Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FMP - Forward & Futures Price Determination - SSEI
Uploaded by
kk ppOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FMP - Forward & Futures Price Determination - SSEI
Uploaded by
kk ppCopyright:
Available Formats
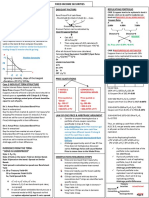
Forward & Futures Price Determination
Priced by the Prevention of Arbitrage Principle. ( Arbitrage means “Making Risk-less Profit” )
2 Types
Go long & short in 2 diff. derivatives Take a simultaneous long & short position
Today,such that there is +ve cash flow such that cash flow Today is nil & non- zero
Today & no risk of future loss. Prob. Of future profit.
PRICING OF A FWD CONTRACT VALUE OF A FWD CONTRACT OTHER LEARNING OUTCOMES
Price-The F/W Rate decided It refers to the amount that will be received or paid on A)
initially based on Prevention the cancellation or sale of the fwd contract. Investment Asset Consumption Asset
of Arbitrage. Value=ZERO ,to begin with.
Fwd Rate in the market
changes as time passes. Asset held for Asset held for
A)In case of Asset having no storage cost & no income investment. consumption eg.
copper,oil.
A)In case of Asset having no Value to the Long = S- Ke
-rt
storage cost & no income OR F/W /Futures price- F/W /Futures price-
CAN be determined by CANNOT be
rt
F=Se ( F-K )*e
-rt Arbitrage Arguments determined by
i.e. F=Spot Price + Funding where,F is the new F/W Rate Arbitrage Arguments
Cost & K is the old F/W Rate
rt
B) Short Selling-Borrow stock,sell it short
Case 1: If actual F > Se B)In case of Asset which provides known income Adv- Price fall,Short Int Rebate etc
-
Sell F/W, Buy spot & Borrow Disadv-Short squeeze, Price/Div Risk etc
funds at Rf
Value to the Long= S*-ke-rt C) Currency F/W Contracts
-CASH & CARRY ARBITRAGE
where, S =Ex coupon Spot Price=(S-I)
*
F= S e (rA-rB)t (if the quote is A/B)
Remember,
f= S*- ke-rAt
rt
Case 2: If actual F < Se
-Buy F/W,Shot sell spot & Value is denoted by f (Small f)
i.e.
Invest proceeds at Rf
f= S e-rBt-ke-rAt
-REVERSE CASH & CARRY Relationship btw F & E(S)
ARBITRAGE
F=E(S) {Pure Expectations Theory} D) Futures Price on commodities incorporating
F>E(S) {Normal Contango} income/storage cost and/or convenience yield.
Arbitrage Profit= Amt of
Mispricing
F<E(S) {{Normal Backwardation} F=(S+U)ert
Where U=PV of the storage cost
F ~ Sert FIRST EXPLANATION
KENES & HICKS
If storage cost is given as ctsly compounded rate,
Case 1:Hedgers are net short on the commodity
B)In case of Asset which (Eg. Bakery Firms)
To hedge, they wish to go long--- speculators wl go short F=Se(r+u)t
provides known income
,if, F>E(S) –NORMAL CONTANGO
(r+u)t
rt If F< Se , EVEN THEN,Reverse Cash & Carry
F=(S-I)e Case 2: Hedgers are net long on the commodity Arbitrage doesn’t occur-bcoz it’s a consumption
Where ;I = PV of div or coupon (Eg. Wheat farmers) asset.Convenience Yield is derived out of it.
within the maturity of the F/W To hedge, they wish to go short---speculators wl go long
Contract ,if, F<E(S) –NORMAL BACKWARDATION
So, F=Se(r+u-y)t
Case 3:Hedgers are neither net long nor net short
So, F= S*ert i.e. F=E(S) E) Delivery Options available in the Futures
*
where, S =Ex coupon Spot Market
Price SECOND EXPLANATION -which grade to deliver & when to deliver –
CAPM enjoyed by Short.
