Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SI Perry's
SI Perry's
Uploaded by
Alfredo del Giudice0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pagetavola periodica
Original Title
SI Perry's - Copia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenttavola periodica
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageSI Perry's
SI Perry's
Uploaded by
Alfredo del Giudicetavola periodica
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
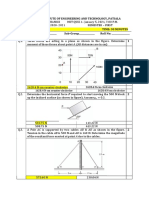
TABLE 1-1 SI Base and Supplementary Quantities and Units TABLE 1-2b Additional Common Derived Units of SI
SI unit symbol Quantity Unit Symbol
(“abbreviation”);
Use roman acceleration meter per second squared m/s2
Quantity or “dimension” SI unit (upright) type angular acceleration radian per second squared rad/s2
angular velocity radian per second rad/s
Base quantity or “dimension” area square meter m2
length meter m concentration (of amount of mole per cubic meter mol/m3
mass kilogram kg substance)
time second s current density ampere per square meter A/m2
electric current ampere A density, mass kilogram per cubic meter kg/m3
thermodynamic temperature kelvin K electric-charge density coulomb per cubic meter C/m3
amount of substance mole* mol electric-field strength volt per meter V/m
luminous intensity candela cd electric-flux density coulomb per square meter C/m2
Supplementary quantity or “dimension” energy density joule per cubic meter J/m3
plane angle radian rad entropy joule per kelvin J/K
solid angle steradian sr heat capacity joule per kelvin J/K
heat-flux density, watt per square meter W/m2
*When the mole is used, the elementary entities must be specified; they may irradiance
be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, other particles, or specified groups of such luminance candela per square meter cd/m2
particles. magnetic-field strength ampere per meter A/m
molar energy joule per mole J/mol
molar entropy joule per mole-kelvin J/(mol⋅K)
molar-heat capacity joule per mole-kelvin J/(mol⋅K)
moment of force newton-meter N⋅m
TABLE 1-2a Derived Units of SI that Have Special Names permeability henry per meter H/m
permittivity farad per meter F/m
Quantity Unit Symbol Formula radiance watt per square-meter- W/(m2⋅sr)
frequency (of a periodic phenomenon) hertz Hz l/s steradian
force newton N (kg⋅m)/s2 radiant intensity watt per steradian W/sr
pressure, stress pascal Pa N/m2 specific-heat capacity joule per kilogram-kelvin J/(kg⋅K)
energy, work, quantity of heat joule J N⋅m specific energy joule per kilogram J/kg
power, radiant flux watt W J/s specific entropy joule per kilogram-kelvin J/(kg⋅K)
quantity of electricity, electric charge coulomb C A⋅s specific volume cubic meter per kilogram m3/kg
electric potential, potential difference, volt V W/A surface tension newton per meter N/m
electromotive force thermal conductivity watt per meter-kelvin W/(m⋅K)
capacitance farad F C/V velocity meter per second m/s
electric resistance ohm Ω V/A viscosity, dynamic pascal-second Pa⋅s
conductance siemens S A/V viscosity, kinematic square meter per second m2/s
magnetic flux weber Wb V⋅s volume cubic meter m3
magnetic-flux density tesla T Wb/m2 wave number 1 per meter 1/m
inductance henry H Wb/A
luminous flux lumen lm cd⋅sr
illuminance lux lx lm/m2
activity (of radionuclides) becquerel Bq l/s
absorbed dose gray Gy J/kg TABLE 1-3 SI Prefixes
Multiplication factor Prefix Symbol
1 000 000 000 000 000 = 1018
000 exa E
1 000 000 000 000 = 1015
000 peta P
1 000 000 000 = 1012
000 tera T
1 000 000 = 109
000 giga G
1 000 = 106
000 mega M
000 = 103
1 kilo k
100 = 102 hecto* h
10 = 101 deka* da
0.1 = 10−1 deci* d
0.01 = 10−2 centi c
0.001 = 10−3 milli m
0.000 001 = 10−6 micro μ
0.000 000 001 = 10−9 nano n
0.000 000 000 001 = 10−12 pico p
0.000 000 000 000 001 = 10−15 femto f
0.000 000 000 000 000 001 = 10−18 atto a
*Generally to be avoided.
