Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eee F426 1259
Eee F426 1259
Uploaded by
shwetaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eee F426 1259
Eee F426 1259
Uploaded by
shwetaCopyright:
Available Formats
BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, Pilani
Pilani Campus
Instruction Division
First Semester 2019-2020
Course Handout (Part II)
Date: 02/08/2019
In addition to Part I (General Handout for all courses appended to the Time Table), this portion gives further specific
detail regarding the course:
Course No: EEE F426
Course Title: Fiber Optics and Optoelectronics
Instructor-in-charge: RAHUL SINGHAL
1. Course Description:
Optical communication systems and components; optical sources and transmitters (basic concept, design and
applications); modulators (electro- optic, acousto-optic and laser modulation techniques); beam forming; focusing and
coupling schemes to optical repeaters; optical amplifiers; optical field reception; coherent and non-coherent light wave
systems; fiber optic communication system design and performance; multichannel light wave systems; long haul
communications; fiber optic networks.
2. Scope & Objective:
In the recent past, tremendous advances have been achieved in fiber optics and associated optoelectronics. These
developments have made fiber - optic communication synonymous with the current worldwide revolution in
information technology. This course aims at providing the students with a firm grounding in the major aspects of this
emerging technology. Thus the course deals with the study of various building blocks of fiber optic systems, e.g. optical
fibers, sources, detectors, modulators, optical amplifiers, etc. together with overall system design and performance
analysis for communication applications.
3. Text Book (TB):
Khare, R.P.: “Fiber Optics and Optoelectronics” Oxford University Press (2004)
4. Reference Book (RB):
Keiser, G. ,"Optical Fiber Communications", 5/e, McGraw Hill, 2013
5. Course Plan:
Reference to
Module Lect. No. Topic (s) to be covered chapter of Learning Outcomes
TB/RB
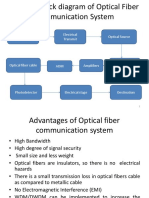
A generalized configuration of a fiber Basic configuration of a fiber-optic system,
Chapter
1,2 optic system, Advantages, Role of Merits of FO system, Role-play in the
1(TB, RB)
fiber optic systems. sociological evaluation
Review of fundamental laws of optics,
I Ray propagation in step index fibers, Ray propagation through different types of
Ray propagation in graded index Chapter 2 optical fibers, Estimation of causes of pulse
3, 4
fibers, Effect of material dispersion, (TB, RB) broadening, Calculation of different
Effect of multipath-dispersion and parameters of optical fibers
combined effect, Numerical problems
Please Do Not Print Unless Necessary
BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, Pilani
Pilani Campus
Instruction Division
Maxwell's equations, Solution in an
inhomogeneous medium, Planar
optical waveguide, TE modes of a Chapter 2 Familiarization with the background for
5, 6, symmetric step index planar (RB), Chapter learning electromagnetic wave propagation,
II waveguide, Power distribution and 3 (TB), Modal analysis of planar optical wave
7, 8 confinement factor, Wave propagation Chapter 4 guides, Modal analysis of cylindrical optical
in an ideal SI fiber, Modal power (TB) waveguide
distribution in SI fibers, Wave
propagation in GI fiber
Characteristic parameters of SM fibers,
Propagation through Single mode
Dispersion in SM fibers, Attenuation in SM
fibers, Single mode fibers, Fabrication
9, 10, fibers, Design of SM fibers and related
of low loss optical fibers, Design Chapter 2, 3,
III problems, Fiber material requirements, Fiber
11, 12 aspects of optical fiber cables and 14 (RB)
fabrication methods, Fiber optic cables,
connections, Evaluating the
connection and related losses,
performance of optical fibers
Characterization of optical fibers
Intrinsic and extrinsic semi-conductors, p-n
junction, Life time and diffusion length of
Fundamental aspects of optoelectronic
minority carriers, Current density and
sources, Principle of operation of light
13, 14, injection efficiency, LED, its internal and
emitting diodes(LED), Design aspects Chapter 4, 5
IV external quantum efficiency, Heterojunction,
15, 16 of LED, Principles of injection laser (RB)
LED designs, ILD, condition for laser
diode (ILD), Design aspects of ILD
action, laser modes & laser action in semi
and source fiber coupling.
conductors, ILD structures, Source Fiber
coupling.
17, 18, Principle of operation and types of Chapter 6, 7 Basic principle of opto-electronic detection,
V
19, 20 optoelectronic detectors. (RB) Types of photodiodes
Review of basic principles of
Polarization, birefringence, retardation
21, 22, optoelectronic modulator, Electro
Chapter 9 plates, Electro optic modulators and related
VI optic effect and related modulators,
23, 24 (TB) problems, Acousto-optic modulators &
Acousto-optic effect and related
related problems.
modulators
25, 26, Semiconductor optical amplifiers, Erbium
Chapter 11
VII Optical amplification and amplifiers doped fiber amplifiers, Fiber Raman
27, 28 (RB)
amplifiers
29, 30, WDM & DWDM, Components, System
Wavelength division multiplexing, Chapter 8, 9,
VIII design considerations, System architectures,
31, 32 Fiber- optic communication systems 10, 13 (RB)
Non-linear effects and system performance
32,34, Fiber Optic Sensors, Classification of Chapter 13 Sensors based on fiber optic cable, sensing
IX
35,36 Fiber optic sensors (TB) principles, Extrinsic and Intrinsic Sensors
37,38, Intensity-, Phase-, Spectrally-
Chapter 13 Distinct Types of Sensors, Industrial
X Modulated Sensors, Distributed Fiber-
39,40 (TB) Applications
optic Sensors.