rt kt (r-k)t (r+u-y)t
F/e = E(ST)/e i.e. F=E(S)e ,where k= Rf+(Rm-Rf)Be In the eq:- F=Se i.e. F=Sect ,where
Remember, C=COST OF CARRY
Price is denoted by F (Capital Case 1: Beta=0 i.e. r=k i.e. F=E(S) Case 1: If c>0
F) Pure Expectations Theory r+u>y ( Assume delivery at the beginning of Month)
Case 2: +ve Beta i.e. k>r i.e. F<E(S) Case 2: If c<0
NORMAL BACKWARDATION y> r+u ( Assume delivery at the end of Month)
Case 3: -ve Beta i.e. k<r i.e. F>E(S)
NORMAL CONTANGO Page 20
You might also like
- FMP Mechanics of Futures SSEIDocument1 pageFMP Mechanics of Futures SSEIDIVYANSHU GUPTANo ratings yet
- FMP Mechanics of Futures SSEIDocument1 pageFMP Mechanics of Futures SSEIDIVYANSHU GUPTANo ratings yet
- Financial Risk Management Complete Notes PDFDocument305 pagesFinancial Risk Management Complete Notes PDFSagar KansalNo ratings yet
- HEDGING STRATEGIESDocument5 pagesHEDGING STRATEGIESasmaagartoum20No ratings yet
- Determine Forward and Futures PricesDocument36 pagesDetermine Forward and Futures PricesSherina JaneNo ratings yet
- BB - 3 - Futures & Options - Hull - Chap - 3Document31 pagesBB - 3 - Futures & Options - Hull - Chap - 3Ibrahim KhatatbehNo ratings yet
- BB - 5 - Futures & Options - Hull - Chap - 5Document21 pagesBB - 5 - Futures & Options - Hull - Chap - 5Ibrahim KhatatbehNo ratings yet
- 03 Forward Futures Pricing PDFDocument37 pages03 Forward Futures Pricing PDFSulaiman AminNo ratings yet
- Financial Derivatives: Prof. Scott JoslinDocument43 pagesFinancial Derivatives: Prof. Scott JoslinarnavNo ratings yet
- Unit FDocument73 pagesUnit Fsprayzza tvNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 ForwardsPrDocument29 pagesLecture 4 ForwardsPrKessellie T MulbahNo ratings yet
- Determination of Forward and Futures PricesDocument23 pagesDetermination of Forward and Futures PricesJitin MehtaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Forward and Futures: Lorenzo BretscherDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Forward and Futures: Lorenzo BretscheraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document10 pagesLecture 3Nhung Phuong Ha Nguyen100% (1)
- Financial Engineering and Risk Management: Martin Haugh Garud IyengarDocument10 pagesFinancial Engineering and Risk Management: Martin Haugh Garud IyengarWX YZNo ratings yet
- Hedging, Portfolio Insurance & Cascade TheoryDocument44 pagesHedging, Portfolio Insurance & Cascade TheorystanNo ratings yet
- DERVFOP - Lecture 3 (Hedging Strategies Using Futures)Document29 pagesDERVFOP - Lecture 3 (Hedging Strategies Using Futures)RedNo ratings yet
- Hedging StrategiesDocument19 pagesHedging StrategiesFirly IrhamniNo ratings yet
- L2 DRM - PricingDocument58 pagesL2 DRM - PricingAjay Gansinghani100% (1)
- 1.2 Forwards and Futures, Pricing - NotesDocument9 pages1.2 Forwards and Futures, Pricing - NotesTGCNo ratings yet
- Hedging and Related Risk Management TechniquesDocument18 pagesHedging and Related Risk Management TechniquesGaurav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Hedging Strategies Using Futures (MFFINTECH 6003Document29 pagesHedging Strategies Using Futures (MFFINTECH 6003Jessie DengNo ratings yet
- Soln CH 22 Futures IntroDocument5 pagesSoln CH 22 Futures IntroSilviu TrebuianNo ratings yet
- Long-Horizon Investing in A Non-CAPM World: Christopher Polk Dimitri Vayanos Paul WoolleyDocument42 pagesLong-Horizon Investing in A Non-CAPM World: Christopher Polk Dimitri Vayanos Paul WoolleyTom HardyNo ratings yet
- Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives: Using Futures For HedgingDocument19 pagesOptions, Futures, and Other Derivatives: Using Futures For HedgingDwijesh RajwadeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Derivatives and Risk Management Chance 9th Edition Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Derivatives and Risk Management Chance 9th Edition Solutions ManualRobertSchmidttjcdw100% (74)
- Unit-5 3 Put-Call Parity PrincipleDocument18 pagesUnit-5 3 Put-Call Parity PrincipleJack SparrowNo ratings yet
- Default Risk as an OptionDocument5 pagesDefault Risk as an OptionVeeken ChaglassianNo ratings yet
- Futures PDFDocument10 pagesFutures PDFYassine MalkiNo ratings yet
- Futures PDFDocument10 pagesFutures PDFsathvikNo ratings yet
- 11 LecturesDocument23 pages11 LecturesHa PhanNo ratings yet
- 2 Forwards&FuturesDocument4 pages2 Forwards&FuturesShivani Patnaik RajetiNo ratings yet
- SS 4 Mindmaps EconomicsDocument25 pagesSS 4 Mindmaps Economicshaoyuting426No ratings yet
- FM Section 15 SlidesDocument40 pagesFM Section 15 SlidesarmailgmNo ratings yet
- Derivatives - 3 - MFIN - Forward and FuturesDocument50 pagesDerivatives - 3 - MFIN - Forward and FuturesMavisNo ratings yet
- FMP Intro To Derivatives SSEIDocument1 pageFMP Intro To Derivatives SSEIDIVYANSHU GUPTANo ratings yet
- The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) : AssumptionsDocument4 pagesThe Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) : AssumptionsRomazh Sifuentes RamirezNo ratings yet
- Section2 2013Document7 pagesSection2 2013gogogogoNo ratings yet
- Midterm Formula SheetDocument1 pageMidterm Formula SheetPhuc Le Nguyen TrongNo ratings yet
- Forward and FuturesDocument8 pagesForward and Futures杨杨柳No ratings yet
- 55 Comparison of Accounting AssumptionsDocument8 pages55 Comparison of Accounting Assumptionsmanoranjan838241No ratings yet
- Refer Chap 022 SolutionsDocument5 pagesRefer Chap 022 SolutionsRahul BhangaleNo ratings yet
- Immunization With FuturesDocument18 pagesImmunization With FuturesNiyati ShahNo ratings yet
- Determination of Forward and Futures PricesDocument23 pagesDetermination of Forward and Futures PricesKira D. PortgasNo ratings yet
- Set 3 Pricing Forwards and FuturesDocument41 pagesSet 3 Pricing Forwards and Futuresrandom236272No ratings yet
- Hedging Strategies Using FuturesDocument23 pagesHedging Strategies Using FuturesFirly IrhamniNo ratings yet
- DRM 05Document41 pagesDRM 05Kannan MeiyurNo ratings yet
- Financial Engineering - OptionsDocument125 pagesFinancial Engineering - Optionsqari saibNo ratings yet
- 435x Lecture 1 Forward Contracts VfinalDocument37 pages435x Lecture 1 Forward Contracts Vfinalarjunbusiness7012No ratings yet
- Derivative Securities: Forwards and OptionsDocument47 pagesDerivative Securities: Forwards and OptionsDinesh BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Hedging Strategies Using Futures: Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives, 9th EditionDocument19 pagesHedging Strategies Using Futures: Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives, 9th EditionAvNo ratings yet
- Forward and Future Pricing 2 FinalDocument24 pagesForward and Future Pricing 2 FinalRahul Singh100% (1)
- Aakriti Gupta - 303 - FDDocument7 pagesAakriti Gupta - 303 - FDpriyanshu kesarwaniNo ratings yet
- Fin4003 - Lecture04 - Determination - of - Forward - and - Futures - Prices 14 Sep 2019Document39 pagesFin4003 - Lecture04 - Determination - of - Forward - and - Futures - Prices 14 Sep 2019Who Am iNo ratings yet
- Priyanshu Kesarwani 322 FDDocument7 pagesPriyanshu Kesarwani 322 FDpriyanshu kesarwaniNo ratings yet
