Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Viral Hepatitis Table
Uploaded by
John0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesViral Hepatitis can be caused by five main viruses - Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Hepatitis A is transmitted via the fecal-oral route or contaminated food/water and causes a self-limiting disease. Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood or bodily fluids and can cause both acute and chronic infection leading to complications like cirrhosis and liver cancer. Hepatitis C is typically transmitted through blood and can develop into a chronic infection increasing risk for long-term liver damage. Hepatitis D only infects individuals already infected with Hepatitis B and coinfection can result in fulminant hepatitis. Hepatitis E is transmitted similarly to Hepatitis A and while severe in pregnant women, it
Original Description:
123
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentViral Hepatitis can be caused by five main viruses - Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Hepatitis A is transmitted via the fecal-oral route or contaminated food/water and causes a self-limiting disease. Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood or bodily fluids and can cause both acute and chronic infection leading to complications like cirrhosis and liver cancer. Hepatitis C is typically transmitted through blood and can develop into a chronic infection increasing risk for long-term liver damage. Hepatitis D only infects individuals already infected with Hepatitis B and coinfection can result in fulminant hepatitis. Hepatitis E is transmitted similarly to Hepatitis A and while severe in pregnant women, it
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesViral Hepatitis Table
Uploaded by
JohnViral Hepatitis can be caused by five main viruses - Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Hepatitis A is transmitted via the fecal-oral route or contaminated food/water and causes a self-limiting disease. Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood or bodily fluids and can cause both acute and chronic infection leading to complications like cirrhosis and liver cancer. Hepatitis C is typically transmitted through blood and can develop into a chronic infection increasing risk for long-term liver damage. Hepatitis D only infects individuals already infected with Hepatitis B and coinfection can result in fulminant hepatitis. Hepatitis E is transmitted similarly to Hepatitis A and while severe in pregnant women, it
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
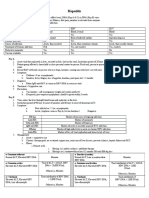
Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E
Non-A, non-B
Previous names Infectious hepatitis Serum hepatitis Delta Agent
hepatitis
Hepatitis A virus Hepatitis B virus Hepatitis C virus Hepatitis D virus Hepatitis E virus
Cause
(HAV) (HBV) (HCV) (HDV) (HEV)
Fecal–oral route, poor Parenteral, Sexual and oral– Parenteral, Sexual and oral– Parenteral, Sexual and oral– Fecal–oral route, poor
sanitation, Person-to-person oral contact, Perinatal oral contact, Perinatal oral contact, Perinatal sanitation, Person-to-person
Mode of transmission contact, Waterborne, transmission transmission transmission contact, Waterborne,
foodborne, Oral–anal sex *occupational hazard for foodborne, Oral–anal sex
health care personnel.
Incubation Period 2-6 weeks 4-24 weeks 2- 22 weeks 4-21 weeks 2-9 weeks
7-10 days before illness Degraded by enzymes, if Not identified in feces Not applicable Probably present in feces
Virus in Feces 2-3 weeks after symptoms present
appear
∙ Anicteric and ∙ Arthralgias and rashes ∙ Same with HBV usually ∙ Simultaneous infection ∙ Similar to hepatitis A,
symptomless ∙ Fever, respiratory mild with HBV and HDV can often milder course
∙ Symptoms Appear: Mild, symptoms(rare) lead to a mild-to-severe
flulike symptoms with ∙ Loss of appetite, or even fulminant
low-grade fever dyspepsia hepatitis
∙ Anorexia ∙ abdominal pain (RUQ)
∙ Jaundice and dark urine ∙ general aching, malaise,
∙ Indigestion mrked by and weakness
vaague epigastric ∙ Jaundice
Signs and Symptoms
distress, nausea, ∙ light-colored stools and
heartburn, flatulence dark urine.
∙ Aversion to cigarette ∙ Liver may be tender and
smoke and strong odor enlarged; spleen is
jaundice enlarged and palpable in
∙ ↑ AST/ALT a few patients.
∙ Children < 6 years often ∙ Posterior cervical lymph
have no symptoms nodes may also be
enlarged.
