Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bloom's Taxonomy "Revised
Uploaded by
Prabhjyot Kaur0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views3 pagesThe document summarizes Bloom's Taxonomy, which categorizes levels of thinking skills. It outlines the six main cognitive levels - Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, and Create. For each level, it provides example verbs for objectives, model questions to prompt students, and suggested instructional strategies to facilitate learning at that level. The levels progress from basic recall to more complex thinking, synthesis of ideas, and generation of new concepts.
Original Description:
Original Title
Bloom's Taxonomy.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes Bloom's Taxonomy, which categorizes levels of thinking skills. It outlines the six main cognitive levels - Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, and Create. For each level, it provides example verbs for objectives, model questions to prompt students, and suggested instructional strategies to facilitate learning at that level. The levels progress from basic recall to more complex thinking, synthesis of ideas, and generation of new concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views3 pagesBloom's Taxonomy "Revised
Uploaded by
Prabhjyot KaurThe document summarizes Bloom's Taxonomy, which categorizes levels of thinking skills. It outlines the six main cognitive levels - Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, and Create. For each level, it provides example verbs for objectives, model questions to prompt students, and suggested instructional strategies to facilitate learning at that level. The levels progress from basic recall to more complex thinking, synthesis of ideas, and generation of new concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Bloom’s Taxonomy “Revised”
Key Words, Model Questions, & Instructional
Strategies
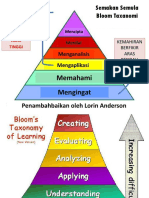
Bloom’s Taxonomy (1956) has stood the test of time. Recently, Anderson &Krathwohl (2001) have
proposed some minor changes to include the renaming and reordering of the
taxonomy. The reference reflects those recommended changes.
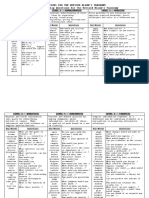
I. REMEMBER (KNOWLEDGE)
(Shallow processing: drawing out factual answers, testing recall and recognition.)
Verbs for Objectives Model Questions Instructional Strategies
Choose Who? Highlighting
Describe Where? Rehearsal
Define Which one? Memorizing
Identify What? Mnemonics
Label How?
List What is the best one?
Locate Why?
Match How much?
Memorize When?
Name What does it mean?
Omit
Recite
Recognize
Select
state
II. UNDERSTAND (COMPREHENSION)
(Translating, interpreting and extrapolating)
Verbs for Objectives Model Questions Instructional Strategies
Classify State in your own words. Key examples
Defend Which are facts? Emphasize connections
Demonstrate What does this mean? Elaborate concepts
Distinguish Is this the same as..? Summarize
Explain Give an example. Paraphrase
Express Select the best definition. STUDENTS explain
Extend Condense this paragraph. STUDENTS state the rule
Give example What would happen if..? “Why does this
Illustrate State in one word... example...?”
Indicate Explain what is happening. Create visual
Interrelate What part doesn’t fit? representations ( concept
Interpret Explain what is meant. maps, outlines, flow charts
Infer What expectations are organizers, analogies,
Judge there? pro/con grids) PRO/ CON
Match Read the graph (table). NOTE: The faculty member
Paraphrase This represents... can show them, but they
Represent What seems to be...? have to do it. Metaphors,
Restate Is it valid that....? rubrics, heuristics.
Rewrite What seems likely?
Select Show in a graph, table.
Show Which statements
Summarize support..?
Tell What restrictions would you
Translate add?
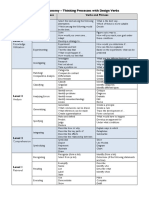
III. APPLY
(Knowing when to apply; why to apply; and recognizing patterns of transfer to situations that are
new, unfamiliar or have a new slant for students)
Verbs for Objectives Model Questions Instructional Strategies
Apply Predict what would happen if Modeling
Choose Choose the best statements that Cognitive apprenticeships
Dramatize Apply “Mindful” practice – NOT
Explain Judge the effects just a “ routine” practice
Generalize What would result Part and whole sequencing
Judge Tell what would happen Authentic situations
Organize Tell how, when, where, why “Coached” practice
Paint Tell how much change there Case studies
Prepare would be Simulations
Produce Identify the results of Algorithms
Select
Show
Sketch
Solve
Use
IV. ANALYZE (breaking down into parts, forms)
Verbs for Objectives Model Questions Instructional Strategies
Analyze What is the function of ...? Models of thinking
Categorize What’s fact? Opinion? Challenging assumptions
Classify What assumptions..? Retrospective analysis
Compare What statement is relevant? Reflection through
Differentiate What motive is there? journaling
Distinguish Related to, extraneous to, not Debates
Identify applicable. Discussions and other
Infer What conclusions? Collaborating learning
Point out What does the author believe? activities
Select What does the author assume? Decision – making
Subdivide Make a distinction. situations.
Survey State the point of view of...
What is the premise?
State the point of view of...
What ideas apply?
What ideas justify the conclusion?
What’s the relationship between?
The least essential statements are
What’s the main idea? Theme?
What inconsistencies, fallacies?
What literary form is used?
What persuasive technique?
Implicit in the statement is…….
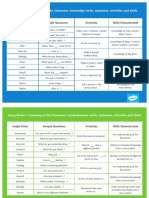
V. EVALUATE (according to some set of criteria, and state why)
Verbs for Objectives Model Questions Instructional Strategies
Appraise What fallacies, consistencies, Challenging Assumptions
Judge Inconsistencies appear? Journaling
Criticize Which is more important, moral, Debates
Defend better, logical, valid, appropriate? Discussions and other
Compare Find the errors. collaborating learning activities
Decision-making situations
VI. CREATE (SYNTHESIS)
(combining elements into a pattern not clearly there before)
Verbs for Objectives Model Questions Instructional Strategies
Choose How would you test…? Modeling
Combine Propose an alternative. Challenging assumptions
compose Solve the following. Reflection through journaling
construct How else would you…? Debates
Create State a rule. Discussions and other
Design collaborating learning activities
Develop Design
Do Decision-making situations
formulate
hypothesize
Invent
Make
make up
originate
Organize
Plan
Produce
role play
Tell
You might also like
- The Skilled Facilitator: A Comprehensive Resource for Consultants, Facilitators, Coaches, and TrainersFrom EverandThe Skilled Facilitator: A Comprehensive Resource for Consultants, Facilitators, Coaches, and TrainersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Barrett's and Bloom's TaxonomyDocument10 pagesBarrett's and Bloom's TaxonomyRaja Letchemy Bisbanathan MalarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Hotel English Term 4Document3 pagesSyllabus - Hotel English Term 4Ruh Mun80% (10)
- Bloom's Taxonomy (Revised) PDFDocument2 pagesBloom's Taxonomy (Revised) PDFJhanina ApduaNo ratings yet
- Fink Bloom TaxonomiesDocument5 pagesFink Bloom TaxonomiesSheila Mae Cordero TabuenaNo ratings yet
- Perfect Phrases For ESL Conversational Skills PDFDocument364 pagesPerfect Phrases For ESL Conversational Skills PDFJane Zhang100% (41)
- Bloom Revised TaxonomyDocument5 pagesBloom Revised TaxonomyquannguyenNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesDocument41 pagesBenjamin Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectivesnight yuiNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy CCDocument3 pagesBlooms Taxonomy CCwanafiqahNo ratings yet
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument3 pagesBlooms TaxonomyAmieMcGuganDavenport100% (2)
- Levels of Learning: Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, EvaluatingDocument6 pagesLevels of Learning: Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, EvaluatingCatalina G. De BelenNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Question Prompts PDFDocument2 pagesCognitive Question Prompts PDFLester Tom CruzNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy in Full - Excellent, Clear VersDocument4 pagesBlooms Taxonomy in Full - Excellent, Clear VersangelicuprisingNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy May 2009Document1 pageBlooms Taxonomy May 2009Alden PaulNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy HandoutDocument5 pagesBloom's Taxonomy HandoutmikoNo ratings yet
- Higher Order Thinking Skills (Bloom 'S Revised Taxonomy) : Advice SheetDocument4 pagesHigher Order Thinking Skills (Bloom 'S Revised Taxonomy) : Advice SheetZedrich MaestoNo ratings yet
- Questions For The Revised BloomDocument2 pagesQuestions For The Revised BloomvempadareddyNo ratings yet
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument35 pagesBlooms Taxonomyromel jericho100% (2)
- Blooms Verbs and Question StemsDocument2 pagesBlooms Verbs and Question StemsJohnry DayupayNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Revised Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesDocument17 pagesBloom's Revised Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesRea GoNo ratings yet
- Levels of Learning:: School-Based INSETDocument41 pagesLevels of Learning:: School-Based INSETPax GarciaNo ratings yet
- Questions For The Revised Bloom TaxonomyDocument2 pagesQuestions For The Revised Bloom Taxonomyapi-360025326No ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy Guide LinesDocument3 pagesBlooms Taxonomy Guide LinesSatish BojjawarNo ratings yet
- Marzano Taxonomy With VerbsDocument1 pageMarzano Taxonomy With VerbsJr MNo ratings yet
- Bloom Taxonomy: Key Words Questions Key Words QuestionsDocument2 pagesBloom Taxonomy: Key Words Questions Key Words Questionseducation forallNo ratings yet
- Revised Bloom's Taxonomy explainedDocument3 pagesRevised Bloom's Taxonomy explainedHoity ToityNo ratings yet
- Costas Question StrategiesDocument7 pagesCostas Question Strategiesalondra barreraNo ratings yet
- Levels of Learning:: School-Based INSETDocument41 pagesLevels of Learning:: School-Based INSETlipNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Strategies Using Bloom's TaxonomyDocument2 pagesCritical Thinking Strategies Using Bloom's TaxonomyWinda Regita PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Level Keywords KnowledgeDocument11 pagesLevel Keywords Knowledgering0No ratings yet
- Developing Higher-Order ThinkingDocument17 pagesDeveloping Higher-Order ThinkingEvelynOmandamVergaraNo ratings yet
- Outcome Statement That Captures Specifically What Knowledge, Skills, AttitudesDocument6 pagesOutcome Statement That Captures Specifically What Knowledge, Skills, AttitudesJessel GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Semakan Semula Bloom Taxanomi: Mengingat MemahamiDocument8 pagesSemakan Semula Bloom Taxanomi: Mengingat Memahamisk lembah beringin kkbNo ratings yet
- Barrett's and Bloom's TaxonomyDocument10 pagesBarrett's and Bloom's Taxonomygpl143No ratings yet
- Bloom Taxonomyename: BloomTaxonomy PDFDocument10 pagesBloom Taxonomyename: BloomTaxonomy PDFAzrul AkmarNo ratings yet
- Verbs Reflecting Learning in 3 DomainsDocument3 pagesVerbs Reflecting Learning in 3 DomainsDzois DzoisNo ratings yet
- Revised Bloom's TaxonomyDocument29 pagesRevised Bloom's TaxonomyBitoy AlarconNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: Note That The Top Two Levels Are Essentially Exchanged From The Old To The New VersionDocument17 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: Note That The Top Two Levels Are Essentially Exchanged From The Old To The New VersionNur ZaraNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy's Model Questions and Key WordsDocument4 pagesBloom's Taxonomy's Model Questions and Key Wordscharles izquierdoNo ratings yet
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument4 pagesBlooms TaxonomyJimmyconnors Chettipally100% (6)
- t2 e 957 Using Blooms Taxonomy in The Classroom Verbs Questions Activities and Skills - Ver - 4Document6 pagest2 e 957 Using Blooms Taxonomy in The Classroom Verbs Questions Activities and Skills - Ver - 4Delia CristeaNo ratings yet
- Higher Order Thinking SkillsDocument38 pagesHigher Order Thinking Skillsglizel diamalNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 Power Point 2Document20 pagesAssessment 1 Power Point 2dhamiltonNGCSUNo ratings yet
- Writing ProcessDocument5 pagesWriting ProcessKhaiZar Haji BarrieNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Planning SheetDocument1 pageBloom's Planning Sheetapi-3724678No ratings yet
- LO Grade 11 Revision Booklet Term 1 - 2023Document8 pagesLO Grade 11 Revision Booklet Term 1 - 2023Keren KotoloNo ratings yet
- 2a - Appropriate Assessment MethodsDocument43 pages2a - Appropriate Assessment MethodsManu LibertyNo ratings yet
- Terabyte Answers 8Document37 pagesTerabyte Answers 8supriya5bNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument30 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentma_tabora6283No ratings yet
- 3 Domains of LearningDocument6 pages3 Domains of LearningCarlz BrianNo ratings yet
- Teaching With The Revised Bloom'StaxonomyDocument33 pagesTeaching With The Revised Bloom'StaxonomyRebenna Bernaldez Lagahit IINo ratings yet
- How To Write Learning Outcomes WorksheetDocument6 pagesHow To Write Learning Outcomes WorksheetAriana Sanchez AlvarezNo ratings yet
- GA2143 Lecture 3 - Critical Thinking and Models of ThinkingDocument20 pagesGA2143 Lecture 3 - Critical Thinking and Models of Thinkingnurul nazifahNo ratings yet
- Computer Answer Key 8Document38 pagesComputer Answer Key 8Alam100% (1)
- Mrs. Janet L. Vitug: SkillsDocument41 pagesMrs. Janet L. Vitug: SkillsALMA LAMPANo ratings yet
- Communicating the UX Vision: 13 Anti-Patterns That Block Good IdeasFrom EverandCommunicating the UX Vision: 13 Anti-Patterns That Block Good IdeasNo ratings yet
- Creating Great Choices: A Leader's Guide to Integrative ThinkingFrom EverandCreating Great Choices: A Leader's Guide to Integrative ThinkingNo ratings yet
