Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 2
Uploaded by
usama juggCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 2
Uploaded by
usama juggCopyright:
Available Formats
COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Lahore
Assignment 2 (SP17)
Course Title: Chemical Process Principles Course Code: CHE113 Credit Hours: 3(3,0)
Course Instructor/s: Dr. Faisal Ahmed Program: BS Chemical engineering
Semester: 2nd Batch: SDP-FA16-CHE-AB Section: A,B Marks 20
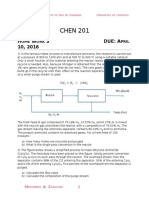
Question: 1
A reactor is used to produce formaldehyde from methanol in the reaction:
CH3OH HCHO + H2
A single-pass conversion of 60% is achieved in the reactor. The reactor product methanol is then
separated from the formaldehyde and hydrogen. The production rate of formaldehyde is 900 kg/hr.
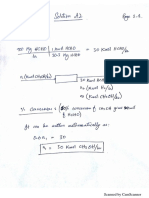
(i) Sketch a labeled flow chart and calculate the required feed rate of methanol to the process
(kmol/hr) if there is no recycle. Molecular mass of HCHO is 30.3 kg.
(ii) Suppose the recovered methanol is recycled to the reactor and the single-pass conversion remains
60%. Sketch a labeled flow chart and determine the required fresh feed rate of methanol
(kmol/hr) and the rates (kmol/hr) at which methanol enters and leaves the reactor.
Question: 2
Methanol is produced by reacting carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
CO + H2 CH3OH
A fresh feed stream containing CO and H2 joins a recycle stream and the combined stream is fed to a
reactor. The reactor outlet stream flows at a rate of 350 mol/min and contains 10.6 wt% H 2, 64 wt% CO,
and 25.4 wt% CH3OH. (Notice that those are percentages by mass, not mole percents.) This stream enters
a cooler in which most of the methanol is condensed. The liquid methanol condensate is withdrawn as a
product, and the gas stream leaving the condenser—which contains CO, H2, and 0.40 mole %
uncondensed CH3OH vapor—is the recycle stream that combines with the fresh feed. Perform the
following actions in order.
(i) Determine the molar flow rates of CO and H2 in the fresh feed.
(ii) Sketch a properly labeled flow chart.
(iii) Perform degrees of freedom analysis to identify where to attack the problem first.
(iv) Determine the production rate of liquid methanol.
(v) Determine the single-pass and overall conversions of carbon monoxide.
You might also like
- In-Class Problem Set 3 - 2021Document5 pagesIn-Class Problem Set 3 - 2021tanishka kucheriaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Principles Assignment 1 SolutionDocument2 pagesChemical Process Principles Assignment 1 SolutionHadia SAULATNo ratings yet
- CBE 202 Homework #2: Deacon process, methanol production, chlorination reactionsDocument2 pagesCBE 202 Homework #2: Deacon process, methanol production, chlorination reactions김민성No ratings yet
- Exercise 12 HYSYSDocument2 pagesExercise 12 HYSYSSiti Hajar Jamaluddin100% (1)
- CHEN 201 Exam 2 Spring 2016 QuestionsDocument1 pageCHEN 201 Exam 2 Spring 2016 QuestionsDiana BeirutiNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document2 pagesQuiz 1Hamza RahimNo ratings yet
- Assignment CPP Jan 2020 PDFDocument5 pagesAssignment CPP Jan 2020 PDFNur Afifah IINo ratings yet
- 2020 CHEE2001 Week 6 Tutorial SheetDocument2 pages2020 CHEE2001 Week 6 Tutorial SheetMuntaha ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Lectut CHN-102 PDF ReactiveDocument4 pagesLectut CHN-102 PDF ReactiveTanmaysainiNo ratings yet
- Politecnico di Milano Fundamentals of Chemical Processes ExercisesDocument4 pagesPolitecnico di Milano Fundamentals of Chemical Processes ExercisesEliot Kh0% (1)
