Professional Documents
Culture Documents
May Grunwald Giemsa Stain PDF 17721 PDF
May Grunwald Giemsa Stain PDF 17721 PDF
Uploaded by
Abdul hameedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
May Grunwald Giemsa Stain PDF 17721 PDF
May Grunwald Giemsa Stain PDF 17721 PDF
Uploaded by
Abdul hameedCopyright:
Available Formats
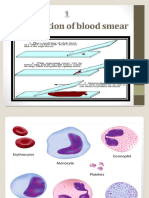
May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining
This is the commonly used staining of blood smears. Similarly, to other methods in
histology it is based on the electrostatic interaction between dye and target molecules. The
staining solutions contain methylene blue (a basic dye), related azures (also basic dyes) and eosin
(an acid dye). The basic dyes carry net positive charges, consequently they stain nuclei (because
of the negative charges of phosphate groups of DNA and RNA molecules), granules of basophil
granulocytes and RNA molecules of the cytoplasm of white blood cells. The eosin carries net
negative charge and stains red blood cells and granules of eosinophil granulocytes. It was
originally thought that the granules of neutrophil granulocytes were stained by a „neutral dye”
that formed when the above-mentioned dyes were combined, but the correct mechanism is not
clear.
The nuclei of white blood cells and the granules of basophil granulocytes appear in blue
(staining with basic dyes), while red blood cells and eosinophil granules in red (because of red
color of eosin). The cytoplasm of white blood cells are light blue, because of the low
concentration of RNA molecules.
Solutions:
1. May-Grünwald stain diluted with an equal volume of distilled water
2. Giemsa stain diluted with 9 volume of distilled water
Procedure of staining:
1. Stain the fixed smears for 5 minutes in May-Grünwald stain diluted with an equal volume of
distilled water!
2. Put the smears without washing for 30 minutes into Giemsa stain diluted with 9 volume of
distilled water!
3. Wash the smears in distilled water and let them dry!
4. Observe the stained blood cells in light microscope!
Results of the staining:
The nuclei of white blood cells appear in blue, whereas the cytoplasm in light blue color. The
cytoplasm of granulocytes contain some granules staining according to the type of the cell. The
red blood cells appear in red. Look for different types of leucocytes! Draw them into the lab
book!
You might also like
- Supravital StainingDocument19 pagesSupravital StainingSagar Sharma71% (14)
- Lesson-09 MODUL PDFDocument9 pagesLesson-09 MODUL PDFanggaririn100% (1)
- Enumeration of WBC - Differential Count (DC)Document10 pagesEnumeration of WBC - Differential Count (DC)Praveen DeepakNo ratings yet
- Stains and DyesDocument2 pagesStains and DyesSer OngNo ratings yet
- Wright's Stain Is A Histological Stain That Facilitates The Differentiation of Blood Cell TypesDocument6 pagesWright's Stain Is A Histological Stain That Facilitates The Differentiation of Blood Cell TypesDorisYsabelMejiaNo ratings yet
- Histology StainsDocument7 pagesHistology StainsFrozenMan100% (2)
- Romanowsky, Automated, and Pearls StainingDocument4 pagesRomanowsky, Automated, and Pearls Stainingادم Prabowo100% (1)
- Staining and Examination of Blood FilmsDocument50 pagesStaining and Examination of Blood FilmsderibewNo ratings yet
- Sysmex SEED The Role of The Peripheral Blood Smear in The Modern Haematology LaboratoryDocument5 pagesSysmex SEED The Role of The Peripheral Blood Smear in The Modern Haematology LaboratoryNona NonicaaNo ratings yet
- Romanowky StainsDocument45 pagesRomanowky StainsFinu FarisaNo ratings yet
- Stains NotesDocument5 pagesStains NotesSheba Dan de WiseNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Mast Cell and BasophilDocument2 pagesDifference Between Mast Cell and BasophilponbohacopNo ratings yet
- Quiz HistopathDocument3 pagesQuiz HistopathLeyNo ratings yet
- Staining of Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesStaining of Cell OrganellesDr Sanjeeb Kumar Dey BaidyaNo ratings yet
- Shashikant Mahadik Cytochemical StainingDocument62 pagesShashikant Mahadik Cytochemical StainingpathologyasthaNo ratings yet
- H&E STAIN (Mantasha)Document25 pagesH&E STAIN (Mantasha)gaminghub2605No ratings yet
- StainingDocument6 pagesStainingvictorymornah017No ratings yet
- Preparation and Staining Methods For Blood and Bone Marrow FilmsDocument7 pagesPreparation and Staining Methods For Blood and Bone Marrow Filmsادم PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Practical Class - Absolute Eosinophil CountDocument10 pagesPractical Class - Absolute Eosinophil CountZainMalik80% (5)
- STAININGDocument8 pagesSTAININGBabatunde AjibolaNo ratings yet
- Materials and MethodologyDocument3 pagesMaterials and Methodologykumar pitakaNo ratings yet
- Stains: For Blood and Bone MarrowDocument8 pagesStains: For Blood and Bone MarrowCahya SeptiaNo ratings yet
- Sample Cost Estimate Worksheets TemplateDocument7 pagesSample Cost Estimate Worksheets TemplateRod PasionNo ratings yet
- Histology-World! Histology Testbank-Blood 2aDocument6 pagesHistology-World! Histology Testbank-Blood 2aSamuel KebedeNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde FuchsinDocument9 pagesAldehyde FuchsinSheba Dan de WiseNo ratings yet
- 5 StainingDocument20 pages5 StainingDebashis SahaNo ratings yet
- What Are Some Common StainsDocument2 pagesWhat Are Some Common StainsaliaNo ratings yet
- Methylene Blue-Methylene Blue Stain Is A General Biological Stain Used To Highlight Parts of AnimalDocument2 pagesMethylene Blue-Methylene Blue Stain Is A General Biological Stain Used To Highlight Parts of AnimalleonorNo ratings yet
- Blood Smear StainingDocument7 pagesBlood Smear StainingParulNo ratings yet
- Blood Smear StainingDocument7 pagesBlood Smear StainingKashishNo ratings yet
- Understanding Romanowsky StainingDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Romanowsky StainingAnonymous eGLIFDNo ratings yet
- Haematology Test 2 Opp1 S5.pdf FinalDocument14 pagesHaematology Test 2 Opp1 S5.pdf FinalEl-rohyKalongoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HistologyDocument32 pagesIntroduction To HistologyPushparaj ShettyNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow ExaminationDocument1 pageBone Marrow ExaminationCloudy GemsNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Cytology Methods and Purpose: de Vera, Jim Ericson F. March 23, 2018 Bmls Histopathology: Tue / 7:00-9:00Document3 pagesDiagnostic Cytology Methods and Purpose: de Vera, Jim Ericson F. March 23, 2018 Bmls Histopathology: Tue / 7:00-9:00Rashedah MartinNo ratings yet
- Staining ProcedureDocument7 pagesStaining ProcedureBabatunde AjibolaNo ratings yet
- Special Staining Cytochemistry: BY Zenaida Capistrano-Cajucom, RMT, Ma - Ed.Mgt, FpametDocument93 pagesSpecial Staining Cytochemistry: BY Zenaida Capistrano-Cajucom, RMT, Ma - Ed.Mgt, FpametyepNo ratings yet
- Special Staining: Intan Chairun Nisa, S.Si., M.BiotechDocument46 pagesSpecial Staining: Intan Chairun Nisa, S.Si., M.BiotechKecil Dek100% (1)
- Papanicolaou StainDocument1 pagePapanicolaou StainRitam JoarderNo ratings yet
- CytochemistryDocument55 pagesCytochemistrySaad Zafar Awan100% (1)
- Histopath LecDocument10 pagesHistopath LecHaki TozakiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30 - CytochemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 30 - CytochemistryNathaniel SimNo ratings yet
- Blood Smear Lab ReportDocument6 pagesBlood Smear Lab ReportSharmilyNo ratings yet
- Giemsa StainDocument5 pagesGiemsa StainBarnali RoyNo ratings yet
- Different Staining MethodsDocument11 pagesDifferent Staining MethodsJermaine BalbanidaNo ratings yet
- Blood SmearDocument4 pagesBlood SmearHussein AlaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-02-15 at 19.49.42Document27 pagesScreenshot 2024-02-15 at 19.49.42hrd5s6zdfxNo ratings yet
- Bloodhana 2019 PDFDocument41 pagesBloodhana 2019 PDFAngelica Parreñas BayonaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1 Hematological StainingDocument20 pagesLecture - 1 Hematological StainingOjambo FlaviaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument24 pagesNotesSapna JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Staining of Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocument18 pagesChapter 20 Staining of Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDes MarquezNo ratings yet
- Color Reactions of Casein Protein and Enzymatic HydrolysateDocument4 pagesColor Reactions of Casein Protein and Enzymatic HydrolysateKat ViscoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Quantitative Color ReactionsDocument5 pagesExperiment 2: Quantitative Color ReactionsIson DyNo ratings yet
- LugolDocument6 pagesLugolJhon carlo CastroNo ratings yet
- Hematology: Ang, Karl Justin L., Mti University of Santo Tomas 4D-MTDocument44 pagesHematology: Ang, Karl Justin L., Mti University of Santo Tomas 4D-MTKarl J. AngNo ratings yet
- Cytochemical StainsDocument4 pagesCytochemical StainsMartin PinedaNo ratings yet
- Different Assays To Detect Presence of Activity of Enzymes in Specific OrganelleDocument8 pagesDifferent Assays To Detect Presence of Activity of Enzymes in Specific Organellefrancis harvey rodulfo100% (1)
- May Grunwald-GiemsaDocument1 pageMay Grunwald-GiemsaAndreeaBubuNo ratings yet
- Light and Colour Theories, and their relation to light and colour standardizationFrom EverandLight and Colour Theories, and their relation to light and colour standardizationNo ratings yet