- TOOLBOX FOR THE MIND: Finding and Implementing Creative SolutionsFrom EverandTOOLBOX FOR THE MIND: Finding and Implementing Creative SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Group Dynamics and Team Interventions: Understanding and Improving Team PerformanceFrom EverandGroup Dynamics and Team Interventions: Understanding and Improving Team PerformanceNo ratings yet
- Altered Perspective: Search Strategies for Innovators (Volume 1)From EverandAltered Perspective: Search Strategies for Innovators (Volume 1)No ratings yet
- Altered Perspective: Search Strategies for Innovators (Box Set)From EverandAltered Perspective: Search Strategies for Innovators (Box Set)No ratings yet
- Communication Toolkit for Introverts: Find your voice in everyday business situationsFrom EverandCommunication Toolkit for Introverts: Find your voice in everyday business situationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 4 Behaviour TypesDocument15 pages4 Behaviour TypesHilmi HamidonNo ratings yet
- 5 Steps To Writing A Position PaperDocument16 pages5 Steps To Writing A Position PaperErdy John GaldianoNo ratings yet
- Activity 01 For Module 01Document5 pagesActivity 01 For Module 01Rachelle AlcantraNo ratings yet
- Ser Vs Estar Review Packege With EjerciciosDocument5 pagesSer Vs Estar Review Packege With EjerciciosHaydenNo ratings yet
- Tiered Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesTiered Lesson PlanlfayerileyNo ratings yet
- Reading Writing Listening Speaking: Lesson PreparationDocument3 pagesReading Writing Listening Speaking: Lesson PreparationCecília AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Readiness For Enhanced Knowledge Related To Preoperative CareDocument1 pageNcp-Readiness For Enhanced Knowledge Related To Preoperative CareAce Dioso Tubasco50% (2)
- Learn Korean verbs and particles for basic sentencesDocument4 pagesLearn Korean verbs and particles for basic sentencesAndi ANo ratings yet
- Analogies Homework HelpDocument7 pagesAnalogies Homework Helpafmtibboa100% (1)
- Assignment 1 Short Essay by Intan ArisyaDocument8 pagesAssignment 1 Short Essay by Intan Arisyaapi-583845111No ratings yet
- Art Unit PlanDocument5 pagesArt Unit PlanMichaela Jayne NolanNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 MaryDocument15 pagesChapter1 Maryfenrose pedrajasNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Epistemology PDFDocument22 pagesA Brief Introduction To Epistemology PDFAnonymous u80JzlozSDNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions For Mathematical AbilityDocument13 pagesSample Questions For Mathematical Abilityagus aminNo ratings yet
- ADKAR Reinforcement EbookDocument12 pagesADKAR Reinforcement EbookErvin PregNo ratings yet
- Misamis Occidental Science and Technology High School: Division of Oroquieta City District VII Pines, Oroquieta CityDocument5 pagesMisamis Occidental Science and Technology High School: Division of Oroquieta City District VII Pines, Oroquieta CityKATRINA MARIE AmayNo ratings yet
- Bsbcmm401 CADocument12 pagesBsbcmm401 CADarcie Jo-aNo ratings yet
- Morphological analysis of Filipino online gamer slangDocument13 pagesMorphological analysis of Filipino online gamer slangRenee Rose Taduran0% (1)
- CS6007 Information RetrievalDocument8 pagesCS6007 Information Retrievaltamil_delhiNo ratings yet
- Awareness and Effectiveness of Ra 11131 AmendmentDocument6 pagesAwareness and Effectiveness of Ra 11131 AmendmentOsannah Irish Insong100% (3)
- Bibliometrics: Historical Development of BibliometricsDocument6 pagesBibliometrics: Historical Development of Bibliometricsrammit2007No ratings yet
- Special Occasion Speeches GuideDocument3 pagesSpecial Occasion Speeches GuideMaia Dela Cruz MindoNo ratings yet
- Susanna Isaacs ElmhirstDocument14 pagesSusanna Isaacs Elmhirstkarine botelhoNo ratings yet
- Summary Report: It Takes Two To Talk - The Hanen Program For ParentsDocument3 pagesSummary Report: It Takes Two To Talk - The Hanen Program For ParentsMel DocampoNo ratings yet
- Self-Regulated Learning - Where We Are TodayDocument13 pagesSelf-Regulated Learning - Where We Are Todayvzzvnumb100% (1)
- Foundations of Individual and Group Behavior: Powerpoint Presentation by Charlie Cook All Rights ReservedDocument39 pagesFoundations of Individual and Group Behavior: Powerpoint Presentation by Charlie Cook All Rights ReservedAli ElattarNo ratings yet
- Communication Process and StylesDocument3 pagesCommunication Process and StylesMyline Ejorcadas Real100% (3)