Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UNIT-I Shorty & Full Form
UNIT-I Shorty & Full Form
Uploaded by
Jitendra Nath SwainCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT-I Shorty & Full Form
UNIT-I Shorty & Full Form
Uploaded by
Jitendra Nath SwainCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit-1(Networking & Open Standards)
Very short type Q & A
Chapter-I
1) Protocol is the set of rules that governs data communication.
2) Data Communication refers to exchange of data or information between two devices.
3) 5 Components of data communication are:-Sender, Receiver, Message, Media & Protocol.
4) In Simplex Transmission mode, signal travels in one direction i.e. from sender to receiver.
5) In Half Duplex Transmission mode, signal travels in both the direction but not at the same time.
6) In Full Duplex Transmission mode, signal travels in both the direction but at the same time.
7) Interconnection of multiple computers through communication channels is called as Network.
8) OSI contains 7 layers.
9) OSI layers:
Physical Data link Network Transport Session Presentation Application
10) The computer that we are currently using is called Local computer/user’s computer.
11) The computer that is located far apart from a user is called Remote computer.
12) The computer that make request for services to a Server computer is called Client Computer.
13) The computer that provides requested services to the client computers is called Server computer.
14) The relationship between Server and Client is usually One to Many.
15) The device which is used to connect one device with another in a network is called
Network device.
16) Network Devices are:- HUB , Repeater , Bridge , Switch , Router ,Gateway.
17) HUB operates in Physical layer of OSI model.
18) HUB is of 2 types i.e. Active HUB & Passive Hub.
19) Active Hub can regenerate but Passive Hub can’t regenerate incoming signal.
20) Switch operates in Data Link layer of OSI model.
21) Switch is called as Switching Hub.
22) Between Switch & Hub, Switch provides Data filtering.
23) Switch is more intelligent & secure than HUB.
24) Repeater is considered as Signal Regenerator.
25) Repeater operates in Physical layer of OSI model.
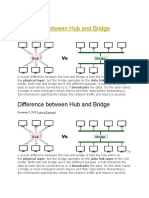
26) Bridge operates in both Physical & Data link layer of OSI layer.
27) Bridge connects two segments of a LAN.
28) Bridge is used to connect different Homogeneous Network.
29) Router operates in Physical, Data link & Network layer of OSI model.
30) Router transmits or route data from one network to other networks.
31) Router is used to connect different Heterogeneous Network.
32) Gateway operates in all 7 layers of OSI model.
33) Gateway is called as Protocol Converter.
34) A LAN network can be formed by connecting computers of two adjacent buildings.
35) Network Interface Card (NIC) is also called as LAN card.
36) Cable TV network is a type of MAN network.
37) Topology refers to physical or logical arrangement of links in a network.
38) 5 types of Topologies are : Star, Tree, Ring, Mesh & Bus
© 2018 IT-Networking Prepared By: J.N.Swain
39) Mesh Topology is very much robust & Reliable.
40) In Ring Topology token passes from one device to another in a Ring.
41) WAN network covers maximum geographical area among LAN, MAN & WAN.
42) A PAN network can be formed by connecting a computer with peripheral devices
within a short range.
43) PAN network is generally Wireless Based.
44) INTRANET can only be used by members & Employees of an Organization.
45) INTRANET is more secure than INTERNET because it uses FIREWALL protection.
46) EXTRANET not only used by members & Employees, but also used by some registered
Outsiders of an Organization.
47) EDI technology is more used by EXTRANET.
48) Baud rate can be measured by unit bit per second (bps).
49) Bandwidth can be measured by unit Hertz/KHz/MHz/GHz.
50) Wired Technology is also called as Guided Media that uses Physical cable.
51) Wireless Technology is also called as Un-Guided Media that doesn’t use any physical cable.
52) Wired Technologies are:- a. Co-axial cable, b. Twisted Pair-cable, c. Fiber-optic cable
53) Co-axial cable is generally used in cable network for digital transmission.
54) Faster data transmission is possible through Fiber optic cable.
55) Twisted-pair cable are twisted together to prevent Cross-Talk.
56) Some wireless technologies are: - Radio Wave, Micro Wave, Infrared, Bluetooth, and Satellite.
57) Bluetooth is named after Harald Bluetooth.
58) Bluetooth can penetrate physical barrier, but Infrared can’t.
59) Bluetooth is used to connect 8 devices at a time.
60) Infrared requires line of sight, but Bluetooth doesn’t.
61) Typical range of Bluetooth is 10m/30 ft.
Chapter-II
1) The first network over the world was ARPANET.
2) ARPANET gave rise to development of Internet.