1-2
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Gear TerminologyDocument21 pagesGear TerminologyAns ahmed100% (1)
- HC Verma Part 1 Chapter 4Document3 pagesHC Verma Part 1 Chapter 4prayasjindal281No ratings yet
- ISUD 6 ProceedingsDocument192 pagesISUD 6 ProceedingsManea GrosuNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Damage Models For Laminated Composite StructuresDocument100 pagesFatigue Damage Models For Laminated Composite StructuresBaşar ZamanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 432 Problem Set 11 Spring 2018 SolutionsDocument7 pagesChemistry 432 Problem Set 11 Spring 2018 SolutionssaiNo ratings yet
- Gear ClassificationDocument13 pagesGear Classificationprkphani1984100% (1)
- Applications of Schrodinger Wave Equation: V (X), A X 0Document4 pagesApplications of Schrodinger Wave Equation: V (X), A X 0jasonNo ratings yet
- MST Quiz 1 AnswersDocument4 pagesMST Quiz 1 AnswersWilleyNo ratings yet
- RA01 Magnetic Force1 - Amit SharmaDocument27 pagesRA01 Magnetic Force1 - Amit SharmaPadam MantryNo ratings yet
- Numericals XIIDocument17 pagesNumericals XIISyed Tanveer100% (1)
- Exit Conveyor Belt TWINDocument9 pagesExit Conveyor Belt TWINUsman SadikinNo ratings yet
- Rankine-Froude Model: Blade Element Momentum Theory Is A Theory That Combines BothDocument111 pagesRankine-Froude Model: Blade Element Momentum Theory Is A Theory That Combines BothphysicsNo ratings yet
- Me2134 2Document18 pagesMe2134 2FlancNo ratings yet
- 30th MPA SeminarDocument529 pages30th MPA SeminarGeert Henk WijnantsNo ratings yet
- Water Landing of Space Flight Re-Entry Vehicles Using Abaqus/Explicit 2011Document4 pagesWater Landing of Space Flight Re-Entry Vehicles Using Abaqus/Explicit 2011SIMULIACorpNo ratings yet
- Motion of A Charged Particle in A Magnetic FieldDocument31 pagesMotion of A Charged Particle in A Magnetic FieldJumar Cadondon100% (1)
- Introduction To Boundary LayerDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Boundary LayerOmar Horna Pinedo100% (1)
- Coupling BeamDocument27 pagesCoupling Beam''Jeff Leong ManzanilloNo ratings yet
- "Chapter 9 - Influence Lines For Statically Determinate Structures" in "Structural Analysis" On Manifold @tupressDocument33 pages"Chapter 9 - Influence Lines For Statically Determinate Structures" in "Structural Analysis" On Manifold @tupressrpsirNo ratings yet
- Class IX - Physics NLMDocument3 pagesClass IX - Physics NLMNirjhar MazumderNo ratings yet
- Physics PosterDocument1 pagePhysics PosterSamuel ParishNo ratings yet
- MSG 00305Document15 pagesMSG 00305Nazeeh Abdulrhman AlbokaryNo ratings yet
- Effects of Staircase On The Seismic Performance of Reinforced Concrete Frame Buildings Considering The Position of The StaircaseDocument15 pagesEffects of Staircase On The Seismic Performance of Reinforced Concrete Frame Buildings Considering The Position of The Staircasel_pintoNo ratings yet
- Unit IIIDocument8 pagesUnit IIIPrashant NandanNo ratings yet
- Cyclone SeparatorsDocument8 pagesCyclone SeparatorsMorrison Huallpa VargasNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Simulating Thermal Expansion PDFDocument20 pagesAbaqus Simulating Thermal Expansion PDFhasib75% (4)
- Doctoral Thesis by S ChaterjeeDocument159 pagesDoctoral Thesis by S ChaterjeeSaikat ChaterjeeNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Controller Design For Dynamic Positioning of Unmanned Surface VehicleDocument6 pagesFuzzy Controller Design For Dynamic Positioning of Unmanned Surface VehicleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet