Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transformer Oil
Transformer Oil
Uploaded by
Arshad Ahmeed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Transformer oil.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesTransformer Oil
Transformer Oil
Uploaded by
Arshad AhmeedCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Transformer:
Transformer is one of the most useful appliances
ever invented. Transformer can raise or lower the
voltage or current in alternating current (AC)
network, it can transfer power from one section to
another on the same frequency but different
voltage levels and currents. Transformer basically
consists of two coils of a conductor which acts as
an inductor electrically separate but magnetically
attached. With the help of transformer the circuit
can be isolated from one another, and to increase
or decrease the apparent value of a capacitor,
inductor, or resistor. Furthermore, the transformer
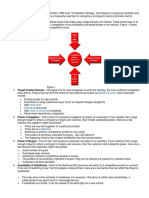
allows us to transmit electricity long distances and Fig 2: Parts and cooling of transformer
to circulate safely in factories and homes.
(Electrical Machines, Drives, and Power Systems, Transformer oil serves three basic functions which
6th Edition). are to insulate, to cool and maintain the
transformer functions at all times. Transformer oil
The cost of a transformer is high. The failure of is also used to preserve the transformer’s core and
one transformer resulted in a loss in terms of the windings – as these are fully immersed inside the
price of one transformer or in terms of energy oil. Another important property of the insulating
supply disruptions to consumers. Therefore, to oil is its ability to prevent oxidation of the
monitor the transformer oil is one the right way cellulose-made paper insulation. The transformer
and good for detecting the causes of damage to oil acts as a barrier between the atmospheric
transformers. oxygen and the cellulose – avoiding direct contact
and hence minimizing oxidation. The level of
transformer oil is typically measured using a
MOG (Magnetic Oil level Guage).
Transformer Oil Properties:
The properties (or parameters) of transformer oil
can be classified as:
1. Electrical properties: Dielectric strength,
specific resistance, dielectric dissipation
factor.
2. Chemical properties: Water content,
acidity, sludge content.
3. Physical properties: Interfacial tension,
Fig 1:Transformer viscosity, flash point, pour point.
What is Transformer Oil? The main function of transformer oil is insulating
and cooling of the transformer. It should have the
Transformer oil (also known as insulating oil) is following properties:
a special type of oil which has excellent electrical 1. High dielectric strength and good
insulating properties and is stable at high dielectric properties resulting in minimum
temperatures. Transformer oil is used in oil-filled power loss.
electrical power transformers to insulate, stop 2. Low viscosity improves cooling.
arcing and corona discharge, and to dissipate the 3. Freedom from inorganic acids, alkali, and
heat of the transformer (i.e. act as a coolant). corrosive sulphur.
Transformer oil is likened to be the blood within 4. Resistant to emulsification.
the transformer body. It must be periodically 5. Rapid settling of arc products.
tested to monitor condition of the transformer. 6. Low pour point.
7. High flash point resulting in low
evaporation losses due to high thermal
stability.
8. High resistivity gives better insulation
values between windings.
9. Excellent interfacial tension for quick
water separation.
10. Proven resistance to electrical stresses.
11. High electrical strength.
12. Remarkably low sludge and acidity
formation in both ageing and oxidation
tests gives longer life to oil and equipment
during storage and service.
Fig 3: Transformer Oil
TRANSFORMER OIL CLASSIFICATIONS
1. Good Oils
NN 0.00 - 0.10
IFT 30.0 - 45.0
Colour Pale Yellow
OQIN 300-1500
2. Proposition A Oils
NN 0.05 - 0.10
IFT 27.1 - 29.9
Colour Yellow
OQIN 271 – 600
3. Marginal Oils
NN 0.11 - 0.15
IFT 24.0 - 27.0
Colour Bright Yellow Types of Transformer Oil:
OQIN 160 – 318
4. Bad Oils
NN 0.16 - 0.40
IFT 18.0 - 23.9
Colour Amber
OQIN 45 – 159
5. Very Bad Oils
NN 0.41 - 0.65
IFT 14.0 - 17.9
Colour Brown
OQIN 22 – 44
6. Extremely Bad Oils
NN 0.66 - 1.50
IFT 9.0 - 13.9
Colour Dark Brown
OQIN 6 – 21
7. Oils in Disastrous Condition
NN 1.51 or more
Colour Black Fig 4: Types of transformer oil
Mineral Transformer Oil (Mineral Based Oil): Regular maintenance and upgrading of the oil will
A mineral oil or liquid petroleum is a liquid by- add years to the life of both your car and your
product of the distillation of petroleum to produce transformer.
