Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Urology Referral Recommendations Summary
Uploaded by
michelle octavianiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Urology Referral Recommendations Summary
Uploaded by
michelle octavianiCopyright:
Available Formats
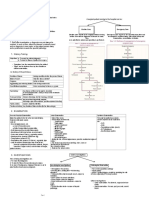
REFREC025
UROLOGY REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS
Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines
These referral recommendations are provided for core Urology Services in the public health system. They exclude social or cultural circumcision, vasectomy
reversal, and access to impotence treatment. In cases of urological emergency requiring urgent treatment or admission – Category 1 & 2, the duty Urological
Registrar may be contacted via the Hospital switchboard.
In the context of these referral Evaluation is indicated from a primary Treatment options at a primary level Circumstances for referral are
recommendations, Urology Specialist care perspective. Standard history and may be minimal for surgical diagnoses; indicated below with reference to the
Services have been grouped under the examination is required for all however, options are indicated where appropriate specialty/specialties.
following headings: situations. Key points in relation to appropriate.
individual diagnoses are highlighted Telephone/fax/e-mail communication
• Female incontinence and investigations indicated. will enhance access to the service.
• Hematuria
• Lower urinary tract symptoms
(male)
• Male genitalia
• Male infertility
• Paediatrics – congenital
abnormality
• Paediatrics – male genitalia
• PSA screening
• Stones
• Suspected cancer of the prostate
Last updated February 2006 Page 1 of 12
REFREC025
Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines
Female incontinence
KEY POINTS: Conservative management by a Refer for OPD assessment – Category
trained physiotherapist or continence 3 if conservative measures fail.
• Predominantly stress specialist.
incontinence.
• Predominantly urge incontinence. Surgery for stress incontinence can be
– Review by continence advisor Urology or Uro-Gynaecology
• Urge/stress incontinence.
– Bladder drills.
• Does the patient require pads,
number per day? – Pelvic floor exercises
• History of UTIs. – Treat UTI’s
• Duration of symptoms. – Anticholinergics if low residuals on
bladder scan
• Obstetric history.
• Previous gynaecological/urological
surgery.
PV findings, Neurological signs.
Last updated February 2006 Page 2 of 12
REFREC025
Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines
Hematuria
Macroscopic (gross). KEY POINTS: Continuous gross hematuria – refer as
• ?Complete (urine uniformly blood- Category 2, OPD assessment,
stained). otherwise – Category 3.
• ?Initial stream, ?end stream?
clots. An open access Hematuria Clinic will
Confirm Hematuria on MSU if not sure.
• ?Pain/dysuria. be opened in the future for immediate
Even if urine clear after event, always
assessment of patients with hematuria,
• Onset, duration, episodes. investigate. All patients over 45 years
eg Hollywood Public Hospitals.
even with UTI must be fully evaluated.
Females:
• Other gynaecological symptoms.
• PV findings.
Males:
• Other urological symptoms.
• DRE.
Treat infection, treat symptoms. IVU
INVESTIGATIONS: probably best investigation.
Refer for ? Cystoscopy
• MSU (RBCs, WCCs, culture).
• PSA.
Consider: KUB
US } in consultation
IVU } with specialist
Urology service
(See Imaging Referral
Recommendations.)
Microscopic (defined as >25RBCs in 3 INVESTIGATIONS: Routine referral – Category 3.
urine specimens).
• MSU x 3
Last updated February 2006 Page 3 of 12
REFREC025
Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (Male)
Known as B.O.O (Bladder Outflow KEY POINTS: Refer to OPD assessment – Category
Obstruction) • Previous lower urinary tract Continence advisors can provide 3 after trial of alpha adrenergic
surgery. triage, MSU, flow rate and bladder blockers.
Most ‘troublesome’ symptoms need • Has the patient required residuals
assessment, eg nocturia, urgency, catheterisation? Bothersome symptoms refer category
incontinence, hematuria or pain
• Is he catheterised? Trial of alpha adrenergic blockers after 3
flow rate and bladder scan residual.
• Documented previous UTIs?
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION:
• Palpable/percussible bladder?
• DRE – asymmetry, hardness,
nodules, induration.
INVESTIGATIONS:
MSU – WCC, RBC culture.
PSA.
Last updated February 2006 Page 4 of 12
REFREC025
Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines
Male genitalia
Testicular Abnormality. KEY POINTS:
Hard mass, painless, ultrasound and
• Right, left, bilateral. urgent referral Intra-Testicular mass refer urgently
– Category 2.