- Quiz 3a: Material and Energy Balance BKF2343Document1 pageQuiz 3a: Material and Energy Balance BKF2343Az Zahra AzmiNo ratings yet
- CHEN 200 Mid Term Questions Spring 2015Document2 pagesCHEN 200 Mid Term Questions Spring 2015Diana BeirutiNo ratings yet
- Design (Ch.1 Problems)Document5 pagesDesign (Ch.1 Problems)John UnkNo ratings yet
- Revision On Material BalanceDocument15 pagesRevision On Material BalanceSyarif Wira'iNo ratings yet
- University of Mauritius 2010 Chemical Engineering ExamDocument7 pagesUniversity of Mauritius 2010 Chemical Engineering ExamPriyam RamsokulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18Document1 pageLecture 18KALINDI SINGHNo ratings yet
- Bridge To Ch. 5 - More On Recycle and PurgeDocument17 pagesBridge To Ch. 5 - More On Recycle and PurgeMwanarusi MwatondoNo ratings yet
- Assignment ReactiveDocument2 pagesAssignment ReactiveNUREEN DAYANA BINTI MOHD IZMANIZAN A21ET01940% (1)
- Tute 3Document4 pagesTute 3ArunNo ratings yet
- Che 201 - Che Fundamentals Class Problem 5: O H Oh CH H CoDocument1 pageChe 201 - Che Fundamentals Class Problem 5: O H Oh CH H Cokirbyhuber37_7316115No ratings yet
- ChE 251A: Chemical Process Calculations Problems Set 1Document5 pagesChE 251A: Chemical Process Calculations Problems Set 1Deepak TholiaNo ratings yet
- Process System Analysis CHEM2002: Simulation of The Methanol ProcessDocument10 pagesProcess System Analysis CHEM2002: Simulation of The Methanol ProcessSaeed AlzeediNo ratings yet
- Material Balance CalculationsDocument2 pagesMaterial Balance CalculationsSergio Rugerio TorresNo ratings yet
- Mass Balance Tutorial 2 - 2021 Fin-StuDocument2 pagesMass Balance Tutorial 2 - 2021 Fin-StuToanique HeadmanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2AhmedAlnazer0% (1)
- University of Melbourne Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering 411-102 Chemical Process Analysis Tutorial Sheet CDocument3 pagesUniversity of Melbourne Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering 411-102 Chemical Process Analysis Tutorial Sheet CAn FakeihahNo ratings yet
- CHEM 2002 Tutorial Sheet 6 - Process for Monochlorodecane ProductionDocument20 pagesCHEM 2002 Tutorial Sheet 6 - Process for Monochlorodecane Productionajali1957No ratings yet
- Che F244 1183 C 2015 2Document4 pagesChe F244 1183 C 2015 2shubhamNo ratings yet
- CL 201 Tutorial 4 Time: 1 Hour Marks: 70 Oct 21, 2020: C C / (1 + KV/)Document2 pagesCL 201 Tutorial 4 Time: 1 Hour Marks: 70 Oct 21, 2020: C C / (1 + KV/)Rishiraj KamdarNo ratings yet
- 0405-2 AbsDocument9 pages0405-2 AbsJay MaradiyaNo ratings yet
- Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesPractice QuestionsAhmad MuzammilNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 7 Recycle and PurgeDocument3 pagesWorksheet 7 Recycle and PurgeLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Che 201 - Che Fundamentals Due Oct 7 (On-Campus) Due Oct 11 (Dedp)Document2 pagesChe 201 - Che Fundamentals Due Oct 7 (On-Campus) Due Oct 11 (Dedp)Andrew YauNo ratings yet
- Cpe 420 Tutorial 2Document3 pagesCpe 420 Tutorial 2Muhamad Baihakhi ShamsudinNo ratings yet
- SKKK1113 Tutorial Assignment-04-ReactiveDocument2 pagesSKKK1113 Tutorial Assignment-04-ReactiveNUREEN DAYANA BINTI MOHD IZMANIZAN A21ET0194No ratings yet