3) Ethernet & Token ring are LAN technologies Specified by IEEE standard.
4) Data transfer rate in Dial-up connection is up to 56kbps.
5) Data transfer date in Broadband connection is more than 200kbps.
6) Broadband Connection supports Maximum Bandwidth.
7) Broadband carries Analog signal & baseband carries Digital signal.
8) TCP/IP protocol is a connection oriented protocol.
9) HTTP is a stateless protocol.
10) FTP protocol is used for file uploading & downloading.
11) TELNET protocol is a remote login program.
12) IP address is a unique address to identify a particular computer in a network.
13) Length of an IP address is 32 bit.
14) Length of IPv4 is 32 bit.
15) Length of IPv6 is 128 bit.
16) IP address has 5 classes: Class A ,Class B, Class C ,Class D, Class E
17) “@” Symbol represents Domain name.
18) .com, .org, .edu, .in are Domain indicators.
© 2018 IT-Networking Prepared By: J.N.Swain
Domain indicators Indicates
.com Commercial organization
.org Non-profit Organization
.ac.in Academic Institution
.in Institution
.nic.in Website hosted by National Informatics Center (NIC)
.gov.in Government Authority/Agency
.net Networking Organization
.mil Military Agency
.edu Educational Institution
19) Domain name system (DNS) converts domain name into IP address & vice versa.
20) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) converts IP address into MAC address.
21) Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) converts MAC address into IP address.
22) Media access Control (MAC) is the sub layer of data link layer in OSI model.
23) MAC address is also called Physical address/hardware address/Ethernet address.
24) The length of MAC address is 48 bit.
25) MAC address is represented by hexadecimal no.
26) URL is the addressing method to access a particular file or document from a server.
27) First E-mail was sent by Ray Tomlinson in 1971.
28) E-mail is One to One and One to Many communication.
E-Mail Terms Purpose
Sign Up Process of creating an E-mail account
Sign In Process of entering into an E-mail account.
Sign Out Process of moving out from an E-mail account.
Compose Mail Process of writing an E-mail message.
Inbox Contains trusted and legal E-mails
Draft Contains composed E-mails that will sent later
SPAM Contains unwanted and entrusted e-mails
Trash Contains deleted E-mails
29) SMTP protocol is used to send E-mail message.
30) POP protocol is used for receiving E-mail message.
31) E-Mail is usually written in Lower Case letters.
32) E-Mail address has two parts i.e. User Name & Domain Name.
33) Some Free E-mail providers are: G-Mail, Yahoo Mail, Rediff mail, Zinga Mail, Hotmail Etc
34) WWW or W3 is the most exciting area for discovery & innovation.
35) WWW was first invented by Tim Berner’s Lee in 1990.
36) WWW uses HTTP protocol.
37) Each and every page or file in a website is called as Web Page.
38) Website is the collection of WebPages.
39) The first page of a Web site is called Home Page.
40) Web page is created using HTML language.
41) Hypertext refers to the text within text.
© 2018 IT-Networking Prepared By: J.N.Swain
42) SMS is the form of short text message.
43) Voice mail is a voice message that a person sends , when the receiving person is absent or not
picked up the phone.
44) Chatting is the real time interaction between two or more uses at the same time using internet.
45) Instant messaging(IM):- It is the instant or immediate exchange of message between two uses
using Internet
46) Instant Messaging Applications: a.Whatsapp Messenger, b. Face book Messenger, c.Hike,
d. Telegram, e. Line, f. Instagram
47) Emoticons/Smilies are the symbols used during Chatting to express feelings and facial
expression.
48) Internet Lingo is the short form or acronyms used during chatting for faster message delivery.
49) Video conferencing is the two –way audio-visual conversation among multiple participants using
internet.
50) Internet Relay chat (IRC) is a internet discussion forum in which multiple participants are
joined in a channel to discuss on a particular topic.
51) Web browser is the software used for web searching/web surfing/web browsing.
a. Internet Explorer, b. Google chrome, c. Mozilla Firefox,
52) Example of Web browser:-
d. Opera, e. Safari, f. Nexus
53) Web browsing is the process of interacting with internet.
54) Search Engine Examples:- a. Google ,b. Yahoo ,c. Bing, d. Alta Vista ,e. Info seek ,f. Msn ,g. Ask
55) File uploading is the process of copying a file from client computer to server computer.
56) File downloading is the process of copying a file from server computer to client computer.