• Body of testis.
Scrotal Abnormality. • Right, left, bilateral ?. Refer for OPD assessment – Category
Any mass outside the testis, eg 3, if problem is bothersome.
• Cord or vas including varicocoele Epididymal. Cyst is never malignant.
?. U/sound and reassurance
• Epididymal cyst.
Penis Deformity. • Foreskin. Phimosis – Use steroid creams Refer for OPD assessment – Category
3.
• Glans.
Peyronie’s – Rare, Use Vitamin E
• Shaft.
• Functional.
Last updated February 2006 Page 5 of 12
REFREC025
Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines
Male infertility
KEY POINTS: Refer for OPD assessment – Category
3.
– Has the patient had unprotected
intercourse for 12 months or
more?
– Has the patient previously
biologically fathered children?
– Has the current partner had
previous pregnancies?
– Has his partner undergone any
investigations?
• Does the patient have a past
history of: Semen Analysis must be done with at
least 5 days abstinence and sent to a
– Mumps orchitis. laboratory geared for fresh semen
analysis
– Inguinal hernia repair.
– Testicular torsion.
Blood Tests are fasting testosterone,
– Orchidopexy. FSH and LH
– Varicocoele repair.
– Any significant illness in the last six
months.
– Smoking marihuana
Physical examination
?Male habitus testes
Last updated February 2006 Page 6 of 12
REFREC025
Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines
Paediatrics – Congenital Abnormality
Paediatric Urology – (See Paediatric Surgery Referral Recommendations)
Inguinal and/or Scrotal Swellings. Non-acute hernia and hydrocoeles can Child under 3 months with Hernia or
be difficult to differentiate in children. It uncertain diagnosis:
is important to recognise a hernia in a Refer urgently – Category 2 to
child under the age of 3 months. Paediatric Surgery/Urology Service.
Varicocoeles are difficult to
differentiate. If suspected, refer as per
Hernia over the age of 3 months:
hernia Recommendation.
Refer semi-urgently to Paediatric
Surgical Service or local General
Surgical Service – Category 3.
Difficult Hernia:
Any hernia that is reduced with
difficulty, is at significant risk of
strangulation and should be referred
urgently – Category 2 – irrespective of
age.
Hydrocoele:
If a hydrocoele is confidently
diagnosed, it can be treated
expectantly. If it persists past the age
of 2 or causes symptoms, or grows
rapidly, it should be referred routinely –
Category 3.
Acute Scrotal Pathology. Epidydimo-orchitis is very rare in Scrotal Pain with or without swelling:
children and should not be diagnosed
Always consider torsion or Refer immediately – Category 1.
Last updated February 2006 Page 7 of 12
REFREC025
clinically. strangulation and refer urgently
The following conditions are included:
– Torsion of testis.
– Torsion of appendix of testis.
– Strangulated hernia.
– Incarcerated hernia.
– Idiopathic scrotal oedema.
– Uncertain mumps orchitis.
Undescended testis. Risk of infertility if orchidopexy is Refer from the age of 6 months to
delayed, increases with age. It is now Paediatric Surgery or Urology Service.
recommended that orchidopexy should Routine referral – Category 3.
be performed by the age of 1 year.
An undescended testis is one that In a clinically obvious associated
After age 40 may be best left alone
cannot be manipulated into the bottom hernia, they should be managed as
of the scrotum. All testes should be hernia Referral Recommendation.
situated within the scrotum by the age
of 3 months.
Retractile testis. Retractile testes are not normally Refer routinely at the age of 2 to the
situated within the scrotum, but can be Paediatric Surgery or Urology Service
manipulated into the scrotum. The – Category 3.
current recommendation is that they be
fixed in the scrotum surgically if they
remain retractile after the age of 2.
Last updated February 2006 Page 8 of 12
REFREC025
Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines
Paediatrics – Male Genitalia
Phimosis/Paraphimosis. No problem if good urinary stream. A Phimosis:
large percentage of foreskins are fused Teach hygiene, cleansing, washing,
Indications for referral:
to the glans and will separate gentle retraction, Reassure
spontaneously over a number of • Inability to retract after the age of
months or years. There is no 5.
necessity to retract or be able to retract • Recurrent balanitis.
the foreskin (at least before 5 years of • Pinhole prepucial orifice with very
age). poor urinary stream.
Ballooning with micturition frequently • Refer routinely – Category 3.
occurs and is acceptable providing
Paraphimosis:
there is a good urinary stream.
Refer immediately – Category 1.
Social/Religious Circumcisions. Not provided in public health system.
Hypospadias. Do not circumcise. Refer at diagnosis routinely – Category
Evaluate adequacy of urinary stream. 3, to Paediatric Surgery or Urology
May need renal tract ultrasound Service.
Often abnormalities, undescended Refer immediately if poor urinary
testis? stream – Category 1.
Urethral Meatal Stenosis. Usually neonatally circumcised boys. Urethral dilations from continence Refer routinely – Category 3.
Evaluate urinary stream. advisors
Balanitis. Accumulation of smegma under the Frank infection requires treatment with Recurrent balanitis – refer routinely, as
foreskin is common and normal, but oral antibiotics (eg cotrimoxazole) and above – Category 3.
can be mistaken for pus. Referral surgery if it is recurrent.
and/or intervention is not required. It
will continue to extrude spontaneously
until all the prepucial adhesions have
disappeared. Foreskin retraction and
cleaning is not necessary.
Other Genital Anomalies. Refer routinely Category 3 to
Paediatric Surgical Service or
appropriate local Paediatric Medical
Service.
Last updated February 2006 Page 9 of 12
REFREC025
Urinary Tract
Antenatally Diagnosed Applies to hydronephrosis at any Referral to Paediatric or Urology
Hydronephrosis. gestation. Post natal examination for Seek specialist review Service if dilation is present – Category
abdominal mass. Ultrasound after 5 2.
days of age.
Note: Majority of urinary abnormalities
LMC has responsibility to ensure GP is present as either UTI or as
informed. hydronephrosis following antenatal
ultrasound.
Urinary Tract Infection. Evaluation of urinary tract infections: Start antibiotics pending culture report. Refer for assessment patients with
Many urological abnormalities will The diagnosis of UTI requires great Five day course. Consider long term abnormal imaging results or if requiring
present as an urinary tract infection. care and skill. surveillance and prophylactic investigations, noting local
antibiotics until investigations are Recommendations. Routine Category
These include: Clear evidence of UTI is essential.
completed. 3.
• Vesicoureteric reflex. (Note: Guidelines of UTI in Children is
attached.)
• Pelvi-ureteric junction obstruction. Treat constipation, toileting hygiene. Refer recurrent urinary tract infections.
Urine results must be provided with the
• Vesicoureteric junction referral. Routine Category 3.
obstruction.
• Primary Mega-ureter.
INVESTIGATION:
• Neurogenic bladder.
With reference to local
• Duplex system +/- ureterocoele. recommendation.
• Posterior urethral valves.
Neuropathic Bladder. Check for spinal abnormality, ie mass • Treat constipation. Refer to Paediatric or Urology Service
or spina bifida occulta. Exclude • Long term antibiotics. if diagnosis suspected.
constipation.
Regular urine check-ups.
Last updated February 2006 Page 10 of 12
REFREC025
Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines
Stones
KEY POINTS: Poorly controlled renal/ureteric colic
refer for OPD assessment – Category
• Past history of stones and stone Fever, pain, rigors – Immediate 2. This is usually via an A&E
surgery. admission department. Otherwise – Category 3
• Pain score : obstructed kidney, refer Category 2.
Indicid suppositories, 100mg bd –
– Severe, poorly controlled. useful for proven renal colic if stone
passes Many Stone cases are offered early
– Moderate controlled. intervention, stents or lasertripsy,
– Minimal well controlled.
– Asymptomatic. Specialised units have access to
lasers.
• Analgesia requirement.
• Acute renal coli – right/left –
duration of symptoms.
• Known urinary tract calculus.
– size of stone.
– location.
– how diagnosed.
Metabolic Disease ? Gout.
INVESTIGATIONS: (Xrays are the
only way to diagnose)
• MSU (microscopy).
Consider: KUB } in conjunction with
USS } urology service
IVU } CT Spinal scan best modality for
(See Primary Referred Imaging investigation
Referral Recommendations.)
Last updated February 2006 Page 11 of 12
REFREC025
Diagnosis / Symptomatology Evaluation Management Options Referral Guidelines
Suspected Cancer of the Prostate
Including elevated PSA. KEY POINTS:
• Family history of Ca prostate.
Usually in older men. Men below 70 Often the worried will want
usually have PSA screening. • Weight loss. assessment. PSA Screening in over
• Bony pain. 75 yrs should be discouraged.
Symptomatic patients should have
Over 70 – 75, symptoms that are • Hematuria. urological review – Category 3
worrying should be evaluated.
Screening of asymptomatic men over • Previous bladder/prostate surgery.
75 is not recommended. Refer Category 2 – Patients with
advanced disease, pain, etc
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION:
• Palpable/percussible bladder? Prostate biopsies with transrectal
• DRE – asymmetry, hardness, U/Sound are only performed where
nodules, induration. uroligically evaluated.
INVESTIGATIONS:
• PSA, Percentage Ratio
• FBC, + ESR.
• U + E.
• Creatinine.
• Alkaline Phosphatase.
Last updated February 2006 Page 12 of 12
You might also like
- Gynobs EmergencyDocument52 pagesGynobs Emergency95kscbyqxmNo ratings yet
- Acute Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (Aub) : AlgorithmDocument8 pagesAcute Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (Aub) : AlgorithmPhiyaNo ratings yet
- Feline Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis and ManagementDocument8 pagesFeline Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis and ManagementXenia FernandezNo ratings yet
- 3 Urinary Incontinence in WomenDocument4 pages3 Urinary Incontinence in WomenDanilo Pereira Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Urinery IncontinsetenceDocument1 pageUrinery IncontinsetenceLanaAmerieNo ratings yet
- Làm Gì Khi SDMA TăngDocument1 pageLàm Gì Khi SDMA TăngNguyễn Tấn TàiNo ratings yet
- Home Care RN Skills ChecklistDocument2 pagesHome Care RN Skills ChecklistGloryJaneNo ratings yet
- ATSPDocument24 pagesATSPch wNo ratings yet
- GASTRODocument11 pagesGASTRONatricia TrondilloNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Incontinent Woman: Yeditepe University, Medical Faculty Dept of Ob&GynDocument47 pagesEvaluation of The Incontinent Woman: Yeditepe University, Medical Faculty Dept of Ob&GynAdnan WalidNo ratings yet
- Undescended Testicle PathwayDocument8 pagesUndescended Testicle PathwayJessa MaeNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged 2-69Document1 pageIlovepdf Merged 2-69qwivy.comNo ratings yet
- ATSP Booklet 2019 FinalDocument24 pagesATSP Booklet 2019 FinalShreya BNo ratings yet
- Infertility: PGI Ira Mikkaella GenobisDocument49 pagesInfertility: PGI Ira Mikkaella GenobisIra Mikkaella GenobisNo ratings yet
- finalsURINARY ELIMINATION DIAGNOSTICSDocument11 pagesfinalsURINARY ELIMINATION DIAGNOSTICSFrances LiqueNo ratings yet
- Atsp Book 2011Document24 pagesAtsp Book 2011Chengyuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- CM OBGYN 8,9 Copy.Document8 pagesCM OBGYN 8,9 Copy.jamierogers427No ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta. Final OutputDocument15 pagesAbruptio Placenta. Final OutputCharles Loriaga Cruz IINo ratings yet
- Fast DPL CTDocument6 pagesFast DPL CTnmyza89No ratings yet
- Acute AUBDocument9 pagesAcute AUBJessa MaeNo ratings yet
- UrolithiasisDocument9 pagesUrolithiasisJessa MaeNo ratings yet
- Emergenze Addome RXDocument9 pagesEmergenze Addome RXBrovazzo PieroNo ratings yet
- Approach To Abdominal Pain in EDDocument29 pagesApproach To Abdominal Pain in EDAneeq Nayer KhanNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdomen Practical Approach FransDocument29 pagesAcute Abdomen Practical Approach FransAbel MncaNo ratings yet
- Atsp Re:: DR Gillian Jackson DR Fran Bennett DR Tom HannanDocument24 pagesAtsp Re:: DR Gillian Jackson DR Fran Bennett DR Tom HannanSagarJobanNo ratings yet
- Incontinence: DR - Swathi Singh MPT Orthopaedics, MiapDocument69 pagesIncontinence: DR - Swathi Singh MPT Orthopaedics, MiapSonu GuptaNo ratings yet
- GI Liver PerceptionDocument9 pagesGI Liver PerceptionJUDE ARIZALANo ratings yet
- Acute Abdominal Pain Pathway: Management - Primary Care and Community SettingsDocument2 pagesAcute Abdominal Pain Pathway: Management - Primary Care and Community Settingsshella1selinaNo ratings yet
