Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lagrange Multiple
Uploaded by
nn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views5 pagesLagrange
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLagrange
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views5 pagesLagrange Multiple
Uploaded by
nnLagrange
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
ven 2s and DP, . ;
the stationary point 1s the
minima 4 AFC nepative,
Ths, Znin = 2 -
min 2 N25) #191 4 3 x (49) #50 + BB + 24 = 100
= 381 ~ 100 = 93)
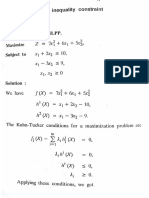
5. (b) Constrai
x . li hed extremal problem with more than one
quality constraint,
soe the non-linear programming problem giver below +
Optimize Zar tah
subject (0X) Hay + Bry = 2
Sxy + 2vy tay =5
X,X2,43 20
Solution :
Lagrangean function can be written as
7a) = 243 4x31 G1 tat 38-2) = Ay (Sey t2ep ht)
The necessary conditions for the maxima or minima are
of
Of = a, - ay - 54
ax] 1 1 2
OL = rw -4y- 24, = 0
Ox
0 .. (2)
il
2f = 2w,-34;-22 = 0
0x3 7
Resource Management Tec
CI Ini
af 2 (yt t3a7-2) = 0 o (4
aa @
ad 2 = Gate Br) a0 Ky)
2
Substituting the values of xy, %2. “3 from (1), (2), and (3) in
and (5), we get
Sly A +
atthe AA fA) -2=0
2 2
(or) 114, +104, = 4 (6)
5 A
5 (y+ 542), 20r +242) 3A t4n
and ere a 5 0
(or) Way FWAy = 10 (Or) Ay +34g = 1 =)
Solving (6) and (7) we get, Ay = 0.087 and 42 = 0.304
+ Equations (1), (2) and (3) yield x =
x3 = 0.283 as the solution. <
804, x = 0.348 and
To determine whether this solution point is a maxima or minima,
the following bordered Hessian matrix is constructed.
HB = [s 4|
P J
: (m +n) x (m +n)
\ ic optimisation Theory
ss 4.37
since, = 3, = 2 n—m=1 and I+ 1 = 5, This hi
Gia at f 5. This shows tha
aay oe principal minor of HP of order 5 needs to be solved. ;
e solved.
For maximization, the sign should be (—1)"** 5
= (-1)5 = ~1e
Foe eee i
and for mini ion, the sign should be (=1)™ = (-1)? = ye, Now
tie determinant of H® of order 5 is
feo1 4 3
soos 24 Orr Oae2Hat 00 5 |
Ihs 20 of =t]2 5 9 Of _, ft 5.2 0}
20 2 0 feetzaeeo eee 1200
'ib1g 0 2 Seeateee OHH Scceescea
Pa
iP 005 2
lee eee ual)
| ato]
gh Slee OaO
| 15 0 15 Ol]
=1l2]1 2 io) -1]1 2 2
a ee
15 0 |! 2 >|
fae Sie Oey
Salant B meu
ee ole (dee
5 2 4-2]! 2
+315 Mo 0| 1
460)
|
Since, the value is +ve, the above solution Minimizes the Objecy
function and
Zmin = (0.804)? + (0.348)? + (0.283)?
= 0,847
Solve the following non.
Lagrangean multipliers ;
‘linear programming problem, using the
Optimize = 4h +23 +53 — ary x,
X +x 443 = 15,
2x1 = x9 + 2x5 = 2%
X4,X2,x3 = 0
Subject to
Solution ;
The Lagrangean function can be written ag
SKA) =f 4234.3 — “eh Gr tay b4y—15) — A, (2) -xy-+205-20)
The necessary Conditions for the maxima and minima of U
objective function are
of
Ox,
of
ay Maat Ata, =0
of
ed 23-2; -24,
OX ag 24
les
— G1 tay tay
dA, tata as
0 - (dy, — x.
and # B= (2k) Xa + ey
BH = 40 ay 24 _
Bn
sic Optimisation Theory 4.39
a2g8i0
determine whether the stationary point is a maxima or a minima,
ple (m +n) x (m +n)
Since. n =3 and m=2,n—m=1 and 2n+1=5. This means
eat only one principal minor of Hy of the order 5 needs to be solved.
maximis
= —ve and
should be (—1)™" =(-1)? = +ve. In the
tion, the sign should be (-1)™*" = (-1)) =
+ve, hence Xp is a minimum point.
the solution Xp = (4.22.23) = (11/3, 10, 8) minimizes
¢ function, and
10) _ 820
oo.
$4 Kubn-Tucher condition - Simple problems
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Bhopal Gas TragedyDocument4 pagesBhopal Gas TragedynnNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Kuhntucker MultipleDocument5 pagesKuhntucker Multiplenn100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Bhopal Gas TragedyDocument4 pagesBhopal Gas TragedynnNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Ut3-Multicore QB UpdatedDocument9 pagesUt3-Multicore QB UpdatednnNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Multi-Core Processors: Page 1 of 25Document25 pagesMulti-Core Processors: Page 1 of 25nnNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- A5 FORMAT MC-RevisedDocument47 pagesA5 FORMAT MC-RevisednnNo ratings yet
- CS6801 PDFDocument2 pagesCS6801 PDFnnNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)