- B.Sc. Engineering Exam Covers Chemical Engineering ConceptsDocument2 pagesB.Sc. Engineering Exam Covers Chemical Engineering ConceptsMuhaiminul Hasan EmonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 Atomic and Molecular BalanceDocument3 pagesWorksheet 3 Atomic and Molecular BalanceLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 DR Azizul PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 DR Azizul PDFjinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Chemical EngineeringDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Chemical EngineeringRas BerryNo ratings yet
- Checal 2 Module ProblemsDocument3 pagesChecal 2 Module Problems5zywgtdkw5No ratings yet
- Final Exam Material & Energy Balance Chemical EngineeringDocument6 pagesFinal Exam Material & Energy Balance Chemical EngineeringrushdiNo ratings yet
- The Design of A Chemical Plant For The Production of Methanol From Synthesis GasDocument4 pagesThe Design of A Chemical Plant For The Production of Methanol From Synthesis GasHenry NwidoNo ratings yet
- CHE 202 TUTORIAL QUESTIONSDocument6 pagesCHE 202 TUTORIAL QUESTIONSFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Green Chemistry and IndustryDocument14 pagesGreen Chemistry and IndustryHimani Singh GaurNo ratings yet
- ChE Cal LE 4 - 1sAY2223 - ANIESDocument1 pageChE Cal LE 4 - 1sAY2223 - ANIESRhean Rheign VergaraNo ratings yet
- PROB3Document7 pagesPROB3Good Food ClpNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Calculations Problems and SolutionsDocument8 pagesChemical Process Calculations Problems and SolutionsrajaraghuramvarmaNo ratings yet
- Process Synthesis for Monochlorodecane ProductionDocument18 pagesProcess Synthesis for Monochlorodecane Productionajali1957No ratings yet
- Producing Titanium Dioxide from OreDocument10 pagesProducing Titanium Dioxide from OreMohamed AlqaisiNo ratings yet
- TOPIC: Acetic Acid Production Through Methanol Carbonylation Route Group MembersDocument3 pagesTOPIC: Acetic Acid Production Through Methanol Carbonylation Route Group MembersThrese AreolaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineerong Calculations PDFDocument5 pagesChemical Engineerong Calculations PDFDamion PayneNo ratings yet
- CPC 2017Document2 pagesCPC 2017Harshith ShettyNo ratings yet
- Assignment L01 (Thursday, 11.30 Am)Document9 pagesAssignment L01 (Thursday, 11.30 Am)MawareNo ratings yet
- The University of Jordan School of Engineering Chemical Engineering Department Process DesignDocument10 pagesThe University of Jordan School of Engineering Chemical Engineering Department Process Designsocial peopleNo ratings yet
- Mass Balances With Reactions 4.1-4.3 ExercisesDocument8 pagesMass Balances With Reactions 4.1-4.3 ExercisesJackson MakgolengNo ratings yet
- U E T, L .: Niversity OF Ngineering AND Echnology Ahore Combined Question Paper For Affiliated Colleges/InstitutesDocument1 pageU E T, L .: Niversity OF Ngineering AND Echnology Ahore Combined Question Paper For Affiliated Colleges/InstitutesUmairNo ratings yet
- Producing Ethyl Chloride in iCONDocument19 pagesProducing Ethyl Chloride in iCONlynNo ratings yet
- Mta Che471 01052020Document3 pagesMta Che471 01052020afifiNo ratings yet
- 001lecture Petroleum Refinery History and Intro B&W 001Document50 pages001lecture Petroleum Refinery History and Intro B&W 001Ahmed MustafaNo ratings yet
- Lec 11-Online Lect 1Document13 pagesLec 11-Online Lect 1usama juggNo ratings yet
- A2 Solution PDFDocument7 pagesA2 Solution PDFusama juggNo ratings yet
- 4 3RTDandO2programmesDocument52 pages4 3RTDandO2programmesusama juggNo ratings yet
- Reactor TypesDocument81 pagesReactor TypesLenin PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2usama juggNo ratings yet
- Ball and Basket MillDocument2 pagesBall and Basket Millusama juggNo ratings yet