- Postcoital Bleeding GuideDocument4 pagesPostcoital Bleeding GuideSalsabila HMNo ratings yet
- Lower Urinary Tract SymptomsDocument18 pagesLower Urinary Tract SymptomsRererloluwaNo ratings yet
- Uterine ProlapseDocument45 pagesUterine ProlapseAnusree AnusreervNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia 2001 11 SlidesDocument46 pagesDysphagia 2001 11 SlidescafemedNo ratings yet
- Altered Urinary Elimination - ADPCN Resource UnitDocument5 pagesAltered Urinary Elimination - ADPCN Resource UnitChillette FarraronsNo ratings yet
- TOPNOTCH MEDICAL BOARD PREP - COMMON OB-GYN EMERGENCIESDocument8 pagesTOPNOTCH MEDICAL BOARD PREP - COMMON OB-GYN EMERGENCIEScarmsNo ratings yet
- General Surgery IntroductionDocument1 pageGeneral Surgery IntroductionAndrew BonusNo ratings yet
- Abortion and Its Complications 2Document17 pagesAbortion and Its Complications 2api-3705046100% (2)
- Antepartum Haemorrhage PDFDocument5 pagesAntepartum Haemorrhage PDFRaditya TaslimNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System AssessmentDocument8 pagesFemale Reproductive System Assessmentluna nguyenNo ratings yet
- Colorectal CancerDocument8 pagesColorectal Cancersouthernlady218No ratings yet
- Urinary RetentionDocument28 pagesUrinary RetentionSchoeb MuhammadNo ratings yet
- BMJ Volume 339 Issue Nov11 1 2009 (Doi 10.1136/bmj.b4418) Goyder, C. McPherson, A. Glasziou, P. - Self Diagnosis PDFDocument9 pagesBMJ Volume 339 Issue Nov11 1 2009 (Doi 10.1136/bmj.b4418) Goyder, C. McPherson, A. Glasziou, P. - Self Diagnosis PDFMuhammad FaizNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (Non Structural Abnormalities) : Journal ReadingDocument32 pagesAbnormal Uterine Bleeding (Non Structural Abnormalities) : Journal ReadingSamdiSutantoNo ratings yet
- ConstipationDocument6 pagesConstipationاحمد محمدNo ratings yet
- OBGYN Roisin Doubly UpdatedDocument71 pagesOBGYN Roisin Doubly UpdatedDanny SchNo ratings yet
- Office Gynecology Dr. SSM Source: PPT + Recordings: Initial Assessment - Communication Medical History and PeDocument74 pagesOffice Gynecology Dr. SSM Source: PPT + Recordings: Initial Assessment - Communication Medical History and PePrecious MedinaNo ratings yet
- NICE Guidance: Routine Preoperative Tests For Elective SurgeryDocument5 pagesNICE Guidance: Routine Preoperative Tests For Elective Surgeryachmad mustikaNo ratings yet
- ch2 fs1Document2 pagesch2 fs1ry beNo ratings yet
- 64-Year-Old With Postmenopausal BleedingDocument3 pages64-Year-Old With Postmenopausal BleedingMorita TakaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection and Pyelonephritis AIIMS Kalyani 7th SemesterDocument39 pagesUrinary Tract Infection and Pyelonephritis AIIMS Kalyani 7th Semesterrakesh raushanNo ratings yet
- Examination and Investigation of The Urogenital System For GUUDocument40 pagesExamination and Investigation of The Urogenital System For GUUJake MillerNo ratings yet
- STEPS MalrotationDocument30 pagesSTEPS MalrotationsyafiqNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders Assessment Methods 2Document27 pagesEndocrine Disorders Assessment Methods 2May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Urinary Incontinence: (Text Update March 2009)Document12 pagesGuidelines On Urinary Incontinence: (Text Update March 2009)69016No ratings yet
- Breast AssessmentDocument2 pagesBreast AssessmentHNo ratings yet
- Creog Urogyn ReviewDocument97 pagesCreog Urogyn ReviewAlexandriah AlasNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Medical Nursing IiiDocument614 pagesLecture Notes On Medical Nursing IiiAnim Richard DuoduNo ratings yet
- Bahan Tugas Tokolitik Ulfadiya Putri 1Document25 pagesBahan Tugas Tokolitik Ulfadiya Putri 1hopa shopNo ratings yet
- Epididymo-orchitis Management GuidelinesDocument3 pagesEpididymo-orchitis Management GuidelinesfirmankamalNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Trauma Diagnosis and ManagementDocument9 pagesAbdominal Trauma Diagnosis and ManagementMyrtle Yvonne RagubNo ratings yet