MOBILE TECHNOLOGIES/STANDARDS
GENERATION
FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access)
1G AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System)
NMT (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
TACS (Total Access Communication System)
TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access)
2G GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication)
2G CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access)
2.5 G GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)
2.75 G EDGE (Enhanced data rate for GSM evolution)
HSPA (High Speed Packet Access)
3G WCDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access)
3G UMTS (Universal mobile Telecommunication System)
3.5 G HSPA+
3.75 G EHSPA (Evolved HSPA)
LTE (Long term Evolution)
4G VOLTE (Voice Over Long Term Evolution)
4G WIMAX (Wireless Interoperability for Microwave Access )
4.5 G LTE-A (Long Term Evolution -Advanced)
© 2018 IT-Networking Prepared By: J.N.Swain
Abbreviation
Chapter-I
1. Net:- Network
2. Internet:-Internetwork
3. LAN:—Local Area Network
4. MAN:—Metropolitan Area Network
5. WAN:—Wide Area Network
6. WLAN:-Wireless Local Area Network
7. Wi-Fi:-Wireless Fidelity
8. PAN:-Personal Area Network
9. WPAN:-Wireless Personal Area Network
10. SAN:-Storage Area Network
11. EPN:-Enterprise Private Network
12. VPN:-Virtual Private Network
13. ISDN:-Integrated Service Digital Network
14. PSTN:-Public Switched Telephone Network
15. PSDN:-Public Service Digital Network
16. VAN:-Value Added Network
17. NIC:-Network Interface Card
18. NIU:-Network Interface Unit
19. OSI:-Open System Interconnection
20. ISO:-International Standard Organization
21. Co-ax:-Co-Axial Cable
22. UTP:-Unshielded Twisted Pair
23. STP:-Shielded Twisted Pair
24. IEEE:-Institute Of Electrical And Electronics Engineers
25. ANSI:-American National Standard Institute
26. FDDI:-Fiber Distributed Data Interface
27. EDI:-Electronic Data Interchange
28. BPS:-Byte Per Sec (MBPS:-Megabyte Per Sec, GBPS: -Gigabyte Per Sec)
29. bps:-Bit Per Sec (Kbps:-Kilobit Per Sec, Mbps:-Megabit Per Sec, Gbps: -Gigabit Per Sec)
30. Hz:-Hertz (MHz:-Mega Hertz, GHz:-Giga Hertz)
31. RF:-Radio Frequency
32. IR:-Infrared
33. NOC:-Network Operation Center
34. VSAT:-Very Small Aperture Terminal
35. GEO:-Geo- Stationary Orbit
36. MEO:-Medium Earth Orbit
37. LEO:- Low Earth Orbit
38. GPS:- Global Positioning System
39. GIS:-Geographical Information System
© 2018 IT-Networking Prepared By: J.N.Swain
Chapter-II
40. ARPA:-Advanced Research Project Agency
41. ARPANET:-Advanced Research Project Agency Network
42. NSFNET:-National Science Foundation Network
43. AT&T :- American Telephone & Telegraph Company
44. ISP:-Internet Service Provider
45. AOL:-American Online
46. BSNL:-Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited
47. VSN:-Videsh Sanchar Nigam Limited
48. MODEM :-Modulator And Demodulator
49. DSL:-Digital Subscriber Line
50. ADSL:- Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line
51. SDSL:- Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line
52. TCP/IP:-Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
53. HTTP:-Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
54. FTP:-File Transfer Protocol
55. Telnet:-Telecommunication Network
56. WAIS:-Wide Area Information Server
57. TLD:-Top Level Domain
58. DNS:-Domain Name System
59. ARP:-Address Resolution Protocol
60. RARP:-Reverse Address Resolution Protocol
61. URL:-Uniform Resource Locator
62. MAC:-Media Access Control
63. WWW Or W3:-World Wide Web
64. W3C:-World Wide Web Consortium
65. HTML:-Hypertext Markup Language
66. E-Mail:-Electronic Mail
67. SMTP:-Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
68. POP:-Post Office Protocol
69. IMAP:-Internet Mail Access Protocol
70. CC:-Carbon Copy
71. BCC:-Blind Carbon Copy
72. IE:-Internet Explorer
73. SERP:-Search Engine Result Pages
74. VC:-Video Conferencing
75. SMS:-Short Message Service
76. MMS:-Multimedia Message Service
77. IM:-Instant Messaging
78. IRC:-Internet Relay Chat
79. VOIP:-Voice Over Internet Protocol
80. GSM:-Global System For Mobile Communication
81. TDMA:-Time Division Multiple Access
82. FDMA:-Frequency Division Multiple Access
83. CDMA:-Code Division Multiple Access
