Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flyer. Geotech
Uploaded by
zarakkhan masoodCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flyer. Geotech
Uploaded by
zarakkhan masoodCopyright:
Available Formats
The tri-axial shear test is most versatile of all the
shear test testing methods for getting shear strength
of soil i.e. Cohesion (C) and Angle of Internal 1. A saturated porous stone is placed on the pedestal and the
To determine the shearing strength of the
Friction (Ø), though it is bit complicated. This test cylindrical soil specimen is placed on it
can measure the total as well as effective stress soil using the Tri-axial shear apparatus. 2. The specimen is encased in a rubber membrane and sealed
to the pedestal at the bottom as well as to the loading cap
parameters both. a at the top by rubber O-ring the membrane is used to
To determine Cohesion (C) and internal prevent the water from penetrating in to the soil sample
angle of friction (Φ) of the soil. 3. The tri-axial cell is filled with water and pressure is
Pore water pressure measurements can applied to the water, which in turn is transmitted to the soil
specimen all-round and at top. This pressure is called
be made accurately “Cell Pressure”(Pc)
4. With the cell pressure held is constant, additional axial
stress (Pd) is applied through the ram gradually until the
sample is fails. This additional axial stress is called
“Deviator Stress” (Pd)
Chamber Pressure Application Device 1. Before starting the test, the air pressure 1. Internal angle of friction for the taken soil will be
Specimen Cap and Base should be checked to confirm complete determined
Dial gauge removal of air voids in the specimen.
2. The Excess Pore Water Pressure will be determined
Proving ring
2. Before subjecting the specimen to shear, the
O-Ring membrane should be properly attached to
3. Proper Mohr’s Circle will be constructed which will
help in finding Cohesion(Cu)
Porous stones the O-ring.
Axial Loading Device
Balance, sensitive to 0.1 gm 3. The rate of strain should be constant
Tri-Axial Compression Chamber throughout the test.
Rubber Impervious Membrane
You might also like
- Group Timings For Mini Project/Final Exam Viva (Sec-B) : Wednesday, 5th August 2020Document1 pageGroup Timings For Mini Project/Final Exam Viva (Sec-B) : Wednesday, 5th August 2020zarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Announcement (Assignment and Quiz)Document1 pageAnnouncement (Assignment and Quiz)zarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Salvadora Persica (Miswak) : An Effective Way of Killing Oral PathogensDocument74 pagesSalvadora Persica (Miswak) : An Effective Way of Killing Oral Pathogenszarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- GTE Declaration - Unsw Sydney ModifiedDocument1 pageGTE Declaration - Unsw Sydney Modifiedzarakkhan masood100% (1)
- Assignment #01 Zarak Khan Mahsud CU-255-2016 Civil-B "Digital Elevation Model" 02/05/2020Document2 pagesAssignment #01 Zarak Khan Mahsud CU-255-2016 Civil-B "Digital Elevation Model" 02/05/2020zarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Group Timings For Mini Project/Final Exam Viva (Sec-C) Thursday, 6th August 2020Document1 pageGroup Timings For Mini Project/Final Exam Viva (Sec-C) Thursday, 6th August 2020zarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Group Timings For Mini Project/Final Exam Viva (Sec-A) Tuesday, 4th August 2020Document1 pageGroup Timings For Mini Project/Final Exam Viva (Sec-A) Tuesday, 4th August 2020zarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- FinalexamDocument2 pagesFinalexamzarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Assignment Khalid RafiqDocument3 pagesAssignment Khalid Rafiqzarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Assignment No - 2Document2 pagesAssignment No - 2zarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- CECOS-Fee Deposit GuidelinesDocument1 pageCECOS-Fee Deposit Guidelineszarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Lab (I)Document16 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Lab (I)zarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Himmler's Diary, 1945 - A Calendar of Events Leading To SuicideDocument369 pagesHimmler's Diary, 1945 - A Calendar of Events Leading To Suicidezarakkhan masood80% (5)
- Dismantling The Ottoman Empire - Britain, America and The Armenian QuestionDocument281 pagesDismantling The Ottoman Empire - Britain, America and The Armenian Questionzarakkhan masood100% (1)
- ArcSWAT Documentation 2012Document464 pagesArcSWAT Documentation 2012puja76100% (12)
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1zarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Flash and Fire Point TestDocument11 pagesFlash and Fire Point TestWily RustamNo ratings yet
- LF-5 IntersectionsDocument35 pagesLF-5 Intersectionszarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - To Determine Flash and Fire Point of BitumenDocument30 pagesLecture 8 - To Determine Flash and Fire Point of Bitumenzarakkhan masood0% (1)
- Bkreviewsw The Culture o P and G PDFDocument14 pagesBkreviewsw The Culture o P and G PDFTooba XaidiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document37 pagesLecture 1zarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
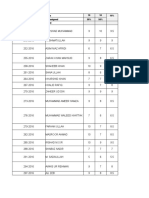
- Cecos University 2016 Batch ScoresheetDocument2 pagesCecos University 2016 Batch Scoresheetzarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Progress PresentationDocument16 pagesProgress Presentationzarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Bu 100 4 Invitation To Return To The Quran 2Document288 pagesBu 100 4 Invitation To Return To The Quran 2ISLAMIC LIBRARYNo ratings yet
- Streets and FurnitureDocument36 pagesStreets and Furniturezarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Pile Test LoadingDocument10 pagesPile Test LoadingFeyisayo Ayomide OgunladeNo ratings yet
- National Testing ServiceDocument1 pageNational Testing Servicezarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Mamlouk2 PDFDocument115 pagesMamlouk2 PDFzarakkhan masoodNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Highway Lab - Introduction To Highway LabDocument30 pagesLecture 1 - Highway Lab - Introduction To Highway Labzarakkhan masood100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)