Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Perioperative Cardiac Arrest Focus On Anaphylaxis.1
Uploaded by
Ika KartikaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Perioperative Cardiac Arrest Focus On Anaphylaxis.1
Uploaded by
Ika KartikaCopyright:
Available Formats
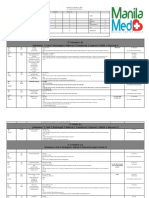
Infographic
Perioperative Cardiac
c Arrest:
Focus on Anaphylaxiss
When compared to out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, such events that occur in the perioperative
setting are unique with respect to their etiology, the fact that they are often witnessed firsthand
and their significant departure from standard ACLS algorithms. A mnemonic device for the general
Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/anesthesia-analgesia by BhDMf5ePHKav1zEoum1tQfN4a+kJLhEZgbsIHo4XMi0hCywCX1AWnYQp/IlQrHD3StWKv21Bgex+ohYLe7J48pTaI8IAT0O1+Ch3OgIxX+B/o99e26CWHg== on 02/12/2020
approach to anaphylaxis is illustrated below.
NMBs Anti
Antibiotics
i ics Bl
Blood Contrast
C n r st Latex
L te
Rx
Fluids
R 100-300 mcg IV or
300-500 mcg IM
Epinephrine for impending arrest
100-1000 mcg IV
Steroids (50 - 150 mg hydrocortisone or equivalent)
cardiac arrest
Histamine blockers (50mg diphenhydramine
20 mg famotidine)
Airway
CPR
For a Tryptase
minimum of
ICU 2 U IV
24 hours for impending arrest
Vasopressin
unresponsive to epi
40 U IV
ECMO
during arrest
unresponsive
to epi
Review articles contained in this issue elaborate the unique characteristics of in-hospital, periopera-
tive cardiac arrest and delineate the approach to eight clinical scenarios1,2. The reader is encour-
aged to explore these reviews for further detail.
March 2018 • Volume 126 • Number 3 www.anesthesia-analgesia.org 735
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Acanthosis Nigricans: A Cutaneous Marker For Metabolic SyndromeDocument6 pagesAcanthosis Nigricans: A Cutaneous Marker For Metabolic SyndromeIka KartikaNo ratings yet
- Neisseria Meningitidis and Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Bacteremia AssociatedDocument4 pagesNeisseria Meningitidis and Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Bacteremia AssociatedIka KartikaNo ratings yet
- Slit Skin SmearsDocument6 pagesSlit Skin SmearspargoNo ratings yet
- Coursera COVID UPDATEDocument18 pagesCoursera COVID UPDATEIka KartikaNo ratings yet
- Bact Chron Inf WEEK 4-6Document21 pagesBact Chron Inf WEEK 4-6Ika KartikaNo ratings yet
- Bact & Chronic Inf (Week 1-3)Document16 pagesBact & Chronic Inf (Week 1-3)Ika KartikaNo ratings yet
- JNC 7 PDFDocument104 pagesJNC 7 PDFbellaNo ratings yet
- VdBerg PLoSOne2009Document10 pagesVdBerg PLoSOne2009Ika KartikaNo ratings yet
- (Ernst Schering Research Foundation Workshop 56) B. Skurkovich, S. Skurkovich (auth.), R. Numerof, C. A. Dinarello, K. Asadullah (eds.) - Cytokines as Potential Therapeutic Targets for Inflammatory Sk.pdfDocument224 pages(Ernst Schering Research Foundation Workshop 56) B. Skurkovich, S. Skurkovich (auth.), R. Numerof, C. A. Dinarello, K. Asadullah (eds.) - Cytokines as Potential Therapeutic Targets for Inflammatory Sk.pdfIka KartikaNo ratings yet
- Cole JACI2013Document6 pagesCole JACI2013Ika KartikaNo ratings yet
- The Economist (Calibre) - The World in 2019 (Wed, 28 Nov 2018) - Calibre (2018) PDFDocument401 pagesThe Economist (Calibre) - The World in 2019 (Wed, 28 Nov 2018) - Calibre (2018) PDFIka Kartika100% (4)
- GooglepreviewDocument16 pagesGooglepreviewIka KartikaNo ratings yet
- Management of Knowlesi MalariaDocument12 pagesManagement of Knowlesi MalariaIka KartikaNo ratings yet
- Rapid B-Natriuretic Peptide Assay in Differentiating Congestive Heart Failure From Lung Disease in Patients Presenting With DyspneaDocument8 pagesRapid B-Natriuretic Peptide Assay in Differentiating Congestive Heart Failure From Lung Disease in Patients Presenting With DyspneaIka KartikaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- MicrospheresDocument67 pagesMicrospheresSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Toksikologi Pada Organ 3-Sistem Imun-Reproduksi PDFDocument40 pagesToksikologi Pada Organ 3-Sistem Imun-Reproduksi PDFArchangela GrethaniaNo ratings yet
- TTDexDocument2 pagesTTDexSparKY NIghtcoreNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach The Mcgraw-Hill CompaniesDocument83 pagesPharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach The Mcgraw-Hill CompaniesLohith BasavarajuNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics of PG Degree Mdms Submitted For The Academic Year 2018-19-2019 20 and 2020 21Document227 pagesDissertation Topics of PG Degree Mdms Submitted For The Academic Year 2018-19-2019 20 and 2020 21Asra QuadriNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6 PPT PainDocument22 pagesWEEK 6 PPT PainDanica FrancoNo ratings yet
- Obat PsikiatriDocument1 pageObat Psikiatriice rumkoremNo ratings yet
- Neuroendocrine TumorsDocument21 pagesNeuroendocrine TumorsAnonymous 8KN8IR1GTWNo ratings yet
- Angina Pectoris: Dr. Naitik D Trivedi & Dr. Upama N. TrivediDocument15 pagesAngina Pectoris: Dr. Naitik D Trivedi & Dr. Upama N. TrivediNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- D10W (Anything D5W) - 3% Normal Saline ( 0.9% Hypertonic) - Mannitol - Parenteral NutritionDocument6 pagesD10W (Anything D5W) - 3% Normal Saline ( 0.9% Hypertonic) - Mannitol - Parenteral NutritionAlec Anon100% (1)
- Assignment:: Course Title Course Code:Bph-115Document14 pagesAssignment:: Course Title Course Code:Bph-115toushif ahmedNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms: Mscs in Pharmaceutical SciencesDocument77 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage Forms: Mscs in Pharmaceutical SciencesObada Sibai100% (1)
- Sambungan Data Persediaan Obat PuskesmasDocument7 pagesSambungan Data Persediaan Obat PuskesmasMerry OctafiaNo ratings yet
- Cintias AMC QUICK REVIEWDocument217 pagesCintias AMC QUICK REVIEWFlavin AmbroseNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics Sixth EditionDocument1 pageClinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics Sixth EditionBishnu Prasad BeheraNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - WikipediaDocument15 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - Wikipediaاحمد احمدNo ratings yet
- Pcol MidtermsDocument13 pagesPcol MidtermsJoyce VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 9 Extension: (6) (Admission: '1 Card: 0 Discharged: 0 Referral: 0 Transferred: 1 Expired: 0 HAMA: 0 Abscond: 0Document7 pages9 Extension: (6) (Admission: '1 Card: 0 Discharged: 0 Referral: 0 Transferred: 1 Expired: 0 HAMA: 0 Abscond: 0Patrick JohnNo ratings yet
- 101-Local RX MCQsDocument31 pages101-Local RX MCQsHybat ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- DR M Ushashree 1 Yr PG Gandhi Medical CollegeDocument58 pagesDR M Ushashree 1 Yr PG Gandhi Medical CollegeRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- Risk Screening of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Romanian Aquatic EnvironmentDocument16 pagesRisk Screening of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Romanian Aquatic EnvironmentBárbara Rani BorgesNo ratings yet
- Xarelto Tablet Salut Selaput 20 MG - Rivaroksaban - DKI1251602517C1 - 2020Document26 pagesXarelto Tablet Salut Selaput 20 MG - Rivaroksaban - DKI1251602517C1 - 2020Dimas RfNo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida Concept Map PDFDocument1 pageSpina Bifida Concept Map PDFnot realNo ratings yet
- Step 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK) : Sample Test QuestionsDocument59 pagesStep 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK) : Sample Test QuestionsmarceloabadNo ratings yet
- Wa0008Document2 pagesWa0008chiragg0701No ratings yet
- Clinical Treatment of Rabbits Experimentally Infected With Staphylococcus Aureus Using Different AntibioticsDocument4 pagesClinical Treatment of Rabbits Experimentally Infected With Staphylococcus Aureus Using Different Antibioticsarum pratiwiNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Dental SedationDocument209 pagesA Guide To Dental SedationZilan MengütayNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Childhood Motor StereotypiesDocument9 pagesA Guide To Childhood Motor StereotypiesAna HounieNo ratings yet
- ADMED Product ListDocument22 pagesADMED Product ListadmedoverseasNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicines - Molecular Structures, Pharmacological Activities, Natural Sources and Applications - Vol. 3 - Isolated Compounds H-MDocument702 pagesEncyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicines - Molecular Structures, Pharmacological Activities, Natural Sources and Applications - Vol. 3 - Isolated Compounds H-MThaís Hélène100% (1)