_
Please Do Not Print Unless Necessary
BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, Pilani
Pilani Campus
Instruction Division
6. Evaluation Scheme:
EC. Evaluation Component Weightage Duration Date, Time & Nature of
No. (%) Venue Component
1. Mid Semester Test 30 90 min. TBA CB/OB
2. Quiz (Surprise) 20 Details in Class CB/OB
3. Assignment 10 Details in Class OB
CB/OB
4. Comprehensive Exam 40 3 hrs. 12/12/2019 FN
7. Chamber Consultation Hour: Anytime during working hours but with prior appointment through email.
Chamber Number: - 2210-K in EEE cubicals.
8. Notices: Notices concerning this course will be displayed on Nalanda site.
9. Make-up Policy: Make-up in Mid-Sem/ Comprehensive Examination will be given only for genuine
reasons (e.g. medical, personal emergencies, etc.). No make-up for quiz component, although buffers will be
applicable.
Instructor-in-Charge
EEE F426
Please Do Not Print Unless Necessary
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- OptiX OSN 9800 Operation and Maintenance Training (Part 1)Document160 pagesOptiX OSN 9800 Operation and Maintenance Training (Part 1)Bahaa Alaboud100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Fiber Characterization ReportDocument24 pagesFiber Characterization ReportEugene BeliankaNo ratings yet
- JNKBDocument1 pageJNKBshwetaNo ratings yet
- Planar StructureDocument4 pagesPlanar StructureshwetaNo ratings yet
- TMT PreCompre V1 0Document3 pagesTMT PreCompre V1 0shwetaNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistors: HCM City University of Natural Sciences, VietnamDocument26 pagesModeling of Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistors: HCM City University of Natural Sciences, VietnamshwetaNo ratings yet
- Simple ProgramDocument14 pagesSimple ProgramshwetaNo ratings yet
- State Institute of Educational Research & Training, UdaipurDocument5 pagesState Institute of Educational Research & Training, UdaipurshwetaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Engineering Seismology For Site CH PDFDocument10 pagesApplications of Engineering Seismology For Site CH PDFAlejandro MejiaNo ratings yet
- DispersionDocument58 pagesDispersionSumanta KunduNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Communication Engineering R13 Iv-I Elective Ii Optical Communications (Rt4104A) Previous End Examination Questions (R13 & R10)Document7 pagesElectronics & Communication Engineering R13 Iv-I Elective Ii Optical Communications (Rt4104A) Previous End Examination Questions (R13 & R10)jaganmohanrsNo ratings yet
- Chap 12Document13 pagesChap 12api-3702256100% (4)
- Chapter 24: Electromagnetic Waves and Nature of LightDocument2 pagesChapter 24: Electromagnetic Waves and Nature of LightAlarcon KendrickNo ratings yet
- Testing Fso WDM Communication System in Simulation Software Optiwave Optisystem in Different Atmospheric EnvironmentsDocument12 pagesTesting Fso WDM Communication System in Simulation Software Optiwave Optisystem in Different Atmospheric EnvironmentsNguyễn NhungNo ratings yet
- HCIP-Transmission V2.5 Training MaterialDocument840 pagesHCIP-Transmission V2.5 Training MaterialEDWARD KIWALABYENo ratings yet
- Physics 11-04 Total Internal ReflectionDocument2 pagesPhysics 11-04 Total Internal ReflectionBALI RAONo ratings yet
- Synthesis 3Document10 pagesSynthesis 3altisinNo ratings yet
- Determining The Optical Properties of Gelatine GelDocument17 pagesDetermining The Optical Properties of Gelatine GelCorynaNo ratings yet
- Ultrawideband MicrowaveDocument13 pagesUltrawideband MicrowaveIhya UlumiddinNo ratings yet
- Design of Aerodynamically Stabilized Free RocketsDocument334 pagesDesign of Aerodynamically Stabilized Free RocketsVishnu Sankar100% (1)
- NitrogenDocument45 pagesNitrogen001tabNo ratings yet
- Fibre Optic CommunicationDocument10 pagesFibre Optic CommunicationsriramanbalajiNo ratings yet
- Chew, 2009Document258 pagesChew, 2009Mahmoud ElTayiebNo ratings yet
- OFC Design ExamplesDocument8 pagesOFC Design Examplesbkmmizan0% (1)
- Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD), Its Limits, Compensation and Effect On Optical Fiber NetworksDocument6 pagesPolarization Mode Dispersion (PMD), Its Limits, Compensation and Effect On Optical Fiber NetworksJournal of ComputingNo ratings yet
- Source of Information Electrical Transmit Optical SourceDocument37 pagesSource of Information Electrical Transmit Optical SourcesubashNo ratings yet
- Systems Engineering - Concepts, Tools and Applications PDFDocument149 pagesSystems Engineering - Concepts, Tools and Applications PDFBiteMe76No ratings yet
- Hybrid and Organic CrystalsDocument504 pagesHybrid and Organic CrystalsHally-BaabaNo ratings yet
- Medium Color Coatings R1040, R1035, R1180, R1255Document4 pagesMedium Color Coatings R1040, R1035, R1180, R1255nchoangNo ratings yet
- 7 - Fiber Attenuation and DispersionDocument74 pages7 - Fiber Attenuation and DispersionSalim KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document17 pagesLecture 4gsathyascewNo ratings yet
- Diffoptics PDFDocument10 pagesDiffoptics PDFRobert KemperNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Modes and ConfigurationsDocument37 pagesOptical Fiber Modes and ConfigurationsDhivya GunasekarNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Dispersion Engineered Rib Waveguides For On-Chip Mid-Infrared SupercontinuumDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of Dispersion Engineered Rib Waveguides For On-Chip Mid-Infrared SupercontinuumSHIVANK NIGAMNo ratings yet