1 pageGoods and Services TaxAli JanNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) Is An: o o o o o o o oDocument5 pagesGoods and Services Tax (GST) Is An: o o o o o o o oIshpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- The Reform Process of IndiaDocument3 pagesThe Reform Process of Indiashaikhnazneen100No ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) Is An: Indirect Tax Consumption Tax IndiaDocument26 pagesGoods and Services Tax (GST) Is An: Indirect Tax Consumption Tax Indiabest of all youtuberNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services TaxDocument12 pagesGoods and Services TaxBikram Jeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services TaxDocument5 pagesGoods and Services TaxAnonymous Jqzvi8xaeqNo ratings yet
- Goods & Services Tax CouncilDocument1 pageGoods & Services Tax CouncilDebabrata SarkarNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax (India) : This November Is Wikipedia Asian Month. Join The Contest and Win A Postcard From AsiaDocument13 pagesGoods and Services Tax (India) : This November Is Wikipedia Asian Month. Join The Contest and Win A Postcard From AsiaChander GcNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services TaxDocument2 pagesGoods and Services TaxThalir NeethimaniNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax DetailsDocument27 pagesGoods and Services Tax DetailsAyush MishraNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax (India) - WikipediaDocument58 pagesGoods and Services Tax (India) - WikipediaDubey ShraddhaNo ratings yet
- GST Impact On SME'sDocument6 pagesGST Impact On SME'sShiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax (India)Document10 pagesGoods and Services Tax (India)Skaytrender DotinNo ratings yet
- History: FormationDocument4 pagesHistory: Formationtinasoni11No ratings yet
- Prospectus of GST in IndiaDocument12 pagesProspectus of GST in IndiaDr.P. Siva RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax (India) - WikipediaDocument10 pagesGoods and Services Tax (India) - Wikipediaamit srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services TaxDocument15 pagesGoods and Services TaxSai Kumar ThirandiNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax INTRODUCTIONDocument7 pagesGoods and Services Tax INTRODUCTIONHrash guptaNo ratings yet
- 12 % GSTDocument103 pages12 % GSTAnonymous MhCdtwxQINo ratings yet
- Major Project On GSTDocument52 pagesMajor Project On GSTdeepakadhanaNo ratings yet
- Internal - I: Name - Ayush Kumar Singh PRN - 18010126240 Div - CDocument6 pagesInternal - I: Name - Ayush Kumar Singh PRN - 18010126240 Div - CAyush singhNo ratings yet
- History: FormationDocument6 pagesHistory: FormationIshpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Ambit Economy Thematic GST OverhypedDocument14 pagesAmbit Economy Thematic GST Overhypedsathiaseelans5356No ratings yet
- GST in India: A Key Tax Reform: ManagementDocument9 pagesGST in India: A Key Tax Reform: ManagementmainakroniNo ratings yet
- GST in India: A Key Tax Reform: ManagementDocument9 pagesGST in India: A Key Tax Reform: ManagementChandan SinghNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax (India) : HistoryDocument10 pagesGoods and Services Tax (India) : HistoryAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- GST WordDocument5 pagesGST WordkanchanakudaNo ratings yet
- GST Unit 1Document18 pagesGST Unit 1darshansah1990No ratings yet
- Project WorkDocument26 pagesProject WorkgoswamiphotostatNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST On IndiaDocument9 pagesImpact of GST On IndiaK'aundal AKNo ratings yet
- GST Management System: Samarth Polytechnic, BelheDocument24 pagesGST Management System: Samarth Polytechnic, BelheRohit GadekarNo ratings yet
- GST in India - Everything We Need To Know - Taxguru - inDocument3 pagesGST in India - Everything We Need To Know - Taxguru - inChandrika RajaramNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) Is A Successor To VAT Used in India On The Supply of Goods andDocument3 pagesGoods and Services Tax (GST) Is A Successor To VAT Used in India On The Supply of Goods andTPA LVBD PARAMAKUDINo ratings yet
- Gst-General Studies Project - Krishna Agarwal.11-DDocument17 pagesGst-General Studies Project - Krishna Agarwal.11-DKrishna AgarwalNo ratings yet
- BE Assignment 1Document20 pagesBE Assignment 1AdityaPalNo ratings yet
- ImplementationDocument1 pageImplementationVISHAL GUPTANo ratings yet
- ImplementationDocument1 pageImplementationVISHAL GUPTANo ratings yet
- A Synopsis On Impact and Challenges of GST in IndiaDocument8 pagesA Synopsis On Impact and Challenges of GST in IndiaPrince RamananNo ratings yet
- Omkar Black Book PDFDocument99 pagesOmkar Black Book PDFsam torresNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Good and Service TaxDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Good and Service TaxShubham KuberkarNo ratings yet
- Effect of GST On The Indian EconomyDocument4 pagesEffect of GST On The Indian EconomyShubham GargNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax REASERCH - EditedDocument6 pagesGoods and Services Tax REASERCH - EditedRohit Tripathi ModicareNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax: Benefits and Its Impact On Indian EconomyDocument7 pagesGoods and Services Tax: Benefits and Its Impact On Indian EconomyBADDAM PARICHAYA REDDYNo ratings yet
- BCO 08 Block 01Document38 pagesBCO 08 Block 01Anand GhadeiNo ratings yet
- Project Report On GST-2018Document32 pagesProject Report On GST-2018Piyush Chauhan50% (6)
- Project LaikaDocument77 pagesProject LaikaManju JhurianiNo ratings yet
- A Review On GST Execution and Its Effect PDFDocument9 pagesA Review On GST Execution and Its Effect PDFAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Awareness of GST Filing Among Retail Business in Hyderabad 1528 2635 SI 1 24-1-635Document21 pagesA Study On Awareness of GST Filing Among Retail Business in Hyderabad 1528 2635 SI 1 24-1-635BasavarajNo ratings yet
- GSTDocument5 pagesGSTAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Key Features: HistoryDocument3 pagesKey Features: HistorypranitaNo ratings yet
- GST (Goods and Services Tax) : An Analysis ofDocument3 pagesGST (Goods and Services Tax) : An Analysis ofMayank SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Types of Taxation Direct TaxDocument27 pagesChapter 1: Types of Taxation Direct TaxPriyanka SatamNo ratings yet
- GST NotesDocument47 pagesGST NotesChetanya KapoorNo ratings yet
- What Is The GST BillDocument6 pagesWhat Is The GST BillArun SharmaNo ratings yet
- GSTDocument7 pagesGSTStudy AllyNo ratings yet
- GST Bill A Study On India and Malaysia: Prepared By: Tushar AroraDocument9 pagesGST Bill A Study On India and Malaysia: Prepared By: Tushar AroraTushar AroraNo ratings yet