- Determination of Forward and Futures PricesDocument42 pagesDetermination of Forward and Futures Priceskarthik chamarthyNo ratings yet
- Hedging Strategies Using FuturesDocument46 pagesHedging Strategies Using FuturesAradhita BaruahNo ratings yet
- Gen MathDocument25 pagesGen MathAndreaaAAaa TagleNo ratings yet
- 1 Binomial, Trinomial and More General One-Period ModelsDocument12 pages1 Binomial, Trinomial and More General One-Period Modelshenry37302No ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandCorporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
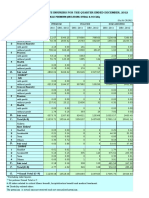
- December, 2012 (Life Segment-Wise)Document6 pagesDecember, 2012 (Life Segment-Wise)kk ppNo ratings yet
- Brigade Tranquil QuotationDocument4 pagesBrigade Tranquil Quotationkk ppNo ratings yet
- 7.GARP Code of ConductDocument2 pages7.GARP Code of ConductImran ShikdarNo ratings yet
- FRM II Notes and TrackerDocument4 pagesFRM II Notes and TrackerNitin PorwalNo ratings yet
- Brigade Painting TemplateDocument4 pagesBrigade Painting Templatekk ppNo ratings yet
- List of Courses in AustriaDocument37 pagesList of Courses in AustriaDiya MinhasNo ratings yet
- Premium Booklet Zone 1Document176 pagesPremium Booklet Zone 1kk ppNo ratings yet
- Fixed Income - Part I - SSEI PDFDocument1 pageFixed Income - Part I - SSEI PDFpare121No ratings yet
- QM - Monte Carlo & Gaussian - SSEIDocument1 pageQM - Monte Carlo & Gaussian - SSEIkk ppNo ratings yet
- QM - Monte Carlo & Gaussian - SSEIDocument1 pageQM - Monte Carlo & Gaussian - SSEIkk ppNo ratings yet
- QM Sampling SSEIDocument1 pageQM Sampling SSEIkk ppNo ratings yet
- Foundations - Financial Disasters - SSEIDocument1 pageFoundations - Financial Disasters - SSEIkk ppNo ratings yet
- FRM FormulasDocument104 pagesFRM Formulasprincelyprince100% (6)
- FMP - Hedging Strategies Using Futures 2 - SSEIDocument1 pageFMP - Hedging Strategies Using Futures 2 - SSEIkk ppNo ratings yet
- Prof. Spira's Top Ten Best Mucus-Free FoodsDocument17 pagesProf. Spira's Top Ten Best Mucus-Free Foodsetanksley50% (2)
- How Gut Bacteria Produce Key Brain Chemical: Last Updated: Friday, April 10, 2015 - 13:32Document2 pagesHow Gut Bacteria Produce Key Brain Chemical: Last Updated: Friday, April 10, 2015 - 13:32kk ppNo ratings yet
- Fixed Income - Part I - SSEI PDFDocument1 pageFixed Income - Part I - SSEI PDFpare121No ratings yet
- 01.05.17 IamjDocument4 pages01.05.17 IamjChintamani VeerrajuNo ratings yet
- Nism Series IV Interest Rate Derivatives Exam WorkbookDocument105 pagesNism Series IV Interest Rate Derivatives Exam Workbooksrv 99No ratings yet
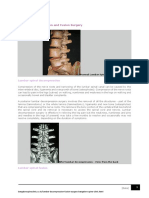
- Lumbar Decompression and Fusion Surgery (Dr. Kishen)Document5 pagesLumbar Decompression and Fusion Surgery (Dr. Kishen)kk ppNo ratings yet
- What Is A Mutual Fund ?: 3-Tier Structure of Mutual Funds & Other MF ConstituentsDocument9 pagesWhat Is A Mutual Fund ?: 3-Tier Structure of Mutual Funds & Other MF Constituentskk ppNo ratings yet
- Links To Books and Additional MaterialDocument2 pagesLinks To Books and Additional MaterialCarl FernandesNo ratings yet
- Mindless ReadingDocument3 pagesMindless Readingkk ppNo ratings yet
- FISHDocument183 pagesFISHkk ppNo ratings yet
- Adjacency ResumeDocument1 pageAdjacency Resumekk ppNo ratings yet
- Embryology - An Illustrated Colour TextDocument87 pagesEmbryology - An Illustrated Colour Text523mNo ratings yet
- Bai Salam & IstisnaDocument41 pagesBai Salam & IstisnaAlHuda Centre of Islamic Banking & Economics (CIBE)No ratings yet
- 2018 Bar Exam Syllabus in Mercantile Law PDFDocument16 pages2018 Bar Exam Syllabus in Mercantile Law PDFRalph Christian Lusanta FuentesNo ratings yet