Carrier state No Yes Yes Yes Unknown
None specifically for Hepatitis
Vaccine Available Available None D. Hepatitis B vaccine should None
be given
Safe sex; screening of blood
products; use of sterile Use of sterile instruments
Food and water hygiene
Prevention instruments and needles and needles, safe sex Prevention of HBV infection Food and water hygiene
Immunization
HBV vaccination, post-
exposure prophylaxis
Fulminant hepatitis, Chronic Fulminant hepatitis Fulminant hepatitis
No chronic hepatitis is Chronic disease (possibly
Complication disease (possibly Hirrhosis, High risk of severe chronic High mortality rate in
associated cirrhosis, HCC)
Hepatocellular Carcinoma) liver disease pregnant women
You might also like
- Internal Medicine NotesDocument54 pagesInternal Medicine NotesHayley Welsh75% (4)
- Pathology Polycystic Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesPathology Polycystic Kidney DiseaseOnyedika EgbujoNo ratings yet
- Part 2 of Medical VirologyDocument113 pagesPart 2 of Medical Virologygatete samNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis - An Overview: Dr. JayalakshmiDocument77 pagesHepatitis - An Overview: Dr. JayalakshmiNithin SundarNo ratings yet
- Project Investigatory BiologyDocument24 pagesProject Investigatory BiologyVVM. S.4669100% (2)
- Hepatitis BDocument23 pagesHepatitis BMarty Asis100% (1)
- HIV&HepatitisDocument46 pagesHIV&HepatitisRaja RuzannaNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument55 pagesHepatitisSUTHAN100% (1)
- Viral HepatitisDocument64 pagesViral Hepatitisapi-19916399No ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument70 pagesHepatitisSartika Napitupulu100% (1)
- LIVERDISEASEDocument82 pagesLIVERDISEASEHervis FantiniNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis: Dr. Amany A. GhazyDocument44 pagesHepatitis: Dr. Amany A. GhazyJosé Luis García GarcíaNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument47 pagesQuestionsCharizza Yvette100% (1)
- Hepatitis: Dr. Leonardo B Dairi SPPD KgehDocument105 pagesHepatitis: Dr. Leonardo B Dairi SPPD Kgehraja_hafizullahNo ratings yet
- Ascites Case PresentationDocument44 pagesAscites Case PresentationAman Mehla75% (4)
- Hepatitis A - Typhoid Fever - KBKDocument50 pagesHepatitis A - Typhoid Fever - KBKanggunNo ratings yet
- Acute Biologic CrisisDocument143 pagesAcute Biologic CrisisAprylL22100% (5)
- Hepatitis A VirusDocument27 pagesHepatitis A VirusAna KarlaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B Kronik Pada Kehamilan - Dr. Dr. Anita Rachmawati, SpOG (K)Document92 pagesHepatitis B Kronik Pada Kehamilan - Dr. Dr. Anita Rachmawati, SpOG (K)Rustan VickyNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument8 pagesHepatitisGilankNo ratings yet
- Virus Hepatitis RevDocument83 pagesVirus Hepatitis RevSukma WinahyuNo ratings yet
- Topics For Oral Exam Hep Pneu DengueDocument4 pagesTopics For Oral Exam Hep Pneu DenguePCRMNo ratings yet
- Viral InfectionsDocument59 pagesViral Infectionsrenato renatoNo ratings yet
- Acute Viral Hepatitis (Final)Document5 pagesAcute Viral Hepatitis (Final)Kim LompotNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis TableDocument2 pagesHepatitis Tableampogison08No ratings yet
- Acute Hepatitis DR NjokuDocument43 pagesAcute Hepatitis DR Njokufrankozed1No ratings yet
- 05 Prevention of TransmissionDocument35 pages05 Prevention of TransmissionANUAR ASISNo ratings yet
- Virus Hepatitis - KBKDocument53 pagesVirus Hepatitis - KBKfifi anggraeniNo ratings yet
- Grid AbcdeDocument1 pageGrid AbcdeStephanieDardaNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument8 pagesHepatitisglazykimjorquiaNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Disorders: Michael D. Manglapus, RN, RM, MANDocument108 pagesHepatic Disorders: Michael D. Manglapus, RN, RM, MANMichael Baylon DueñasNo ratings yet
- Abc Hep EngDocument1 pageAbc Hep EngDonna LopezNo ratings yet
- 2018 Hepatitis Viral InfectionDocument51 pages2018 Hepatitis Viral Infectionkomang nickoNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Viral - Dr. José Gonzáles BenavidesDocument64 pagesHepatitis Viral - Dr. José Gonzáles BenavidesEfrain Brian SilvaNo ratings yet
- 15 HepatitisDocument48 pages15 HepatitisAlvin LaurenceNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis Training Manual: Federal Ministry of Health National Hepatitis Control Program 2017Document44 pagesViral Hepatitis Training Manual: Federal Ministry of Health National Hepatitis Control Program 2017Eleni HagosNo ratings yet
- L9-Viral Hepatitis A and E (Edited)Document12 pagesL9-Viral Hepatitis A and E (Edited)Ahmed Al-KhaleelNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis (Part I)Document12 pagesViral Hepatitis (Part I)Maarveen RajNo ratings yet
- Infeksi Virus Pada Sistem Pencernaan Bawah: Hepatitis: Ety AprilianaDocument27 pagesInfeksi Virus Pada Sistem Pencernaan Bawah: Hepatitis: Ety AprilianaAsmorowatiNo ratings yet
- Jaundice and Hepatitis in Children: Dr. MwendwaDocument46 pagesJaundice and Hepatitis in Children: Dr. MwendwaAlvin OmondiNo ratings yet
- HEPATOBILIER Pemicu 2 AlfindraDocument107 pagesHEPATOBILIER Pemicu 2 AlfindraHartomas BumiharjoNo ratings yet
- Gi L17 - HabcdvDocument2 pagesGi L17 - HabcdvIan Evan LeeNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument29 pagesHepatitisRose Anne AbivaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B & DDocument40 pagesHepatitis B & DMeena CtNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis VirusesDocument1 pageHepatitis VirusesDanica Mae SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 - HepatitisDocument8 pagesNCM 112 - HepatitisMara Jon Ocden CasibenNo ratings yet
