0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views2 pagesBSA
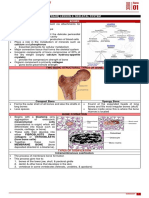
The document outlines the Bradford Assay, a method for determining protein concentration using Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 dye, which changes color based on its interaction with proteins. It details the absorbance shifts from 465 nm to 595 nm when the dye binds to proteins, and emphasizes the importance of measuring absorbance at specific wavelengths for accuracy. Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) is highlighted as a standard protein used in these experiments.
Uploaded by
Dimple May Gianne DumaguitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views2 pagesBSA
The document outlines the Bradford Assay, a method for determining protein concentration using Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 dye, which changes color based on its interaction with proteins. It details the absorbance shifts from 465 nm to 595 nm when the dye binds to proteins, and emphasizes the importance of measuring absorbance at specific wavelengths for accuracy. Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) is highlighted as a standard protein used in these experiments.
Uploaded by
Dimple May Gianne DumaguitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd