Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Credit and Debit Card Fraud Prevention Tips
Uploaded by
Monika Saini0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views3 pages1. Credit and debit card fraud can take several forms such as altered or counterfeit cards, stolen numbers used for mail/phone/online orders, and altered payment terminals.
2. Employees should carefully inspect cards for signs of tampering or inconsistencies and compare signatures to prevent fraud.
3. If fraud is suspected, supervisors can request identification, call the card company for an authorization code, or contact authorities for assistance.
Original Description:
security
Original Title
CreditDebitCardFraudSecurityV1.2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Credit and debit card fraud can take several forms such as altered or counterfeit cards, stolen numbers used for mail/phone/online orders, and altered payment terminals.
2. Employees should carefully inspect cards for signs of tampering or inconsistencies and compare signatures to prevent fraud.
3. If fraud is suspected, supervisors can request identification, call the card company for an authorization code, or contact authorities for assistance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views3 pagesCredit and Debit Card Fraud Prevention Tips
Uploaded by
Monika Saini1. Credit and debit card fraud can take several forms such as altered or counterfeit cards, stolen numbers used for mail/phone/online orders, and altered payment terminals.
2. Employees should carefully inspect cards for signs of tampering or inconsistencies and compare signatures to prevent fraud.
3. If fraud is suspected, supervisors can request identification, call the card company for an authorization code, or contact authorities for assistance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Credit and Debit Card Fraud and Security Procedure
Western Illinois University
Introduction
Credit and Debit Card security is a shared responsibility. Merchants accepting cards must be on
guard against credit and debit card fraud. Basic steps are to be taken to protect both consumers
and the University from fraudulent card transactions.
Examples of Credit and Debit Card Fraud
Altered Cards. On an altered card, the name, expiration date, account number, and/or the
magnetic stripe have been changed in some way.
Altered Equipment. Be aware of any potential altering or tampering of credit and debit card
machines or devices.
Counterfeit Cards. Counterfeit cards bear a valid account number. A valid card number may
appear on the front of the card, in the magnetic stripe on the back of the card, or in both
places.
Lost/Stolen Card. A card is stolen from the cardholder and used fraudulently to purchase goods
or services from a legitimate merchant.
Mail Order/Phone Fraud. Someone other than the authorized cardholder obtains an account
number (often with the expiration date of the account and card validation code from the back
of the card) and uses it to purchase goods or services by mail or by phone.
Online Order Fraud. Someone other than the authorized cardholder obtains an account number
(often with the expiration date of the account and card validation code from the back of the
card) and uses it to purchase goods online.
What is Not Credit and Debit Card Fraud?
There are many legitimate reasons that a credit or debit card transaction may be declined.
Some examples follow.
• A payment on the account is overdue
• A technical malfunction has occurred during transaction processing
• An international purchase has been recently made with the card
• The card issuer has put a hold on the card
• The card was exposed to a potential security threat
• The customer has reached their credit card limit
• The card is expired
Point of Sale Credit and Debit Card Checklist for Employees
Become familiar with new card designs. Some cards are un-embossed. These cards may look
different – they have no raised (embossed) numbers, so you cannot make a manual imprint –
but the brand behind them is the same. Credit card chip technology adds an additional layer of
security protection.
Check the embossed numbers on the front of the card. If an account number is embossed, the
embossing should be clear and uniform in size and spacing. These numbers should not be
chipped away. And no “halos” of previous numbers should appear under the embossed account
number.
Examine the hologram. A hologram may be on the front or back of the card. The three-
dimensional hologram should reflect light and appear to move when the card is rotated.
Compare signatures. The back of the card must be signed, and the signature should reasonably
compare to the cardholder signature on the sales receipt. Check to make sure that it has not
been taped over, mutilated, erased or altered in any suspicious manner. The word “Void” on
the signature panel indicates that the signature panel has been tampered with.
Look at the magnetic stripe. The magnetic stripe on the reverse of the card should appear
smooth and straight, with no signs of tampering.
Examine the expiration date. The card should not be accepted after the last day of the “expires
end” or “valid thru” date embossed on the card. Merchant sales assistants must validate the
card expiration date.
For unsigned Credit and Debit Cards. Ask the customer to sign the credit card and supply an
official government ID. Verify that that the signature on the credit card and ID match.
Contact a Supervisor. If card verification steps have been followed and suspicious activity is
suspected, remain calm, keep hold of the card, inform the customer that additional card
verification is required, and contact a supervisor.
Supervisor Approval of Credit or Debit Card Transactions
Be observant of the customer’s behavior, does it seem normal, or does the person appear
uneasy? For your and your staff’s safety, do not, under any circumstances, confront or try to
apprehend the customer. If safety is a concern, call 911.
To verify that the customer using the card is the actual cardholder. You may request a form of
ID, however the customer has the right to not show an ID if the credit card is signed, or if they
cancel the purchase transaction.
To obtain a voice authorization code. Call the Authorization Center of the credit card company,
or the Merchant Bank of the debit card and request an Authorization Code.
For Credit Cards
• American Express Assistance Center 1-800-528-2121
• Discover Assistance Center 1-800-347-1111
• MasterCard Assistance Center 1-800-622-7747
• VISA Assistance center 1-800-847-2911
For Debit Cards
• Call the number on the back of the customer's debit card
Other Options
• Call your own Merchant Provider's Voice Authorization Number
If a fraudulent activity is suspected. Contact the following for assistance.
• If safety is a concern, call 911
• WIU Business Services – 309-298-1811
You might also like
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- 2708183603policy Initiatives - Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument6 pages2708183603policy Initiatives - Reserve Bank of IndiaMonika SainiNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- International Financial SystemDocument22 pagesInternational Financial SystemMonika SainiNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- DMGT549 International Financial Management PDFDocument249 pagesDMGT549 International Financial Management PDFMonika SainiNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- ClearancesDocument3 pagesClearancesmanchiprasadNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Chapter 16: Managing Risk in An Organization:, January 2003, P. 8Document34 pagesChapter 16: Managing Risk in An Organization:, January 2003, P. 8Monika SainiNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Paper: 08, International Business Operations: ManagementDocument15 pagesPaper: 08, International Business Operations: ManagementMonika SainiNo ratings yet
- Basel Norms for Capital Adequacy ExplainedDocument12 pagesBasel Norms for Capital Adequacy ExplainedMonika SainiNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- VII. International Financial Markets: HighlightsDocument22 pagesVII. International Financial Markets: HighlightsMonika SainiNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Paper: 08, International Business Operations: ManagementDocument15 pagesPaper: 08, International Business Operations: ManagementMonika SainiNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- ClearancesDocument3 pagesClearancesmanchiprasadNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Paper: 08, International Business Operations: ManagementDocument14 pagesPaper: 08, International Business Operations: ManagementMonika SainiNo ratings yet
- Paper: 08, International Business Operations: ManagementDocument12 pagesPaper: 08, International Business Operations: ManagementMonika SainiNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 19 UlabourlawshbDocument197 pages19 UlabourlawshbSaipramod JayanthNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- MIN BRO CHAPTER 2 Final PDFDocument18 pagesMIN BRO CHAPTER 2 Final PDFMonika SainiNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- BuybackDocument7 pagesBuybackRekha SoniNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Financial Derivatives 1Document7 pagesFinancial Derivatives 1Monika SainiNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- IFMDocument46 pagesIFMIvaturiAnithaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Credit PlanningDocument9 pagesCredit PlanningMonika Saini100% (1)
- Theories of MergersDocument8 pagesTheories of MergersRashwanth Tc96% (23)
- IFMDocument46 pagesIFMIvaturiAnithaNo ratings yet
- ClearancesDocument3 pagesClearancesmanchiprasadNo ratings yet
- CREDITDocument26 pagesCREDITMonika SainiNo ratings yet
- FM 406 PDFDocument257 pagesFM 406 PDFWotanngare NawaNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- IFMDocument46 pagesIFMIvaturiAnithaNo ratings yet
- IFMDocument46 pagesIFMIvaturiAnithaNo ratings yet
- FM 406 PDFDocument257 pagesFM 406 PDFWotanngare NawaNo ratings yet
- FileHandler PDFDocument46 pagesFileHandler PDFRab RakhaNo ratings yet
- Merchant Banking and Financial Servicest200813Document281 pagesMerchant Banking and Financial Servicest200813Prashant SaxenaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Security Analysis and Portfolio ManagementDocument352 pagesSecurity Analysis and Portfolio ManagementAnonymous V2hyzY1axNo ratings yet
- Form Vat-52Document2 pagesForm Vat-52khajuriaonlineNo ratings yet
- Marico Fund FlowDocument10 pagesMarico Fund FlowAbhishek KothariNo ratings yet
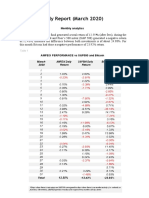
- AMFEIX - Monthly Report (March 2020)Document17 pagesAMFEIX - Monthly Report (March 2020)PoolBTCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Solutions 1Document9 pagesChapter 1 Solutions 1yebegashetNo ratings yet
- Juli 2021Document1 pageJuli 2021Vieny AyuznaNo ratings yet
- Questions On Mariott Case StudyDocument1 pageQuestions On Mariott Case StudyKaran BaruaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Li Mock B-Am-Solutions PDFDocument62 pages2019 Li Mock B-Am-Solutions PDFLucky Sky100% (2)
- Allen Stanford Criminal Trial Transcript Volume 11 Feb. 6, 2012Document317 pagesAllen Stanford Criminal Trial Transcript Volume 11 Feb. 6, 2012Stanford Victims CoalitionNo ratings yet
- Bill statement chargesDocument6 pagesBill statement chargesjjayNo ratings yet
- Reconcile Nostro Februari 2023Document56 pagesReconcile Nostro Februari 2023Riko RudyantoNo ratings yet
- Planet Starbucks Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesPlanet Starbucks Case AnalysisJugraj Dharni50% (2)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- ITO notice for escaped incomeDocument2 pagesITO notice for escaped incomeSukalp WarhekarNo ratings yet
- Submitted From:-Shampa Dhali (06) Priyanka Dhoot (07) Neeraj Gupta (14) Hardik Joshi (18) Jitendra MishraDocument24 pagesSubmitted From:-Shampa Dhali (06) Priyanka Dhoot (07) Neeraj Gupta (14) Hardik Joshi (18) Jitendra MishraShompa Dhali NandiNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of A LoanDocument12 pagesLife Cycle of A LoanSyed Noman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Interview With J Welles WilderDocument7 pagesInterview With J Welles WilderScribd-downloadNo ratings yet
- Cadbury Schweppes DF 2006Document1 pageCadbury Schweppes DF 2006JORGENo ratings yet
- Ghana Stock Exchange CourseDocument7 pagesGhana Stock Exchange CoursePrinceNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Advanced Financial Accounting 8th Edition Baker Chap020 PDFDocument26 pagesSolution Manual Advanced Financial Accounting 8th Edition Baker Chap020 PDFYopie ChandraNo ratings yet
- Dev't Planning - I Chap OneDocument20 pagesDev't Planning - I Chap Oneferewe tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Chicken Business PlanDocument16 pagesChicken Business PlanmschotoNo ratings yet
- Eobi Loan RegDocument6 pagesEobi Loan RegEOBI FEDERATION100% (1)
- Thomas J. Sargent, Jouko Vilmunen Macroeconomics at The Service of Public PolicyDocument240 pagesThomas J. Sargent, Jouko Vilmunen Macroeconomics at The Service of Public PolicyHamad KalafNo ratings yet
- Accounting Instructions 3Document1 pageAccounting Instructions 3Ely DanelNo ratings yet
- A Project On Camparative Study Between Private Sector and Public Sector BanksDocument75 pagesA Project On Camparative Study Between Private Sector and Public Sector Banksthaheerhauf1234No ratings yet
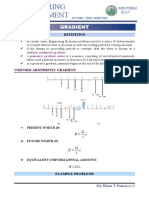
- Engineering Midterm Review: Gradient Series FormulasDocument7 pagesEngineering Midterm Review: Gradient Series FormulasHikaruNo ratings yet
- Neelkanth Palace Shop ValuationDocument3 pagesNeelkanth Palace Shop ValuationRaj GohilNo ratings yet
- 47-Corporate Salary Package - CSPDocument3 pages47-Corporate Salary Package - CSPmevrick_guyNo ratings yet
- ADM 3351-Final With SolutionsDocument14 pagesADM 3351-Final With SolutionsGraeme RalphNo ratings yet
- Working Capital of Coca ColaDocument3 pagesWorking Capital of Coca ColaSagor Aftermath0% (1)
- Original IMPORT INVOICE Number: 5589642625: Total Amount Due Condition Rate Base Value Total (USD)Document2 pagesOriginal IMPORT INVOICE Number: 5589642625: Total Amount Due Condition Rate Base Value Total (USD)AllyNo ratings yet
- My Spiritual Journey: Personal Reflections, Teachings, and TalksFrom EverandMy Spiritual Journey: Personal Reflections, Teachings, and TalksRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (26)
- Becoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonFrom EverandBecoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1478)
- The Book of Shadows: Discover the Power of the Ancient Wiccan Religion. Learn Forbidden Black Magic Spells and Rituals.From EverandThe Book of Shadows: Discover the Power of the Ancient Wiccan Religion. Learn Forbidden Black Magic Spells and Rituals.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Adventures Beyond the Body: How to Experience Out-of-Body TravelFrom EverandAdventures Beyond the Body: How to Experience Out-of-Body TravelRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Notes from the Universe: New Perspectives from an Old FriendFrom EverandNotes from the Universe: New Perspectives from an Old FriendRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (53)
- Conversations with God: An Uncommon Dialogue, Book 1From EverandConversations with God: An Uncommon Dialogue, Book 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (66)