gasoline and other petroleum based products from
crude oil. A mineral oil in this sense is a Oil Quality
transparent, colourless oil composed mainly of Transformer oil is a mineral based oil. It is
alkenes (typically 15 to 40 carbons) and cyclic commonly used in transformers because of its
paraffin, related to petroleum jelly (also known as chemical properties and dielectric strength.
“white petrolatum”). It has a density of around 0.8 Minimal breakdown of the oil occurs under
g/cm3. Mineral oil is a substance of relatively low normal operating conditions.The insulation and
value, and it is produced in very large quantities. cooling properties of the transformer are effected
Mineral oil is available in light and heavy grades, by the quality of the oil. The quality of the oil is
and can often be found in drug stores. reduced by oxidization and contamination. The
results of each of these can be summarized briefly
There are three basic classes of refined mineral as follows:
oils:
Contamination commonly found in oil can be
water and particulate. The presence of either
1. Paraffinic oils, based on n-alkenes.
contaminant will cause reduced insulation quality
2. Naphthenic oils, based on cycloalkanes.
of the oil.
3. Aromatic oils, based on aromatic
Oxidization is the acid that forms in the oil when
hydrocarbons
it reacts to oxygen. This acid will form sludge
which will settle on the windings of the
Naphtha oil is more easily oxidized than paraffin
transformer reducing the heat dissipation from the
oil. But the product of oxidation – i.e. sludge – in
transformer. The heat transfer from the windings
the naphtha oil is more soluble than the sludge
to the oil is limited thus causing the windings to
from the paraffin oil. Thus sludge of naphtha-
run hotter. Sludge formation on the windings has a
based oil is not precipitated in the bottom of the
snowball effect on the transformer with more
transformer. Hence it does not obstruct convection
sludge creating more heat, creating more sludge
circulation of the oil, means it does not disturb the
etc. The high acid content together with the
transformer cooling system.
excessive temperatures will cause the
deterioration of the transformer insulation to be
Although Paraffin oil has a lower oxidation rate
accelerated and if left untreated the transformer
than Naphtha oil, the oxidation product (sludge) is
will fail.
insoluble and precipitated at the bottom of the
tank. This sludge acts as an obstruction to the Transformer Oil Testing Methods:
transformer cooling system. Another problem
with paraffin-based oil that the dissolved waxes
inside of it can lead to a high pour point. Although
this is not an issue in warmer climate conditions
(such as India).Despite the disadvantages
mentioned above, paraffin-based oil is still
commonly used in many countries (such as India)
due to its high availability.
Maintenance of transformer oil:
The easiest way to explain the reasoning for
proper transformer oil maintenance is to compare
a transformer to a car. A car requires oil for
lubrication while a transformer requires oil for 1.Color D1500(standard):Color is determine
insulation and cooling. Just as a car requires meaning of transmitted light and give a numerical
regular checks of both oil quality and oil level, a value based on series color stranded.Therefore
transformer requires the same proactive treatment. Transformer oil testing colors are indicate arcing
Oil in each instance degrades over time resulting is take place of the oil.
in the potential for failure or costly repair bills.
2.Dielectric breakdown voltage D877: This 11. Polychlorinated biphenyls content D4059: It is
standard is measured by apply voltage between tested by these content to detects the concentration
two electrodes and oil entered between both of level of polychlorinated biphenyls in insulating oil
them. Finally Measuring of this voltage are by gas chromatography. Another measured it also
indicate which amount of moisture in transformer applies to the determination of PCB present in
oil. mixtures known as askarels.
