Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Packed Bed RTD Journal
Uploaded by
vyas reddy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views8 pagespacked bed expriment
Original Title
packed bed RTD journal
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentpacked bed expriment
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views8 pagesPacked Bed RTD Journal
Uploaded by
vyas reddypacked bed expriment
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Me
meu corcin
Rro Stupies IN Packep BED Reactor
To plot the RTD curve fora packed bed reactor, using a pulse input asa racer.
22 To determine the dispersion number (OL).
3. IntRopucTion:
‘Atal dfusion and dispersion of ud in packed beds are important for design and
‘operation of separation equipment and chemical reactors. The tracer technique, the
‘most widely used method for the study of axial dlspersion, Is usually used inthe farm of
1. Pulse input
2 Stepinput
3. cycle input
4. Random input
'n stimulus-response experimentation, we perturb the system using elther a pulse input
of tracer or @ step input and then see how the system reacts or responds to this
stimulus. The analysis of the response gives the desired information about the system.
The concentration ime curve atthe vessel out i called the F-Curve when the input
‘signal is a step signal and is called C-curve when the input signalis a pulse signal
THEoRY:
‘The exit age distribution function of fud leaving a vessel or RTD of fd ina vessel is
called the E-CURVE. The normalized curve is such that
ie
In stimulus-response experimentation the system is perturbed and then observes how
the system reacts or responds to this stimulus. The analysis ofthe response gives the
esired information. A pulse tracer input signal coud be used asa stimulus.
rover Pat Lmtd Amie fro TUES WPRCKEO BED REACTOR
KC Expres Pt ‘opens 190
let is called the C-
ignal at the vessel out
time cure for puse 89
Te cent 2 grado ase
‘CURVE. Considering stead
—— 8)
-The mean age ofthe et stream or mean residence time Is
—— @
———- (4)
‘When a trace injected into a packed bed at a location more than two or tree particle
ameters downstream from the enrance and measured some distance upstream from
the ex, the system is analogous to an open-open systen. For such @ system where
there is no e'scontinulty in type of flow atthe point of tracer injection or at the point of
‘racer measurement, the variance fr open system is
a} =Jredt-r «Seen
®
©
—— 7
Models are useful for representing low in real vessels, for scale up, and for diagnosing
‘oor flow. We have diferent kind of models depending on whether flow is close to plug,
‘iced, of somewhere in between, For small deviations from plug flow dispersion model
is used, Suppose an ideal pulse of tracer is introduced into the fuid entering a vessel
‘The pulse spreads as it passes through the vessel, and to characterize the spreading
this model, we assume diffusion lke process superimposed on plug flow. We call this,
some enon ti Ope een pn (2)
imensionless group characterizing the spread inthe whele vessel
For open vessel:
Hj
KC Engones Ute Atle rosneesw mon to rescos
=
° mea Sheen
39 the above equation we get
———-)
———10)
c “
Exit age cstibution at ime @
Earxe, ——— 112)
Pict a graph between 8 vs. Ea
Description:
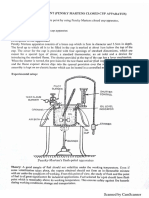
‘The setup consists of a glass column packed with rasching rings and one feed tank:
Water is fd tothe reactor through quid distibuter, fitted at the bottom of the column,
Rotameter is provided to measure the flow o water. The flow rate can be adjusted by
a ‘operating the needle valve provided on rolameter. A special arrangement is provided to
Inject tracer at the lower end of reactor, wing @ syringe. Samples can be taken
Periodically from the top outlet of reactor. Pressure regulator & pressure gauge are fited
inthe compressed ai line.
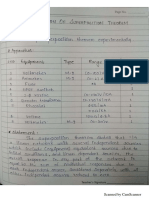
Unumes Require
6:1 Compressed air suply @ 0.25 CFM at1 Bar.
82 Water supply (rita
63. Flooretain required
64 Floor Area Required : 1.0m x1.0m
65 Laboratory glassware required
| Burette (50 mi) 01 No,
|e erpmers cites An ‘RTD STUDIES IN PACKED BED REACTOR
| ‘ope et er 9
othe.
ical flask (250)
ons 01 No.
syringe 0
easing ender 250°
ceils
200ml
NO NSOH
1
oncatted HeSOu ‘00m
prenbthaein inate Few crops °
= RMENTAL PROCEDURE:
TTA Sranrne PRoceDUre:
7.44. Close allthe valves Via
742 Open the valve V-Vs and fil the feed tank wth water.
7.4 Close the vale VrVe
7.44 Conect compressed air supply to the set up at valve Vs,
7.48. Connect electic supply tothe set up
746 Open valve V; and set air pressure 0.7 to 1 kgfem* by pressure regulator
and pressure gauge.
7.1.7 Start the supply of water tothe reactor at particular flow rate with the help
of needle vale Vz of rotameter.
7.18 FHINIO sodium hysroxide in bret
7.49 Flt concentrated H:S0, (10 ml or 20m) inthe syringe.
71.10 Place te syinge atthe tracer inlet
7.1.11 Wait the water comes out rom the outlet
7.142 Push the syringe into the system
7.4.13 At regular time intervals (Say 30 sec for high water flow rate, 1 min for low
Water flow rate), collect 20 ml sample fram the outlet, in measuring
oylnder.
7.4.14 Transfer the sample solution in conical flask
7.1.16 Titrate the sample solution, using phenolptthalein as an indicator against
'N/40 sodium hydroxide (add NaOH rom burt)
7.1.16 Repeat the experiment for diferent flow retes (before changing the flow
rate, drain the reactor fist),
722 Cosine Proceoure:
7.2.41. When experiment is over stop the flow of water by close the valve Vz
7.2.2 Drain the feed tank and reactor by open the valveVs-Ve
§. Opservation & CALCULATION:
"B44 Dara:
‘eng volume area" Vk
‘Volume ofeamieVs
8.2. OsservaTion TABLE:
a:
8.3 CaLcuLaTions:
VN,
N= (geal)
Ny
= Ne (molet)
: )
48 (min
ALE ft in)
1s nPAQHEDEED REACTOR
[RTD STUDIES IN PACKED BED Tn
Taste: 1
(min) | Gi(motnit) | 4c, te, At (min)
Cat
re | ae, | yFo,
t
ont
E,=1xE,
Catcutation Taste: 2
Plot a graph between 0 vs. Ey
NoMENCLATURE:
: -
Nom Column Heading units | Type
©,_| Concentration of H.S0, in sample ‘male | aeuated
Dispersion number ——| eae
vit age istibuton atime =| Caleta
E_ | Bitage dstibuion atte 6 =| ateiated
| Normally of NaOH used for tration geqt | Gen
N_| Normally of FSO, sample soliton geqt | Calculated
Time min | Measured
‘Vi | Wolume of NaOH used or tration mi | Measured
Ve | Walume of sample Toa Given
Ve _ | Wolumetie tow rate TPH | Measured
Va | Working volume ofreator tt Given
=| Experimental mean residence time min | Caleulated
=| Theoretical mean residence time min | Caeulated
@ | Reducedtine 7) Galeatated
[ey | Varianes atime >| Catetated
| Variance atte t vin? | Calculated
‘at _| Average tne ference min | Caleulated
+ Symbols are unitless
10. Precaution & MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS:
40.4 Always use distiled water, good quality chemicals and standard soltion for
tiation,
402 Keep close all the drain valves Vs-Vs and vent valve Vs should be open wile
filing water in the feed tanks.
103 Air pressure must be set below 1 kg/cm.
10.4 Flow should net be disturbed during the experiments
10.5 Handle the chemicals carefully.
Enjoetng row Coven
SHOOTING:
ny type of suspended particles is come in the rotameter, remove the
smeter clean the tube and fitit at its place.
there is any leakage tight that part or fix that again after wrapping teflon tape.