- KOTAK TULIP Digital BrochureDocument7 pagesKOTAK TULIP Digital Brochureantriksh82No ratings yet
- Assignment On PartnershipDocument14 pagesAssignment On PartnershipNabil Islam 26No ratings yet
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor: Buyer BewareDocument2 pagesDoctrine of Caveat Emptor: Buyer BewarenatsumilkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-Rules Governing AcceptanceDocument6 pagesChapter 9-Rules Governing AcceptanceAngelica Joy ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Law of ContractsDocument13 pagesLaw of ContractsMalik Khurram AwanNo ratings yet
- Commercial Suggested Answers 1990 2006 WordDocument102 pagesCommercial Suggested Answers 1990 2006 WordJeimuel SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Notes and CommentsDocument10 pagesNotes and CommentsGracia SullanoNo ratings yet
- Good Evening Task 3Document1 pageGood Evening Task 3ShauryaNo ratings yet
- 250K Mortgage Commitment for 95 Ontario StDocument4 pages250K Mortgage Commitment for 95 Ontario StHarvey SpiegelNo ratings yet
- The Law of Contract 1Document80 pagesThe Law of Contract 1Diana Wangamati0% (1)
- Sell More With A Buyer Credit GuaranteeDocument2 pagesSell More With A Buyer Credit GuaranteeSalah AyoubiNo ratings yet
- Andres v. Manufacturers Hanover: Mistaken Payment RecoveryDocument2 pagesAndres v. Manufacturers Hanover: Mistaken Payment RecoveryHana Danische ElliotNo ratings yet
- 09 Section 9Document6 pages09 Section 9eyuelNo ratings yet
- IbcDocument62 pagesIbcpankaj vermaNo ratings yet
- Share Based Payments-ExercisesDocument6 pagesShare Based Payments-ExercisesReign TambasacanNo ratings yet
- A Reliquia Do Vale Do Trovão - Old DragonDocument81 pagesA Reliquia Do Vale Do Trovão - Old DragonMagno RodriguesNo ratings yet
- BDO Life Money 8secure BrochureDocument4 pagesBDO Life Money 8secure Brochurechedita obiasNo ratings yet
- Contract Drafting Assignment - ShreeyanshiDocument3 pagesContract Drafting Assignment - ShreeyanshiShreeyanshiNo ratings yet
- Sources of Labor Laws Contracts: Garcia, JJ ASSET PRIVATIZATION Promulgated: Trust, Respondent. October 24, 2005Document6 pagesSources of Labor Laws Contracts: Garcia, JJ ASSET PRIVATIZATION Promulgated: Trust, Respondent. October 24, 2005JoeyBoyCruzNo ratings yet
- Contract of AgencyDocument28 pagesContract of AgencyFrancis Ysabella BalagtasNo ratings yet
- MCQs on Contract Act, Sale of Goods Act and AgencyDocument11 pagesMCQs on Contract Act, Sale of Goods Act and AgencyAshish VyasNo ratings yet
- Contract Law Notes Unit 2Document11 pagesContract Law Notes Unit 2Kishore TNo ratings yet
- Role of Banks in Marine Insurance: Submitted To: Shri.N.Chandra Mohan Submitted By: K.Samhitha ROLL NO-FS10-017Document8 pagesRole of Banks in Marine Insurance: Submitted To: Shri.N.Chandra Mohan Submitted By: K.Samhitha ROLL NO-FS10-017Samhitha KandlakuntaNo ratings yet
- AFPRSBS and PEPI jointly liable for land sale rescissionDocument2 pagesAFPRSBS and PEPI jointly liable for land sale rescissionBeverlyn Jamison86% (7)
- 1 Certified Promissory NoteDocument5 pages1 Certified Promissory NoteLouis100% (8)
- Eight Different Kinds of Publishing DealsDocument5 pagesEight Different Kinds of Publishing DealsCharles Spencer Jr.No ratings yet
- CRM - ZuariDocument9 pagesCRM - ZuariKhaisarKhaisarNo ratings yet
- Module Title: Partnership Liquidation: Bcacctg2 - Accounting For Partnership and CorporationDocument25 pagesModule Title: Partnership Liquidation: Bcacctg2 - Accounting For Partnership and CorporationNimfa SantiagoNo ratings yet