3.Dissolved gas analysis D3612:The transformer 12.Pour point D97: It indicates the lowest level of
oil generate different gases are indicates occurring temperature at which the oil will flow. So this test
various types of thermal and electrical stress. So the oil is particularly useful in cold climates. To
an internal faults are remove in oil can earliest ensure that the transformer oil will circulate and
using this test method. serve properly. Since the purpose of oil as an
insulating and cooling medium.
4.Dissolved metals D7151:It is identify to these
testing after that can generate overheating or 13.Power factors D924:Testing of power factor
arcing from transformer oil. Rather it is measured the dielectric losses of oil are dissipate as form of
by inductively dissolved metals in micrometers. heat. While measure of power factor equals to
cosine phase angle between an ac voltage and
5.Flash and fire point D92:It indicates the current. Since mineral oil of power factor not
moisture in insulating oil by measuring the exceed 0.05 percent at 25 degrees Increase.
minimum temperature at insulating oil .Which is
heated transformer oil to gives a sufficient vapor 14.Relative density D1298: To determines relative
in form of unstable and mix with air. density, or API gravity of oil by use of
hydrometer at a reference temperature. After the
6.Interracial tension D971:Its define as interracial testing process high specific gravity to indicates
tension to decrease value indicates an increase in the oil’s ability to suspend in mineral water. All
oxidation products within the transformer oil. whether ice will float on the transformer oil.
Measures to oxidation products in oil are
expressed in mN/m. It is a test of interracial 15. Resistivity D1169: Measures the electrical
tension surface tension in that the surface, after insulating properties of oil under conditions
testing the water is contact with oil instead of air. comparable to those after testing method. In
addition a low resistivity to indicates reflects a
7. Furanic compound D5837:The determines high content of free ions and particles of
testing of furanic compound that present of insulating oil.
degradation in cellulose materials such as paper,
press board, and cotton, etc. Measurements of 16.Visual examination D1524:Oil is passing a
furanic compound are made using high- beam of light transparency medium and identify
performance liquid to used Insulating oil. foreign matters. It has Contamination of the
transformer oil testing is poor transparency and
8.Moisture content D1533:It does not measure the cloudiness.
water content in the insulation paper. Measured
weight of moisture divided by the weight of oil.
Hence Moisture content in oil to insulate dielectric
strength and allows flash overheating that can
damage a oil.
9.Neutralization number D974: This stranded after
testing measures the acids formed by oxidation.
Transformer oils can contain no acids. As a result
after measurements that can acid occur the high
amount of potassium hydroxide (KOH in mg)
in oil.
10.Oxidation inhibitor content D2668:Its define
testing the amount of transformer oil as protection
against oxidation. The oil it measures the amount
remaining after oxidation has reduced its
concentration to used material.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Non Alcholic Perfume From Kashmiri Roses: Nawab Shabir Nayab Dutt Khalid Muzzafar Zubair Bhat Ravish RahejaDocument15 pagesNon Alcholic Perfume From Kashmiri Roses: Nawab Shabir Nayab Dutt Khalid Muzzafar Zubair Bhat Ravish RahejaNeed IsolationNo ratings yet
- The Industry HandbookDocument34 pagesThe Industry HandbookslpypndaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Tax Updates by Atty. Jackie Lou Lamug, CPA PDFDocument112 pages2020 Tax Updates by Atty. Jackie Lou Lamug, CPA PDFNhel JoeNo ratings yet
- Senior Design Project - Gas-to-Liquids Plant DesignDocument95 pagesSenior Design Project - Gas-to-Liquids Plant Designrdskut1030100% (1)
- Chemistry Project CBSEDocument23 pagesChemistry Project CBSEH0% (2)
- Tabela Óleos LubrificantesDocument2 pagesTabela Óleos LubrificantesAndré GraeffNo ratings yet
- 12 - Operation & Maintenance of Framo PumpDocument20 pages12 - Operation & Maintenance of Framo PumpPrabhakar SubramanyaNo ratings yet
- About UsDocument32 pagesAbout UsSubbu Ram PNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Train Lighting Energy Efficiency - LC SarserDocument111 pagesAir Conditioning Train Lighting Energy Efficiency - LC SarserArshad AhmeedNo ratings yet
- Energy Crisis of PakistanDocument12 pagesEnergy Crisis of PakistanM.Tauqeer90% (10)
- Transformer Oil ManualDocument27 pagesTransformer Oil Manualvairam_eee01No ratings yet
- SQL Day 1 1672076703Document7 pagesSQL Day 1 1672076703Arshad AhmeedNo ratings yet
- Document 1672066856Document5 pagesDocument 1672066856Arshad AhmeedNo ratings yet
- SQL Vs PySpark 1678871778Document8 pagesSQL Vs PySpark 1678871778Arshad AhmeedNo ratings yet
- Six Phrase - Myslate - Cocubes - ReasoningDocument123 pagesSix Phrase - Myslate - Cocubes - ReasoningArshad AhmeedNo ratings yet
- Business Communication Skills ToCDocument3 pagesBusiness Communication Skills ToCArshad AhmeedNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil-Article-Very NewDocument5 pagesTransformer Oil-Article-Very NewArshad AhmeedNo ratings yet
- The Use of Coal As Fuel For Cement Rotary KilnDocument23 pagesThe Use of Coal As Fuel For Cement Rotary KilnDheo Ebhee LouVeNo ratings yet
- Report On O.N.G.C. Ltd. Mehsana: Mousumi K. MitraDocument4 pagesReport On O.N.G.C. Ltd. Mehsana: Mousumi K. Mitraashim1006No ratings yet
- United States Patent: Qian Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2016Document29 pagesUnited States Patent: Qian Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2016M FNo ratings yet
- Ostenberg Ross PDFDocument24 pagesOstenberg Ross PDFramdhan_rdhNo ratings yet
- How Africa Maximises Its Oil and Gas Riches - Wood MackenzieDocument7 pagesHow Africa Maximises Its Oil and Gas Riches - Wood MackenzieCenter for Small BusinessNo ratings yet
- Class 10 SP-1 Crude OilDocument2 pagesClass 10 SP-1 Crude OilJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- UOP Introducing The Refinery of The Future John Gugel1 PDFDocument2 pagesUOP Introducing The Refinery of The Future John Gugel1 PDFMirko Calderon RamosNo ratings yet
- POL Prices PKRDocument47 pagesPOL Prices PKRSaad JavedNo ratings yet
- Final LubricantsDocument23 pagesFinal LubricantsjogindersrawNo ratings yet
- Promo PC200 UTPRT DES 2020Document4 pagesPromo PC200 UTPRT DES 2020Syaiful BahriNo ratings yet
- TADOPOLDocument28 pagesTADOPOLFrank DetchokulNo ratings yet
- Review - Spills and Spin: The Inside Story of BPDocument4 pagesReview - Spills and Spin: The Inside Story of BPVaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Maritimenewzealand Accidente RenaDocument20 pagesMaritimenewzealand Accidente RenabernardinodinoNo ratings yet
- Jan Trocki Pres EngDocument28 pagesJan Trocki Pres Engdie_1No ratings yet
- Sicotte - Baku and Its Oil Industry Through War and Revolution - 1914-1920Document9 pagesSicotte - Baku and Its Oil Industry Through War and Revolution - 1914-1920vainhetairaNo ratings yet
- Problems On Linear Programming Formulations - Aug - 2013Document16 pagesProblems On Linear Programming Formulations - Aug - 2013RahulRandy100% (1)
- Chevron 2009 Annual ReportDocument92 pagesChevron 2009 Annual ReportVaibhav BolakheNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document36 pagesBook 1syed faizNo ratings yet
- SolarFeasabilityStudies PiarcoTrinidadTobago Report-July9-webDocument48 pagesSolarFeasabilityStudies PiarcoTrinidadTobago Report-July9-webMardi RahardjoNo ratings yet
- Researching On Factors Affecting Consumers' Decision To Use E5 BIOFUEL in Hanoi CityDocument45 pagesResearching On Factors Affecting Consumers' Decision To Use E5 BIOFUEL in Hanoi CityNhư HảoNo ratings yet