Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EP Notes
Uploaded by
Pratap BilluCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EP Notes
Uploaded by
Pratap BilluCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Physics
1 a) Explain the term “coherence”.
The definition of coherence is something logical or consistent and something that makes
sense as a whole. An example of coherence is an argument that has no inconsistencies.
Noun. 1. coherency - the state of cohering or sticking together. coherence, cohesion,
cohesiveness. connectedness, connection, link - the state of being connected; "the
connection between church and state is inescapable"
b)What are the conditions to obtain total internal reflection in an optical fiber?
Two important conditions for total internal reflection are: Angle of incidence (i) should
be greater than critical angle (ic). Ray should travel from denser medium to rarer medium
Total internal reflection is a very useful natural phenomenon
since it can be used to confine light. One of the most
common applications of total internal reflection is in fibre
optics. An optical fibre is a thin, transparent fibre, usually
made of glass or plastic, for transmitting light. Optical fibres
are usually thinner than a human hair! The construction of a
single optical fibre
c) Explain Meissner effect in superconductors.
Meissner effect, the expulsion of a magnetic field from the interior of a material that is in
the process of becoming a superconductor, that is, losing its resistance to the flow of
electrical currents when cooled below a certain temperature, called the transition
temperature, usually close to absolute zero.
d) State and explain Stoke’s theorem.
Stokes Theorem (also known as Generalized Stoke’s Theorem) is a declaration about the integration of
differential forms on manifolds, which both generalizes and simplifies several theorems from vector
calculus. As per this theorem, a line integral is related to a surface integral of vector fields. Learn the
stokes law here in detail with formula and proof.
f) Define the terms of a) relaxation time and b) mobility.
a) relaxation time
Definition of relaxation time. 1 : the time required for an exponentially decreasing
variable (as the amplitude of a damped oscillation) to drop from an initial value to 1/e or
0.368 of that value (where e is the base of natural logarithms)
b) mobility.
Mobility is formally defined as the value of the drift velocity per unit of electric field
strength; thus, the faster the particle moves at a given electric field strength, the larger the
mobility. The mobility of a particular type of particle in a given solid may vary with
temperature.
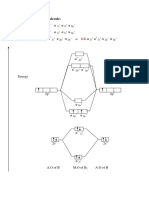
f) Discuss the effect of temperature on fermi level in extrinsic semi conductors.
Fermi level of Extrinsic Semiconductor. Extrinsic semiconductors are formed by
adding suitable impurities to the intrinsic semiconductor. The added impurity is very
small, of the order of one atom per million atoms of the pure semiconductor. The added
impurity may be pentavalent or trivalent.
Fermi level in n-type semiconductor
In n-type semiconductor pentavalent impurity is added. Each
pentavalent impurity donates a free electron. The addition of
pentavalent impurity creates large number of free electrons
in the conduction band.
The Fermi level for n-type semiconductor is given as
Fermi level in p-type semiconductor
In p-type semiconductor trivalent impurity is added.
Each trivalent impurity creates a hole in the valence
band and ready to accept an electron. The addition
of trivalent impurity creates large number of holes in
the valence band.
The Fermi level for p-type semiconductor is given as
Where NV is the effective density of states in the valence band.
NA is the concentration of acceptor atoms.