- Mary Law PEO Model PDFDocument15 pagesMary Law PEO Model PDFalepati29No ratings yet
- Occurrence and Health Risk Assessment of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPS) in Tap Water of ShanghaiDocument8 pagesOccurrence and Health Risk Assessment of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPS) in Tap Water of ShanghaiTiago TorresNo ratings yet
- Administering Blood Transfusion GuideDocument1 pageAdministering Blood Transfusion GuideKyla ManarangNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance in Medical LaboratoriesDocument69 pagesQuality Assurance in Medical Laboratories"DocAxi" Maximo B Axibal Jr MD FPSP100% (1)
- Reflective Essay: Writing in The Genetics DiscourseDocument5 pagesReflective Essay: Writing in The Genetics DiscourseAnonymous AY6XDZHBxPNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Module 4Document13 pagesUnderstanding The Self Module 4Jovet QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Principles of Health AdminDocument42 pagesPrinciples of Health AdminAnne BattulayanNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) - Citric AcidDocument5 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) - Citric AcidMannar1No ratings yet
- Summary of key provisions in the Domestic Workers ActDocument46 pagesSummary of key provisions in the Domestic Workers ActPaul Christopher PinedaNo ratings yet
- KAP regarding BSE among womenDocument30 pagesKAP regarding BSE among womenrandika wijesooriyaNo ratings yet
- Inflammation - The Silent Killer - Terra Health EssentialsDocument6 pagesInflammation - The Silent Killer - Terra Health EssentialshighlanderoneNo ratings yet
- Learning Kit - Q3W3 CeslDocument10 pagesLearning Kit - Q3W3 CeslJoselle Batas MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- 296402-Official ESTA Application Website U.S. Customs and Border Protection PDFDocument5 pages296402-Official ESTA Application Website U.S. Customs and Border Protection PDFLouise Ann TunstallNo ratings yet
- Cancer Fighting StrategiesDocument167 pagesCancer Fighting StrategiesCaptainjillNo ratings yet
- Bailey SafeMedPharmacyTechnicianDocument10 pagesBailey SafeMedPharmacyTechnicianRazak AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Effective Lifting ProgramDocument30 pagesBenefits of Effective Lifting ProgramMoradeke OnasanyaNo ratings yet
- Middle Childhood Physical Development (6-11 YearsDocument13 pagesMiddle Childhood Physical Development (6-11 YearsAngela YlaganNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapists in Private Practice During PandemicsDocument15 pagesPsychotherapists in Private Practice During PandemicsAnup AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Hyatt Amritsar showcases Chinese and Thai cuisineDocument1 pageHyatt Amritsar showcases Chinese and Thai cuisineAnmol MehanNo ratings yet
- 2-1-2021 Response To LandlordDocument2 pages2-1-2021 Response To LandlordJessica SwarnerNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Center Checklist 2Document5 pagesWarehouse Center Checklist 2Sankar ChinnathambiNo ratings yet
- People Pleasing Patterns Are Learned When Needs Are Not Met PDFDocument10 pagesPeople Pleasing Patterns Are Learned When Needs Are Not Met PDFPamela RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Breast Feeding Final ProposalDocument16 pagesBreast Feeding Final ProposalDeborah BoahemaaNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter CAPSTONEDocument30 pages4th Quarter CAPSTONEWallace RamosNo ratings yet
- Antonella Arrieta LaurentDocument24 pagesAntonella Arrieta LaurentEmanueleNo ratings yet
- Blood Typing PDFDocument3 pagesBlood Typing PDFFrances Lau Yee ChinNo ratings yet
- Latest eDocument39 pagesLatest eBasil Baby-PisharathuNo ratings yet
- Definition of Sexual Abuse of ChildrenDocument2 pagesDefinition of Sexual Abuse of ChildrenRadhika RathoreNo ratings yet
- ASCGULF Company: Mohammad Gousu Basha ShaikDocument3 pagesASCGULF Company: Mohammad Gousu Basha ShaikmohammadgouseNo ratings yet
- Fire Retardant Research PaperDocument2 pagesFire Retardant Research Paperapi-318759920No ratings yet