84. GPRS:-General Packet Radio Service
85. EDGE:-Enhanced Data Rate For GSM Evolution
© 2018 IT-Networking Prepared By: J.N.Swain
86. SIM:-Subscriber Identity Module
87. WLL:-Wireless Local Loop
88. 3G:-Third Generation
89. WCDMA:-Wideband Code Division Multiple Access
90. HSPA:-High Speed Packet Access
91. UMTS:-Universal Mobile Telecommunication System
92. LTE:-Long Term Evolution
93. VOLTE:-Voice Over Long Term Evolution
94. WiMAX:- Wireless Interoperability For Microwave Access
Chapter-III
95. PC:-Personal Computer
96. VIRUS:-Vital Information Resources Under Seize
97. WORM:-Write Once Read Many
98. DSC:-Digital Signature Certificate
99. DoS Attack:-Daniel Of Service Attack
100. IPR:-Intellectual Property Right
101. IPC:- Indian Penal Code
102. FIR:-First Information Report
© 2018 IT-Networking Prepared By: J.N.Swain
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Installation Guide XB30330Document68 pagesInstallation Guide XB30330almanis0% (1)
- Operating Manual DAS PLTMG Sumbawa 50 MWDocument21 pagesOperating Manual DAS PLTMG Sumbawa 50 MWerick herdiawanNo ratings yet
- PTS 10-4 CBLM - Maintain Computer Systems and NetworksDocument89 pagesPTS 10-4 CBLM - Maintain Computer Systems and NetworksGenoMaxmillano67% (15)
- Topologies: - The Structure of The NetworkDocument25 pagesTopologies: - The Structure of The NetworkBuneaSabinNo ratings yet
- Irjet V8i9226Document8 pagesIrjet V8i9226AleNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument4 pagesNetwork TopologyAnish VeettiyankalNo ratings yet
- The Data Link Layer: Reading: Ch. 2.2, 2.6, 3.1, 3.2Document108 pagesThe Data Link Layer: Reading: Ch. 2.2, 2.6, 3.1, 3.2Madhu CkNo ratings yet
- CCNA Routing and Switching 200Document490 pagesCCNA Routing and Switching 200novel100% (1)
- CCNA Powerpoint - 1Document111 pagesCCNA Powerpoint - 1Aung KhaingNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 2Document8 pagesCN Unit 2igor iljinNo ratings yet
- Networking DeviceDocument26 pagesNetworking DeviceYe Lin NaingNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2. Computer HardwareDocument3 pagesExercise 2. Computer HardwareMikaela Mae GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Network TopologyDocument3 pagesLesson 4 - Network TopologyGeorgia Andales TaganahanNo ratings yet
- Data and Computer Communications: Chapter 16 - High Speed LansDocument41 pagesData and Computer Communications: Chapter 16 - High Speed LansMeenakshi DhasmanaNo ratings yet
- CCNA Basic QuestionsDocument11 pagesCCNA Basic QuestionsFritz Gerald F. SensengNo ratings yet
- Types of NetworksDocument5 pagesTypes of NetworksVenus Leilani Villanueva-GranadoNo ratings yet
- Flash CardsDocument92 pagesFlash Cardsl3m0ntr33No ratings yet
- The Hows and Whys of Ethernet Networks in Substations: ThernetDocument27 pagesThe Hows and Whys of Ethernet Networks in Substations: ThernetbansalrNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networking: Module - 1Document17 pagesData Communication and Networking: Module - 1velskvmNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Data CommunicationDocument54 pagesUnit - 3 Data CommunicationDr. Rupali TaruNo ratings yet
- Section 4 Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesSection 4 Computer NetworksPamela ChimwaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Lecture 2Document51 pagesComputer Networks Lecture 2Super SpecialNo ratings yet
- Sna 2 ManualDocument131 pagesSna 2 ManualBen MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Ethernet: CCNA Exploration 4.0Document90 pagesChapter 9 - Ethernet: CCNA Exploration 4.0kiennaNo ratings yet
- ch15-SLIDE - (2) Data Communications and Networking by Behrouz A.ForouzanDocument30 pagesch15-SLIDE - (2) Data Communications and Networking by Behrouz A.ForouzanXP2009100% (1)
- Networking PresentationDocument28 pagesNetworking PresentationAbhishek DaveNo ratings yet
- Zfs 3016Document10 pagesZfs 3016cepsamex9108No ratings yet
- WeekEndAssignment 01 1Document5 pagesWeekEndAssignment 01 1adityadas.657No ratings yet
- Ethernet IPDocument126 pagesEthernet IPNam Cao HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Hub and BridgeDocument5 pagesDifference Between Hub and BridgeKabanda YvesNo ratings yet