PART-B
2. (a) Analyze qualitatively double slit diffraction.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 8ch0 01 Rms 20230817Document32 pages8ch0 01 Rms 20230817g8yd7q9cnmNo ratings yet
- Vemanasaipratapbillu - V1Document2 pagesVemanasaipratapbillu - V1Pratap BilluNo ratings yet
- BillDocument5 pagesBillPratap BilluNo ratings yet
- Sample DataDocument432 pagesSample DataPratap BilluNo ratings yet
- Python InterviewsDocument30 pagesPython InterviewsPratap BilluNo ratings yet
- 11 - BT - r13 - Supply Nov 2020 - RevisedDocument1 page11 - BT - r13 - Supply Nov 2020 - RevisedPratap BilluNo ratings yet
- SQL MaterialDocument137 pagesSQL MaterialPratap BilluNo ratings yet
- P6 UK Bank CustomersDocument180 pagesP6 UK Bank CustomersPratap BilluNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics MTH-108: Dr. Abdul Aleem JamaliDocument10 pagesApplied Physics MTH-108: Dr. Abdul Aleem JamaliHassan AliNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument9 pagesChemical BondingsaurabhNo ratings yet
- EDC 2 MarksDocument16 pagesEDC 2 Marksdr mbaluNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices BJTDocument73 pagesElectronic Devices BJTJeeva GarudaNo ratings yet
- Focused Ion BeamDocument90 pagesFocused Ion BeamLotus DarkNo ratings yet
- Schrodinger EquationDocument21 pagesSchrodinger EquationSukhwinder Singh Gill100% (3)
- 5 Renu ChoithraniDocument6 pages5 Renu Choithranibasco costasNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering MCQsDocument11 pagesElectrical Engineering MCQsZaf Feer33% (3)
- Summative Test Tos 2ndquarter Part 1Document1 pageSummative Test Tos 2ndquarter Part 1ARRIANE JOY TOLEDO100% (1)
- Langmuir Adsorption IsothermDocument15 pagesLangmuir Adsorption IsothermDinomanyNo ratings yet
- Physics STPM Sem 3 DefinitionDocument2 pagesPhysics STPM Sem 3 DefinitionBen67% (3)
- Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTutorial 1karanNo ratings yet
- Fieldtheoriesofcondensedmatterphysics: Duardo RadkinDocument854 pagesFieldtheoriesofcondensedmatterphysics: Duardo RadkinawardrNo ratings yet
- B M Breid, D Witthaut and H J Korsch - Manipulation of Matter Waves Using Bloch and Bloch-Zener OscillationsDocument24 pagesB M Breid, D Witthaut and H J Korsch - Manipulation of Matter Waves Using Bloch and Bloch-Zener OscillationsYidel4313No ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocrystalline Nis NanoparticlesDocument5 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Nanocrystalline Nis Nanoparticlespadidela swarochishraoNo ratings yet
- Group Phase VelocityDocument7 pagesGroup Phase VelocityhassscribedNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor: Preparation of Semiconductor MaterialsDocument3 pagesSemiconductor: Preparation of Semiconductor Materialsبنیاد پرستNo ratings yet
- Liquid CrystalDocument44 pagesLiquid Crystalshreeji2017No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument513 pagesUntitledLalit SharmaNo ratings yet
- 43 - The Klein-Gordon Equation PDFDocument7 pages43 - The Klein-Gordon Equation PDFUltrazordNo ratings yet
- Che 126 Complete SlideDocument658 pagesChe 126 Complete Slideabuabdmuqseet2001No ratings yet
- Molecular Orbital Diagram For B, C, N, O, F and NeDocument12 pagesMolecular Orbital Diagram For B, C, N, O, F and NeGods ArmyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - The Chemistry of The Amino Group - S. PataiDocument413 pagesChemistry - The Chemistry of The Amino Group - S. PataiGary SmithNo ratings yet
- 3.) Magnetic+circuitDocument40 pages3.) Magnetic+circuitkujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Lec 02Document42 pagesLec 02zingkovNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9 Core-Shell NanoparticlesDocument19 pagesChapter - 9 Core-Shell NanoparticlesPrasanta KalitaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 13 2023Document3 pagesAssignment 13 2023Linhan ChuNo ratings yet
- Anderson TransitionsDocument63 pagesAnderson TransitionsDanang Suto WijoyoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18 - Phase Transformations - July 7 2022Document18 pagesLecture 18 - Phase Transformations - July 7 2022Ryan MaxwellNo ratings yet