If rotameter fluctuating more than average tight the control knob properly
NCES:
Levenspiel, Octave (2001), Chemical Reacton Enginooring. 3% Ed. NY: John
Wiley & Sons. pp 283-294, 299-301, 305.
Fogler H. Scoot (2008). Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering. 4" Ed, ND:
Prentice-Hall of India Pvt, Ltd. p 869,
You might also like
- DBMS Unit III Part IIDocument64 pagesDBMS Unit III Part IIvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- DM Unit-5 Graph TheoryDocument35 pagesDM Unit-5 Graph Theoryvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6 Unit - 6: 12/29/2020 D.SAMEERA, Assis - Prof, BVRITDocument14 pagesUnit - 6 Unit - 6: 12/29/2020 D.SAMEERA, Assis - Prof, BVRITvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Unit-5: Design and Analysis of Sequential CircuitDocument36 pagesUnit-5: Design and Analysis of Sequential Circuitvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit III CH-1 PART-1 (Till Querying Relational Model)Document68 pagesDBMS Unit III CH-1 PART-1 (Till Querying Relational Model)vyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Dimethyl Ether from Methanol DehydrationDocument8 pagesManufacturing Dimethyl Ether from Methanol Dehydrationvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics (De) (A27H5) : Digital Logic Design and Computer Organizaton (Dld&Co)Document71 pagesDigital Electronics (De) (A27H5) : Digital Logic Design and Computer Organizaton (Dld&Co)vyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Assignment IIDocument2 pagesAssignment IIvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Scan 8 May 2020Document28 pagesScan 8 May 2020vyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Dme Report Word Own LATESTDocument73 pagesDme Report Word Own LATESTvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- CRE 2 AssignmentDocument5 pagesCRE 2 Assignmentvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Process Plant Simulation BabuDocument539 pagesProcess Plant Simulation Babuthakreneeraj93% (28)
- PFRDocument9 pagesPFRvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Properties of Activated Carbon: Iodine NumberDocument11 pagesProperties of Activated Carbon: Iodine Numbervyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Production of Activated CarbonDocument7 pagesProduction of Activated Carbonvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- B.tech - 2-1 - R18 TT Nov-Dec 2019Document4 pagesB.tech - 2-1 - R18 TT Nov-Dec 2019vyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Anigenobro 1Document2 pagesAnigenobro 1vyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Notice NDA II 2019 Engl PDFDocument77 pagesNotice NDA II 2019 Engl PDFSaurabh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Scan Doc by CamScannerDocument1 pageScan Doc by CamScannervyas reddyNo ratings yet
- FTPA Advertisement 2019-20 PDFDocument7 pagesFTPA Advertisement 2019-20 PDFRaja RamNo ratings yet
- Probability and StatisticsDocument703 pagesProbability and StatisticsPrakash Dhage88% (17)
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadDocument5 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabadvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Multiple CamScanner ScansDocument18 pagesMultiple CamScanner Scansvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Final Result Chemical-DDocument2 pagesFinal Result Chemical-Dvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Employment Newspaper Third Week of June 2019 PDFDocument48 pagesEmployment Newspaper Third Week of June 2019 PDFvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Project Report ON Zirconium Oxide Production AT Nuclear Fuel ComplexDocument6 pagesProject Report ON Zirconium Oxide Production AT Nuclear Fuel Complexvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Project Report ON Zirconium Oxide Production AT Nuclear Fuel ComplexDocument15 pagesProject Report ON Zirconium Oxide Production AT Nuclear Fuel Complexvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- Employment Newspaper Third Week of June 2019 PDFDocument48 pagesEmployment Newspaper Third Week of June 2019 PDFvyas reddyNo ratings yet
- CdsDocument14 pagesCdsBimal SikuNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)