- Hepetitis 140722235359 Phpapp01Document34 pagesHepetitis 140722235359 Phpapp01Dharmendra GohilNo ratings yet
- Supreme Institute of Management and Technology Topic - HepatitisDocument5 pagesSupreme Institute of Management and Technology Topic - HepatitisRAHUL MUKHERJEENo ratings yet
- 8.hepatitis VirusesDocument33 pages8.hepatitis VirusesShaibin MuhammadNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument3 pagesHepatitisapi-648401824No ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis OverviewDocument22 pagesViral Hepatitis OverviewNifemi OnatoyeNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis FinalDocument73 pagesHepatitis FinalAkhil MuraliNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A-EDocument34 pagesHepatitis A-EVer Garcera TalosigNo ratings yet
- CD Learning Material 4 Blood Borne DiseaseDocument22 pagesCD Learning Material 4 Blood Borne Disease2C1 - YABES, JenniferNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Virus: Bagian Mikrobiologi FK UnissulaDocument36 pagesHepatitis Virus: Bagian Mikrobiologi FK UnissulaKarina Mega WNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A, B and C VirusDocument46 pagesHepatitis A, B and C VirusChyzhi SylviaNo ratings yet
- HEPATITISDocument1 pageHEPATITISJOHN KENNETH AGUSTINNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Virus A Sampai eDocument48 pagesHepatitis Virus A Sampai eaulia rahmahNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E Hepatitis GDocument9 pagesHepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E Hepatitis Gjamie carpioNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis: Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Sirrosis HepatisDocument48 pagesHepatitis: Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Sirrosis Hepatisfarah maulida martaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Lec 3Document44 pagesHepatitis Lec 3Sarkhell ArazNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument4 pagesHepatitisJelica ConsultadoNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B in PregnancyDocument25 pagesHepatitis B in PregnancyTengku Amir RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis and Hepatic Failure: in ChildrenDocument26 pagesHepatitis and Hepatic Failure: in Childrenchilu20No ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument55 pagesHepatitisdebdeepbhattacharya411No ratings yet
- The Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportFrom EverandThe Complete Guide To HIV / AIDs: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Risks, Treatments & SupportNo ratings yet
- Liver CancerDocument233 pagesLiver CancerandikhgNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Adults With AscitesDocument16 pagesEvaluation of Adults With AscitesMaricruz BracamonteNo ratings yet
- Wilson Disease in Children and Young Adults - State of The ArtDocument11 pagesWilson Disease in Children and Young Adults - State of The ArtJosueNo ratings yet
- Drug Dose CalculationDocument50 pagesDrug Dose CalculationSwaraj SKNo ratings yet
- Paracentesis - SIR GGR Survival GuideDocument4 pagesParacentesis - SIR GGR Survival GuidesirrfsNo ratings yet
- SCHEME of The PEDIATRICS' CASE HISTORYDocument17 pagesSCHEME of The PEDIATRICS' CASE HISTORYManusheeNo ratings yet
- GIT EXAM 2016 CorrectedDocument4 pagesGIT EXAM 2016 CorrectedDEOGRATIAS NDAYISABANo ratings yet
- Pathology TutorialDocument12 pagesPathology TutorialjessbunkerNo ratings yet
- Approach To Peritoneal Fluid AnalysisDocument10 pagesApproach To Peritoneal Fluid AnalysisLady BugNo ratings yet
- Journal GastroenterologyDocument14 pagesJournal GastroenterologySusilo PrihrantoNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis 2020Document27 pagesLiver Cirrhosis 2020Gabriela SalasNo ratings yet
- GIT and LiverDocument28 pagesGIT and LiverUsmanNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Clinical Practice Guidelines 2018 Midyear Review PDFDocument17 pagesInternal Medicine Clinical Practice Guidelines 2018 Midyear Review PDFveerrajuNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Liver SamDocument28 pagesPathology of Liver SamJaks RipperNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Biochemistry For Medical Students (2 Edn) : Universities Press Rafi M DDocument31 pagesTextbook of Biochemistry For Medical Students (2 Edn) : Universities Press Rafi M DPranjali VidhateNo ratings yet
- AnnGastroenterol 30 217 PDFDocument8 pagesAnnGastroenterol 30 217 PDFhusni gunawanNo ratings yet
- Treatment Ciroza HepaticaDocument85 pagesTreatment Ciroza HepaticaMarina TrofimciucNo ratings yet
- Pathology-GIT Answered EssayDocument33 pagesPathology-GIT Answered EssayRancesh FamoNo ratings yet
- Management of Ascites in Children Lane2015Document13 pagesManagement of Ascites in Children Lane2015Henry BarberenaNo ratings yet
- Peritonitis and Abdominal SepsisDocument37 pagesPeritonitis and Abdominal SepsisFernando AsencioNo ratings yet
- Dake Chu: Cui WeiDocument61 pagesDake Chu: Cui WeiDave UlanNo ratings yet
- Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis: Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pagesDecompensated Liver Cirrhosis: Learning ObjectivesAuliaNo ratings yet