Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Introduction
Uploaded by
MohamedFittriCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Introduction
Uploaded by
MohamedFittriCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
0 INTRODUCTION
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are part of the large hydrocarbon family, aliphatic,
aromatic hydrocarbons, halogenated derivatives, alcohols, ketones and aldehydes. VOCs tend to
convert into vapor or gas without any changes in chemical. They are highly reactive hydrocarbons
and engage into the atmospheric photochemical reactions. Some of them have negligible
photochemical activity. However, they can act as crucial role as heat trapping gases in
atmosphere [1]. Majority of VOCs are of natural origin while many owe their existence to
anthropogenic activities. Examples of anthropogenic activities that produce VOCs are vehicular
emissions, petroleum products, chemicals, manufacturing industries, painting operations,
varnishes, coating operations, consumer products, petroleum handling, auto refinishing, cold
clean degreasing, printing inks and dry cleaning. Besides that, without us realizing, the
concentrations of many VOCs are consistently higher indoors which is more than 10 times than
outdoors. VOCs are emitted by a wide array from ten thousand of the products [2].
Organic chemicals are widely used as ingredients in household products. Paints,
varnishes and wax all contain organic solvents and do many cleanings, disinfecting, cosmetic,
degreasing and hobby products. All of these products can release organic compounds while you
are using them or stored [3]. Example of product that containing VOC are perfume where it is one
of the most utilized products in our daily life. Modern perfume fragrances are the mixtures of
natural and synthetic essential oils and aroma compounds. It is found that the component used
in perfume product are possibly contain VOC ingredients. For example, acetone, ethyl alcohol,
isopropyl, methacrylate, methyl or ethyl, acetaldehyde and ethyl acetate. VOC content are
classified as a toxic or hazardous by federal laws and it was found that every single product of
perfume containing VOC component [4]. Some of which may have short- and long-term adverse
health effects to human including eyes, nose, throat irritation, headache, damage liver, kidney
and central nervous system. Moreover, some organic in VOC can cause cancer to human and
animal. Last but not least, the environment also might be affected by the secondary pollutant that
created from VOC content in perfume. When people used the perfume at outdoor, VOC
component are most effective to volatile in air since sunlight is presence. Thus, this factor will
affect the ozone layer.
REFERENCES
A. Srivastava, D. Majumdar, Monitoring and Reporting VOCs in Ambient Air, Air Qual.
Monit. Assess. Manag. (2011) 137–148. doi:10.5772/16774.
Wallace L. A., Pellizzari E., Leaderer B., Zelon H. and Sheldon L. (1987) Emissions of
volatile organic compounds from building materials and consumer products. Atmospheric
Environment 21, 385-393.
Tichenor B. A. and Mason M. A. (1988) Organic emissions from consumer products and
building materials to the indoor environment.) APCA 38, 264-268.
G. Wieslander, D. Norback, E. Bjornsson, Int Arch Occupational Environmental Health
(1997), Paints and varnishes – Determination of volatile organic compound (VOC) content. Part
2: Gaschromatographic method.
Kelly, T.J., Mukund, R., Gordon, S.M., and Hays, M.J., Ambient Measurement Methods
and Properties of the 189 Title III Hazardous Air Pollutants, U. S. Environmental Protection
Agency, EPA Contract No. 68-DO0007, Work Assignment 44, Battelle, Columbus, OH, March
1994.
A. Tipler, The Characterization of Hop Aroma Using GC / MS, Headspace Trap and
Olfactory Port, Perkin Elmer Inc. Application Note. (2013).
M. Singal, D. Vitale, L. Smith, Fragranced products and VOCs, Environ. Health Perspect.
119 (2011). doi:10.1289/ehp.1103466.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Cev440 - Chemical Reaction EngineeringDocument2 pagesCev440 - Chemical Reaction EngineeringMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Cev440 - Chemical Reaction Engineering: Sms/elementary - ReactionsDocument2 pagesCev440 - Chemical Reaction Engineering: Sms/elementary - ReactionsMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Assignment NumecDocument4 pagesAssignment NumecMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- 5 6233135072879312915Document3 pages5 6233135072879312915MohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- 5 6233135072879312915Document3 pages5 6233135072879312915MohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Size Calculation:: T L G GDocument2 pagesSize Calculation:: T L G GMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Size Enlargement Through GranulationDocument1 pageSize Enlargement Through GranulationMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- RESULTSDocument3 pagesRESULTSMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- 5 6233135072879312915Document3 pages5 6233135072879312915MohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 Definitions and Classifications: Notes On This ChapterDocument3 pagesChapter 2.1 Definitions and Classifications: Notes On This ChapterMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- AssigmntDocument11 pagesAssigmntMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Mass BalanceDocument21 pagesChapter 5 - Mass BalanceMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Allergic RhintisDocument10 pagesAllergic RhintisMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- 4 ContentDocument25 pages4 ContentMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
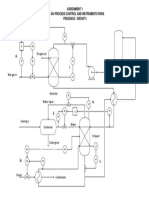
- Assignment 1 Cev 544 Process Control and Instrumentations PEH2246C2 / GROUP 5Document1 pageAssignment 1 Cev 544 Process Control and Instrumentations PEH2246C2 / GROUP 5MohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Biological Wastewater Treatment Case StudyDocument1 pageBiological Wastewater Treatment Case StudyMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document62 pagesChapter 2nidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 Definitions and Classifications: Notes On This ChapterDocument3 pagesChapter 2.1 Definitions and Classifications: Notes On This ChapterMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Elc 590 PersuasiveDocument4 pagesElc 590 PersuasiveMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document13 pagesAssignment 5MohamedFittri100% (1)
- Assignment 5: Optimization: (PO3, CO2)Document3 pagesAssignment 5: Optimization: (PO3, CO2)MohamedFittri0% (1)
- 1 Physico ChemicalWasteWaterTreatmentTechnologiesAnOverviewDocument13 pages1 Physico ChemicalWasteWaterTreatmentTechnologiesAnOverviewMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Asthma, Airway Symptoms and Rhinitis in Office Workers in Malaysia - Associations With House Dust Mite (HDM) Allergy, Cat Allergy and Levels of House Dust Mite Allergens in Office Dust PDFDocument14 pagesAsthma, Airway Symptoms and Rhinitis in Office Workers in Malaysia - Associations With House Dust Mite (HDM) Allergy, Cat Allergy and Levels of House Dust Mite Allergens in Office Dust PDFMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Test2 SolutionDocument5 pagesTest2 SolutionMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document6 pagesAssignment 2MohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- A2 Assignment Distill RedfracDocument1 pageA2 Assignment Distill RedfracMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Concentration Units in Environmental MeasurementsDocument8 pagesConcentration Units in Environmental MeasurementsMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- ObjectivesDocument2 pagesObjectivesMohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document1 pageExercise 1MohamedFittriNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Pantai 2 STP ReportDocument5 pagesPantai 2 STP ReportMoreen Daryl JustineNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics PDFDocument122 pagesThermodynamics PDFPrateek Srivastava100% (1)
- Nutrition Education Program: Department of Workforce ServicesDocument7 pagesNutrition Education Program: Department of Workforce ServicesRobert HartNo ratings yet
- Toluene ViscosityDocument8 pagesToluene ViscosityRajagopala Rao MandadapuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 NMRDocument126 pagesChapter 19 NMRMuchammad RofiiNo ratings yet
- Types of Electrical CablesDocument41 pagesTypes of Electrical CablesAbdullah NasirNo ratings yet
- Anti Cancer DrugsDocument3 pagesAnti Cancer DrugsDheaNo ratings yet
- Ice Cream StructureDocument11 pagesIce Cream StructureHon Le VanNo ratings yet
- STD1494 FRDocument20 pagesSTD1494 FREric FernandoNo ratings yet
- TDC For Plates - SA 516 65Document3 pagesTDC For Plates - SA 516 65Renny DevassyNo ratings yet
- Non MetalsDocument34 pagesNon MetalsDigvijay Patil100% (2)
- Electrostatic CoatingDocument8 pagesElectrostatic CoatingRinox RachidNo ratings yet
- The Petrology of The Abu Zawal Gabbroic Intrusion, Eastern Desert, Egypt: An Example of An Island-Arc SettingDocument11 pagesThe Petrology of The Abu Zawal Gabbroic Intrusion, Eastern Desert, Egypt: An Example of An Island-Arc Settingmohamed elshemyNo ratings yet
- US1744693 Erythritol TetranitrateDocument2 pagesUS1744693 Erythritol Tetranitrateteleson eliasNo ratings yet
- Convert Common UnitsDocument31 pagesConvert Common Unitsintania66No ratings yet
- Sizing An Ion Exchange SystemDocument14 pagesSizing An Ion Exchange Systemgnino2No ratings yet
- Evaluating Polymers and Phosphonates For Use As Inhibitors For Calcium, Phosphate and Iron in Steam BoilersDocument23 pagesEvaluating Polymers and Phosphonates For Use As Inhibitors For Calcium, Phosphate and Iron in Steam Boilersmnasiroleslami100% (3)
- Safety Data Sheet: Ac 9 Long Life Organic CoolantDocument5 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Ac 9 Long Life Organic Coolantraza239No ratings yet
- FakinasolDocument17 pagesFakinasolmasgontarNo ratings yet
- Main Groups in the Modern Periodic TableDocument4 pagesMain Groups in the Modern Periodic TableMohamed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chengpeng Ma 2018Document14 pagesChengpeng Ma 2018Dr.V.K.Bupesh RajaNo ratings yet
- Appendix E PDFDocument9 pagesAppendix E PDFRammiris ManNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis Project ReportDocument74 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis Project ReportnarendermbaNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report (1) .docxNEWDocument16 pagesSeminar Report (1) .docxNEWMd AwesshadabNo ratings yet
- Barium CarbonateDocument114 pagesBarium CarbonateUmakant BallureNo ratings yet
- BPG 01Document12 pagesBPG 01Ka Chun ChanNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2020 physics questions and solutionsDocument29 pagesJEE Advanced 2020 physics questions and solutionsVikash KumarNo ratings yet
- BS en 196-6-2010Document34 pagesBS en 196-6-2010Abey Vettoor100% (1)
- Manual NCT-3000 (En) PDFDocument15 pagesManual NCT-3000 (En) PDFvintiloiusNo ratings yet
- PSF-1,000cSt Pure Silicone Fluid Safety Data SheetDocument8 pagesPSF-1,000cSt Pure Silicone Fluid Safety Data SheetPearl JamNo ratings yet